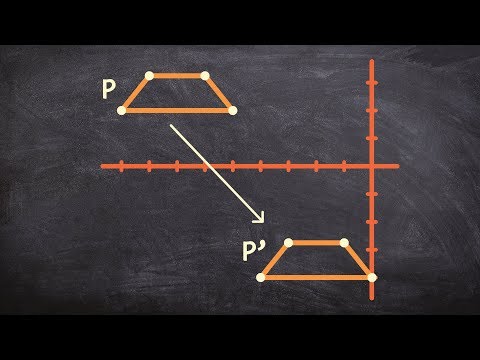
Q. What is a transformation that slides a figure?
Translation is when we slide a figure in any direction. Reflection is when we flip a figure over a line. Rotation is when we rotate a figure a certain degree around a point. Dilation is when we enlarge or reduce a figure.
Q. How can you use transformations in real life?
One real world example of transformations is with planes. A plane at Takeoff is the same size and shape of the same plane while landing or on the runway. It is just a Translation since the plane is just in a different angle.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is a transformation that slides a figure?
- Q. How can you use transformations in real life?
- Q. How do you know if compression is vertical or stretched?
- Q. What is the difference between a vertical stretch and a horizontal shrink?
- Q. What does a vertical stretch do?
- Q. What does a vertical stretch look like on a graph?
- Q. What is a vertical shift?
- Q. How do you know if the vertical shift is up or down?
- Q. How do you know if a function is horizontal or vertical?
- Q. How do you know if there is a vertical shift?
- Q. What is another name for the vertical shift?
- Q. How do you shift a function vertically?
- Q. Are shifting realities dangerous?
- Q. How do you move a function down?
- Q. Why does subtracting shift right?
- Q. Why are horizontal shifts backwards?
- Q. What happens when you shift realities?
- Q. How do you do horizontal shift?
- Q. What are the ways to transform the pre-image to the image?
- Q. Which transformation can change the area of a figure?
- Q. How do you describe transformations in math?
- Q. What is a transformed graph?
- Q. Which one is a parent function?
- Q. How do you identify the parent function?
- Q. What are the transformations of a parent function?
Q. How do you know if compression is vertical or stretched?
When we multiply a function by a positive constant, we get a function whose graph is stretched or compressed vertically in relation to the graph of the original function. If the constant is greater than 1, we get a vertical stretch; if the constant is between 0 and 1, we get a vertical compression.
Q. What is the difference between a vertical stretch and a horizontal shrink?
A vertical compression (or shrinking) is the squeezing of the graph toward the x-axis. if k > 1, the graph of y = k•f (x) is the graph of f (x) vertically stretched by multiplying each of its y-coordinates by k. A horizontal compression (or shrinking) is the squeezing of the graph toward the y-axis.
Q. What does a vertical stretch do?
What are Vertical Stretches and Shrinks? While translations move the x and y intercepts of a base graph, stretches and shrinks effectively pull the base graph outward or compress the base graph inward, changing the overall dimensions of the base graph without altering its shape.
Q. What does a vertical stretch look like on a graph?
Vertical stretch occurs when a base graph is multiplied by a certain factor that is greater than 1. This results in the graph being pulled outward but retaining the input values (or x). When a function is vertically stretched, we expect its graph’s y values to be farther from the x-axis.
Q. What is a vertical shift?
Vertical shifts are outside changes that affect the output ( y- ) axis values and shift the function up or down. Combining the two types of shifts will cause the graph of a function to shift up or down and right or left.
Q. How do you know if the vertical shift is up or down?
A General Note: Vertical Shift All the output values change by k units. If k is positive, the graph will shift up. If k is negative, the graph will shift down.
Q. How do you know if a function is horizontal or vertical?
Once we have determined that a graph defines a function, an easy way to determine if it is a one-to-one function is to use the horizontal line test. Draw horizontal lines through the graph. If any horizontal line intersects the graph more than once, then the graph does not represent a one-to-one function.
Q. How do you know if there is a vertical shift?
If you divide the C by the B (C / B), you’ll get your phase shift. The D is your vertical shift. The vertical shift of a trig function is the amount by which a trig function is transposed along the y-axis, or, in simpler terms, the amount it is shifted up or down.
Q. What is another name for the vertical shift?
transformations
Q. How do you shift a function vertically?
We can express the application of vertical shifts this way: Formally: For any function f(x), the function g(x) = f(x) + c has a graph that is the same as f(x), shifted c units vertically. If c is positive, the graph is shifted up. If c is negative, the graph is shifted down.
Q. Are shifting realities dangerous?
Q) Is shifting dangerous? A) Aside from being mentally exhausted when you come back, shifting is not dangerous whatsoever. Some creators on TikTok claim that you can get stuck in your DR, but that’s just simply false.
Q. How do you move a function down?
Vertical Translation To translate the function up and down, you simply add or subtract numbers from the whole function. If you add a positive number (or subtract a negative number), you translate the function up. If you subtract a positive number (or add a negative number), you translate the function down.
Q. Why does subtracting shift right?
(a+2,b) is 2 to the right from (a,b). Think of it this way, when you graph f(x-2) you need to go two steps further to the right along the x-axis to reach f(x). Therefore it shifts to the right.
Q. Why are horizontal shifts backwards?
Because they’re on the same side as the x, instead of on the opposite side. If you write y=f(x)+3, that’s the same as y-3=f(x).
Q. What happens when you shift realities?
Put simply, the practice of shifting realities entails shifting your consciousness from your current experience, i.e. Current Reality (CR) to another reality, typically your Desired Reality (DR). I know this all sounds a little “woo woo”, and there is of course a very broad spectrum of opinions on the topic.
Q. How do you do horizontal shift?
Horizontal Shifts To shift a graph horizontally, a constant must be added to the function within parentheses–that is, the constant must be added to the angle, not the whole function. Compare the to the graph of y = f (x) = sin(x + ).
Q. What are the ways to transform the pre-image to the image?
The operation that maps(moves)the preimage onto the image is called a transformation. There are 3 basic transformations that are related to congruence(isometries): reflections, rotations, and translations.
Q. Which transformation can change the area of a figure?
Dilations. A dilation is a transformation which preserves the shape and orientation of the figure, but changes its size. The scale factor of a dilation is the factor by which each linear measure of the figure (for example, a side length) is multiplied.
Q. How do you describe transformations in math?
A transformation is a process that manipulates a polygon or other two-dimensional object on a plane or coordinate system. Mathematical transformations describe how two-dimensional figures move around a plane or coordinate system. A preimage or inverse image is the two-dimensional shape before any transformation.
Q. What is a transformed graph?
Graph transformation is the process by which an existing graph, or graphed equation, is modified to produce a variation of the proceeding graph. Sometimes graphs are translated, or moved about the x y xy xy-plane; sometimes they are stretched, rotated, inverted, or a combination of these transformations.
Q. Which one is a parent function?
Parent function definition Parent functions are the simplest form of a given family of functions. These four are all quadratic functions, and their simplest form would be y = x2. Hence, the parent function for this family is y = x2.
Q. How do you identify the parent function?
For example, you can simplify “y=2*sin(x+2)” to “y=sin(x)” or “y=|3x+2|” to “y=|x|.” Graph the result. This is the parent function. For example, the parent function for “y=x^+x+1” is just “y=x^2,” also known as the quadratic function.
Q. What are the transformations of a parent function?
The transformation of the parent function is shown in blue. It is a shift down (or vertical translation down) of 1 unit. A reflection on the x-axis is made on a function by multiplying the parent function by a negative. Multiplying by a negative “flips” the graph of the function over the x-axis.