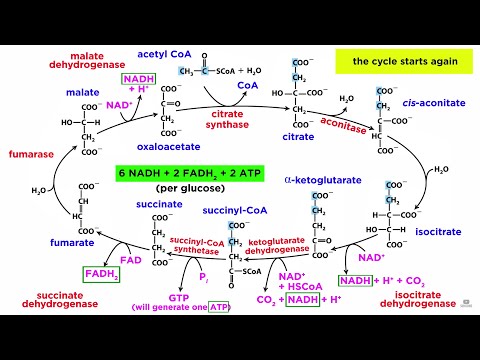
The Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
Q. What is the main function of the citric acid cycle?
The function of the citric acid cycle is the harvesting of high-energy electrons from carbon fuels. Note that the citric acid cycle itself neither generates a large amount of ATP nor includes oxygen as a reactant (Figure 17.3).
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the main function of the citric acid cycle?
- Q. Why is the citric acid cycle important?
- Q. Where does citric acid cycle take place quizlet?
- Q. What goes in the citric acid cycle quizlet?
- Q. What is the main function of citric acid cycle quizlet?
- Q. What are the end products of the citric acid cycle quizlet?
- Q. What is produced from the third stage of cellular respiration?
- Q. What is the net production of ATP in cellular respiration?
- Q. What are the two things needed for cellular respiration?
- Q. What are the main reactants outputs for cellular respiration?
- Q. How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration work together quizlet?
- Q. What are the similarities differences in photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Q. Why is the citric acid cycle important?
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs or citric acid cycle, is the main source of energy for cells and an important part of aerobic respiration. The cycle harnesses the available chemical energy of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) into the reducing power of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH).
Q. Where does citric acid cycle take place quizlet?
mitochondria
Q. What goes in the citric acid cycle quizlet?
The citric acid cycle generates 3 molecules of NADH, 1 molecule of FADH2, and 1 molecule of GTP(ATP) per acetyl-sCoA that enters the cycle. Cycle activity is controlled by the availability of substrate(acetyl-sCoA) and at key irreversible steps.
Q. What is the main function of citric acid cycle quizlet?
The function of the citric acid cycle is to harvest high-energy electrons from carbon fuels.
Q. What are the end products of the citric acid cycle quizlet?
end products are 2 acetyl CoA, 2 NADH, 2 H and 2 Co2. what are the initial reactants in the citric acid cycle?
Q. What is produced from the third stage of cellular respiration?
The third and final stage of cellular respiration is called electron transport. Remember the other energy-storing molecules from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle? Their energy is used in this stage to make many more molecules of ATP. In fact, during this stage, as many as 34 molecules of ATP are produced.
Q. What is the net production of ATP in cellular respiration?
net yield of 34 ATP per glucose molecule. 6 H2O are formed when the electrons unite with O2* at the end of electron transport chain. [* Note: This is the function of oxygen in living organisms!]
Q. What are the two things needed for cellular respiration?
Oxygen and glucose are both reactants in the process of cellular respiration. The main product of cellular respiration is ATP; waste products include carbon dioxide and water.
Q. What are the main reactants outputs for cellular respiration?
The inputs, or reactants, of cellular respiration are glucose and oxygen. The outputs, or products, of cellular respiration are water, carbon dioxide…
Q. How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration work together quizlet?
They work together by photosynthesis producing the reactants for cellular respiration. Cellular respiration then produces the reactants for photosynthesis. All organisms do cellular respiration, but only producers like plants do photosynthesis.
Q. What are the similarities differences in photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of cells. While photosynthesis requires energy and produces food, cellular respiration breaks down food and releases energy. Plants perform both photosynthesis and respiration, while animals can only perform respiration.