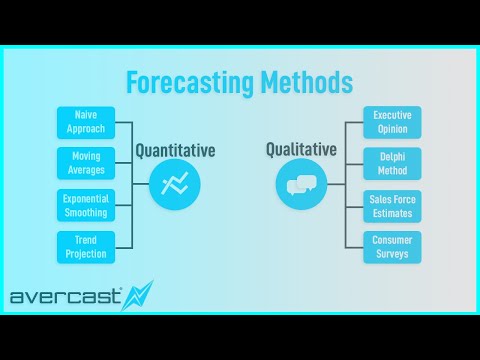
Qualitative forecasting techniques are subjective, based on the opinion and judgment of consumers and experts; they are appropriate when past data are not available. They are usually applied to intermediate- or long-range decisions.
Q. What is quantitative forecasting methods?
Quantitative forecasting models are used to forecast future data as a function of past data. They are appropriate to use when past numerical data is available and when it is reasonable to assume that some of the patterns in the data are expected to continue into the future.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is quantitative forecasting methods?
- Q. Which of the following is not a statistical method in forecasting?
- Q. What are the methods of forecasting?
- Q. Which one of the following is not a type of qualitative forecasting?
- Q. Which type of demand is forecasted quizlet?
- Q. Which type of demand is forecasted?
- Q. What is dependent demand?
- Q. How important is MRP in dependent demand?
- Q. What is the difference between dependent and independent demand?
- Q. Is independent demand forecasted?
- Q. What are the three basic production planning strategies?
- Q. When demand for a product is independent it is called?
- Q. What is independent demand inventory?
- Q. How do you calculate EOQ?
- Q. What is optimal level of inventory?
- Q. Do organizations need to carry inventory Why?
- Q. What is the importance of inventory in every organization?
- Q. What are the reasons for stocking items in inventory?
- Q. What is EOQ model?
- Q. What is the EOQ model used for?
- Q. What is classical EOQ model?
- Q. How do you use EOQ?
- Q. How is MOQ calculated?
- Q. What costs are considered in the basic EOQ model?
- Q. How is EOQ ordering cost calculated?
- Q. Is carrying cost the same as holding cost?
- Q. What companies use EOQ model?
- Q. What are the assumptions of EOQ?
- Q. What are the limitations of EOQ?
Q. Which of the following is not a statistical method in forecasting?
The only non-forecasting method is exponential smoothing with a trend.
Q. What are the methods of forecasting?
Top Four Types of Forecasting Methods
| Technique | Use |
|---|---|
| 1. Straight line | Constant growth rate |
| 2. Moving average | Repeated forecasts |
| 3. Simple linear regression | Compare one independent with one dependent variable |
| 4. Multiple linear regression | Compare more than one independent variable with one dependent variable |
Q. Which one of the following is not a type of qualitative forecasting?
The moving average method is not a type of qualitative forecasting.
Q. Which type of demand is forecasted quizlet?
Forecasting is done on independent demand items only.
Q. Which type of demand is forecasted?
2. Active demand forecasting. If your business is in a growth phase or if you’re just starting out, active demand forecasting is a good choice. An active forecasting model takes into consideration your market research, marketing campaigns, and expansion plans.
Q. What is dependent demand?
Generally, Dependent Demand Item refers to the item whose demand is required by the one-by-one calculation base on the independent demand items such as products and service parts, and includes assemblies, subassemblies, processed parts, purchased parts, and raw materials.
Q. How important is MRP in dependent demand?
MRP automates the planning processes determining how much raw material a business requires based on the projected demands. Material Requirements Planning is basically an inventory management system designed to streamline production schedules and place orders for items of dependent demand.
Q. What is the difference between dependent and independent demand?
Independent demand is demand for a finished product, such as a computer, a bicycle, or a pizza. Dependent demand, on the other hand, is demand for component parts or subassemblies. For example, this would be the microchips in the computer, the wheels on the bicycle, or the cheese on the pizza.
Q. Is independent demand forecasted?
Generally, Independent Demand Items, which have no direct relationship with other demands, are requested only according to the forecast. Such items include products, service parts, which are usually handled by the Sales division. The Independent Demand Items are used for forecasting and production planning.
Q. What are the three basic production planning strategies?
The main strategies used in production planning and control are the chase strategy, level production, make-to-stock, and assemble to order.
Q. When demand for a product is independent it is called?
The demand for a product that is not associated with the demand of other products is known as autonomous or direct demand. The autonomous demand arises due to the natural desire of an individual to consume the product.
Q. What is independent demand inventory?
Independent Demand. Definition. An inventory of an item is categorized independent demand when the demand for such an item is not dependent upon the demand for another item. An inventory of an item is categorized as dependent when demand for such an item is dependent upon another item.
Q. How do you calculate EOQ?
To calculate the economic order quantity, you will need the following variables: demand rate, setup costs, and holding costs. The formula is: EOQ = square root of: [2(setup costs)(demand rate)] / holding costs.
Q. What is optimal level of inventory?
Optimal inventory level is the quantity that covers all sales in the period between two stock arrivals. A lower inventory level without increasing the replenishment frequency will certainly cause stock-outs. Only an increased replenishment frequency allows the inventory level to be moved down with safety.
Q. Do organizations need to carry inventory Why?
Inventory is considered to be one of the most important assets of a business. Its management needs to be proactive, accurate and efficient. The primary objective in terms of holding inventory is to ensure that customer service targets can always be met without compromising cash flow or running out of stock.
Q. What is the importance of inventory in every organization?
Inventory management saves you money and allows you to fulfill your customers’ needs. In other words, it enables successful cost control of operations. Knowing what you have, what is in your warehouse, and how to manage the supply chain properly is the backbone of business.
Q. What are the reasons for stocking items in inventory?
4 Primary Reasons for Carrying Safety Stock
- Protect against unforeseen variation in supply.
- Compensate for forecast inaccuracies (only when demand exceeds the forecast)
- Prevent disruptions in manufacturing or deliveries.
- Avoid stock outs to keep customer service and satisfaction levels high.
Q. What is EOQ model?
Economic order quantity (EOQ) is the ideal order quantity a company should purchase to minimize inventory costs such as holding costs, shortage costs, and order costs. This production-scheduling model was developed in 1913 by Ford W. 1 The formula assumes that demand, ordering, and holding costs all remain constant.
Q. What is the EOQ model used for?
The economic order quantity (EOQ) model seeks to ensure that the right amount of inventory is ordered per batch so a company does not have to make orders too frequently and there is not an excess of inventory sitting on hand.
Q. What is classical EOQ model?
The EOQ model, supply chain management and Just-in-Time (JIT) represent some of the common and oldest classical production scheduling models and efficient inventory management tools. In other words, the classic EOQ is the amount of inventory to be ordered per time for purposes of minimizing annual inventory cost.
Q. How do you use EOQ?
EOQ formula
- Determine the demand in units.
- Determine the order cost (incremental cost to process and order)
- Determine the holding cost (incremental cost to hold one unit in inventory)
- Multiply the demand by 2, then multiply the result by the order cost.
- Divide the result by the holding cost.
Q. How is MOQ calculated?
There is no standard formula for calculating minimum order quantity. To determine the right MOQ for your business, it’s worth forecasting demand, doing scenario planning, calculating volume discounts, and inventory carrying costs. You can then decide the lowest quantity that works for your business.
Q. What costs are considered in the basic EOQ model?
Although we have identified a number of costs associated with inventory decisions in the chapter, only two categories, carrying cost and ordering cost, are considered in the basic EOQ model.
Q. How is EOQ ordering cost calculated?
EOQ Formula
- H = i*C.
- Number of orders = D / Q.
- Annual ordering cost = (D * S) / Q.
- Annual Holding Cost= (Q * H) / 2.
- Annual Total Cost or Total Cost = Annual ordering cost + Annual holding cost.
- Annual Total Cost or Total Cost = (D * S) / Q + (Q * H) / 2.
Q. Is carrying cost the same as holding cost?
Inventory carrying cost, also known as inventory holding cost, is the cost associated with holding inventory or stock in storage or a warehouse, in order to fulfill sales orders.
Q. What companies use EOQ model?
McDonald’s Corporation also uses the EOQ model in order to determine the most optimal order quantity and minimal costs while ordering materials and products or developing the system of producing the brand’s foods.
Q. What are the assumptions of EOQ?
Assumptions of EOQ model
- The rate of demand is constant, and total demand is known in advance.
- The ordering cost is constant.
- The unit price of inventory is constant, i.e., no discount is applied depending on order quantity.
- Delivery time is constant.
- Replacement of defective units is instantaneous.
Q. What are the limitations of EOQ?
Limitations of the EOQ Model: It is necessary for the application of EOQ order that the demands remain constant throughout the year which is not possible. Ordering cost per order can’t be constant because it’s including transport cost.