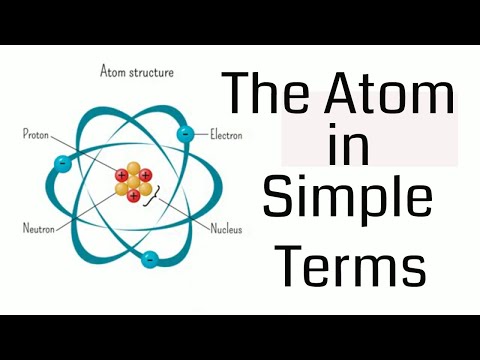
An atom consists of a positively charged sphere with electrons embedded in it. An atom consists of a positively charged particles concentrated at the centre known as the nucleus. The size of the nucleus is very small as compared to the size of the atom. The electrons revolve around the nucleus in well-defined orbits.
Q. What is a molecule class 9?
Gram Atomic Mass: The atomic mass of an element expressed in grams is known as gram atomic mass. Molecules: A group of two or more than two atoms of the same or different elements that are chemically bonded together is called a molecule.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is a molecule class 9?
- Q. What is Atom very short answer?
- Q. What is the structure of an atom Class 9?
- Q. What are isobars Class 9?
- Q. What is called Isobar?
- Q. What do you mean by Tetravalency?
- Q. How do you explain the Tetravalency of 4?
- Q. What are monovalent elements?
- Q. What is Tetravalency with example?
Q. What is Atom very short answer?
Atoms are the basic building blocks of ordinary matter. Atoms can join together to form molecules, which in turn form most of the objects around you. Atoms are composed of particles called protons, electrons and neutrons.
Q. What is the structure of an atom Class 9?
An atom consists of heavy positively charged nucleus. The whole mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus. The electrons in an atom revolve around the nucleus in definite circular paths called orbits or energy level.
Q. What are isobars Class 9?
Isobars are defined as. The atoms that have same number of nucleons. Isobars of different chemical elements have different atomic number but have the same mass number.
Q. What is called Isobar?
Isobars are atoms (nuclides) of different chemical elements that have the same number of nucleons. Correspondingly, isobars differ in atomic number (or number of protons) but have the same mass number. The term “isobars” (originally “isobares”) for nuclides was suggested by Alfred Walter Stewart in 1918.
Q. What do you mean by Tetravalency?
Carbon has a valency of four, so it is capable of bonding with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other monovalent element. This is known as tetravalency of carbon.
Q. How do you explain the Tetravalency of 4?
Tetravalency: Carbon can neither lose nor gain electrons to attains octet. Thus it shares four electrons with other atoms. This characteristics of carbon by virtue of which it forms four covalent bonds, is called Tetravalency of carbon.
Q. What are monovalent elements?
Monovalent. An atom, ion, or chemical group with a valence of one, which thus can form one covalent bond is called monovalent. Examples. Atoms that are monovalent are. Hydrogen.
Q. What is Tetravalency with example?
In chemistry,tetravalency is the state of atom with 4 valence electrons,available for covalent chemical bonding. e.g. CH4 methane. in methane ,tetravalent carbon .. make bond with 4 oxygen atoms.