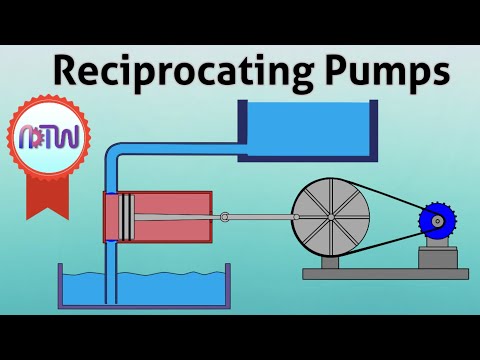
Q. What is a double acting reciprocating pump?
The pumping unit Creation of vacuum resulting in suction and compressing of the water resulting in discharge is the basic principle of operation. Each cycle consists of two strokes. Both the strokes are effective and hence it is known as a Double Acting Reciprocating Pump.
Q. What is the difference between single acting and double acting reciprocating steam compressor?
With a single acting compressor, the air is compressed only on the up-stroke of the piston inside the cylinder. The double acting compressor compresses the air on both the up-stroke and the down-stroke of the piston, doubling the capacity of a given cylinder size.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is a double acting reciprocating pump?
- Q. What is the difference between single acting and double acting reciprocating steam compressor?
- Q. What are the applications of single acting reciprocating pump?
- Q. What are the types of reciprocating pumps?
- Q. What are the 2 types of gear pump?
- Q. What is the principle of reciprocating pump?
- Q. What are the advantages of reciprocating pump?
- Q. What is reciprocating pump and how it works?
- Q. What is the working principle of centrifugal pump?
- Q. What is the working principle of Eductors?
- Q. Why most cargo pumps are centrifugal types?
- Q. What is eductor in chiller?
- Q. How a vacuum is created by an educator?
- Q. How a vacuum is created?
- Q. How many types of ejectors are there?
- Q. How vacuum is created in vacuum pump?
- Q. Which type of vacuum pump is best?
- Q. What are the two most common types of vacuum pumps?
- Q. How are the vacuum pumps broadly classified?
- Q. What are high vacuum pumps?
- Q. Where are vacuum pumps used?
- Q. What should I look for in a vacuum pump?
- Q. Why oil is used in vacuum pump?
- Q. Why do diesel engines need a vacuum pump?
- Q. Why do diesels not have a throttle?
Q. What are the applications of single acting reciprocating pump?
Applications of Reciprocating Pump:
- Gas industries.
- Petrochemical industries.
- Oil refineries.
- Vehicle water servicing centers etc.
Q. What are the types of reciprocating pumps?
There are four common types of reciprocating pumps – power pumps, power diaphragm pumps, air-operated pumps and air-operated piston pumps.
Q. What are the 2 types of gear pump?
There are two basic types: external and internal. An external gear pump consists of two identical, interlocking gears supported by separate shafts. An internal gear pump has two interlocking gears of different sizes with one rotating inside the other.
Q. What is the principle of reciprocating pump?
Introduction of Reciprocating Pump: Reciprocating Pump is a Positive Displacement type pump that works on the principle of movement of the piston in forwarding and backward directions whereas the Centrifugal pump uses the kinetic energy of the impeller to supply the liquid from one place to another place.
Q. What are the advantages of reciprocating pump?
Advantages of reciprocating pump
- High efficiency.
- No priming needed.
- Can deliver water at high pressure.
- Can work in wide pressure range.
- Continuous rate of discharge.
Q. What is reciprocating pump and how it works?
RECIPROCATING PUMP. A reciprocating pump is a positive displacement one which works on the principle of a reversing piston motion within a cylinder drawing in liquid during forward stroke, and delivering it under pressure during return or backward stroke.
Q. What is the working principle of centrifugal pump?
Centrifugal pumps are a category of Dynamic pumps. The working principle of centrifugal pumps involves imparting energy to the liquid by means of a centrifugal force developed by the rotation of an impeller that has several blades or vanes.
Q. What is the working principle of Eductors?
Working Principle of Eductor on Ships Eductor works on Bernoulli’s principle. It states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a reduction in pressure. Refer to the simplified Bernoulli’s equation below for an in compressible flow.
Q. Why most cargo pumps are centrifugal types?
Centrifugal pumps are used to induce flow or raise a liquid from a low level to a high level. These pumps work on a very simple mechanism. A centrifugal pump converts rotational energy, often from a motor, to energy in a moving fluid. While passing through the impeller, the fluid is gaining both velocity and pressure.
Q. What is eductor in chiller?
A refrigeration chiller makes use of the flow of oil from an oil sump location to the chiller’s compressor to power an eductor to return oil which has made its way to the evaporator of the chiller system from the evaporator to the compressor.
Q. How a vacuum is created by an educator?
In general, a vacuum is created by starting with air at atmospheric pressure within a chamber of some sort. When the pumpdown is started at atmospheric pressure, the gas molecules are in a flow regime condition called viscous flow.
Q. How a vacuum is created?
A vacuum can be created by removing air from a space using a vacuum pump or by reducing the pressure using a fast flow of fluid, as in Bernoulli’s principle. …
Q. How many types of ejectors are there?
Ejectors are generally categorized into one of four basic types: single-stage, multi-stage non-condensing, multi-stage condensing and multi-stage with both condensing and non-condensing stages. Single-stage ejectors are the simplest and most commonly used construction.
Q. How vacuum is created in vacuum pump?
The principle behind positive displacement vacuum pump is create a vacuum by expanding the volume of a container. For example in a manual water pump, a mechanism expands a small sealed cavity to create a deep vacuum. Because of the pressure, some fluid from the chamber is pushed into the pump’s small cavity.
Q. Which type of vacuum pump is best?
We recommend higher CFM pumps when you are operating large or multiple presses at once. Large vacuum presses (ex. 3624 model) or running several presses on the same pump with the automated vacuum control system means you have a much higher volume of air to remove from the system when operating.
Q. What are the two most common types of vacuum pumps?
Different types of pumps for these vacuum ranges can then be divided into Primary (Backing) Pumps, Booster Pumps and secondary (High Vacuum) Pumps: High, very high and ultra-high vacuum pressure ranges. There are two basic categories of vacuum pump: Gas Transfer Pumps and entrapment or capture pumps (Figure 1).
Q. How are the vacuum pumps broadly classified?
Vacuum pumps are categorized as gas transfer pumps and gas binding or capture pumps. Gas-displacement pumps, which are also referred to as gas transfer pumps, are classified either as positive displacement pumps or kinetic vacuum pumps.
Q. What are high vacuum pumps?
High vacuum pumps are used when the final absolute pressure required is very low. These pumps may run continuously connected to closed containers to be emptied, and may not run continuously at length, at atmospheric pressure.
Q. Where are vacuum pumps used?
They are used for composite moulding, flight instruments, production of vacuum tubes and electric lamps, CRT’s, semiconductor processing, electron microscopy, photolithography, uranium enrichment, print presses, glass and stone cutting factories, cabinetry fabrication, and medical applications that require suction.
Q. What should I look for in a vacuum pump?
Also consider the following characteristics, which may influence which vacuum pump you choose:
- Chemical compatibility.
- Pumping speed (volume flow) and pressure requirements.
- Pump Installation.
- Pump Maintenance.
- Costs.
Q. Why oil is used in vacuum pump?
The oil in a vacuum pump serves several purposes. In addition to providing lubrication for mechanical components such as found in rotary vane pumps, the oil also provides the following: A seal across the vanes and duo seal between the high pressure and low-pressure side of the pump.
Q. Why do diesel engines need a vacuum pump?
Because a Diesel engine has no throttle butterfies (honestly) then a vacuum is not created in the inlet manifold in the same way as in a petrol engine. So a vacuum pump is needed to create the vacuum needed for the brake-sevo.
Q. Why do diesels not have a throttle?
Diesels don’t have a throttle plate because the fuel is injected directly into the cylinder or into a prechamber with an opening to the cylinder (old tech). Diesel engines run 16-18:1 compression for direct injection and 21-23:1 for indirect injection (prechambers) and turbodiesels add boost on top of that.