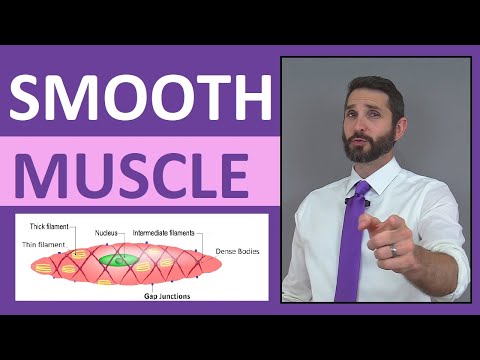
Q. What is a smooth muscle cell?
Smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped and have single elongated nuclei. Smooth muscle cells contain thin (actin) and thick (myosin) contractile filaments as well as cytoskeletal filaments. The thin filaments are the most conspicuous feature of smooth muscle cells.
Q. What is smooth muscle and its function?
Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs like your intestines and stomach. Smooth muscles are involved in many ‘housekeeping’ functions of the body. The muscular walls of your intestines contract to push food through your body. Muscles in your bladder wall contract to expel urine from your body.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is a smooth muscle cell?
- Q. What is smooth muscle and its function?
- Q. What makes smooth muscle cells?
- Q. Where are smooth muscle cells?
- Q. What is smooth muscle Class 9?
- Q. What is meant by smooth muscles are involuntary in action?
- Q. How are smooth muscle cells adapted to their function?
- Q. How does the structure of a smooth muscle cell relate to its function?
- Q. What are characteristics of smooth muscle?
- Q. What is unique about smooth muscle?
- Q. What are smooth muscles Class 11?
- Q. What are striated and smooth muscles Class 11?
- Q. What are the types of smooth muscle?
- Q. What is the function of smooth muscles?
- Q. What is a smooth muscle called?
- Q. What type of muscle is smooth?
Q. What makes smooth muscle cells?
Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins. Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as ATP is freed for use by the myosin.
Q. Where are smooth muscle cells?
Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Q. What is smooth muscle Class 9?
Smooth Muscle These muscle cells do not have striations or stripes. Hence they are called smooth muscle cells. They are also called involuntary muscles. The cells have a single nucleus and the cells are spindle-shaped. They are found in the walls of the hollow organs like the stomach, uterus etc.
Q. What is meant by smooth muscles are involuntary in action?
Smooth muscles are involuntary in action meaning they contract without conscious effort (stomach growls without trying to). Tell where each of the three types of muscle tissue would be found in the body. In regeneration, the injured tissue is replaced by the same type of cells.
Q. How are smooth muscle cells adapted to their function?
Airway and bladder smooth muscles are known to undergo length adaptation under sustained contraction. This adaptation process entails a remodelling of the intracellular actin and myosin filaments which shifts the peak of the active force-length curve towards the current length.
Q. How does the structure of a smooth muscle cell relate to its function?
Summary. Smooth muscle is found in the wall of hollow organs, passageways, tracts, eye and skin. Fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature.
Q. What are characteristics of smooth muscle?
Four characteristics define smooth muscle tissue cells: they are involuntarily controlled, not striated, not branched, and singly nucleated. The unconscious regions of the brain control visceral muscle through the autonomic and enteric nervous systems.
Q. What is unique about smooth muscle?
Smooth muscles are unique in their largely involuntary response, and in their structure. Smooth muscles have a much stronger ability to contract than skeletal muscles, and are able to maintain contraction longer. visceral smooth muscle – all cells work together at the same time as one unit.
Q. What are smooth muscles Class 11?
Smooth muscle is a form of muscle tissue that is used to apply pressure to vessels and organs through different systems. Sheets or chains of smooth muscle cells make up smooth muscle. These cells have actin and myosin fibers that pass through the cell and are protected by a protein matrix.
Q. What are striated and smooth muscles Class 11?
Skeletal or striated muscles: It is a form of striated muscle tissues and is mainly found attached to bones by the tendons. Smooth Muscles or unstriated muscled: These muscles are found inside of organs like the blood vessels, stomach, and intestines.
Q. What are the types of smooth muscle?
Yet, for the sake of simplicity, smooth muscle can generally be divided into two major types, which are shown in Figure 8-1: multi-unit smooth muscle and unitary (or single-unit) smooth muscle. Multi-Unit Smooth Muscle. This type of smooth muscle is composed of discrete, separate smooth muscle fibers.
Q. What is the function of smooth muscles?
The smooth muscles found in the eye’s pupillary sphincter are responsible for shrinking the size of the pupil.
Q. What is a smooth muscle called?
Smooth muscles — sometimes also called involuntary muscles — are usually in sheets, or layers, with one layer of muscle behind the other. You can’t control this type of muscle.
Q. What type of muscle is smooth?
Smooth muscle. Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two subgroups: the single-unit (unitary) and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit cells, the whole bundle or sheet contracts as a syncytium (i.e. a multinucleate mass of cytoplasm that is not separated into cells).