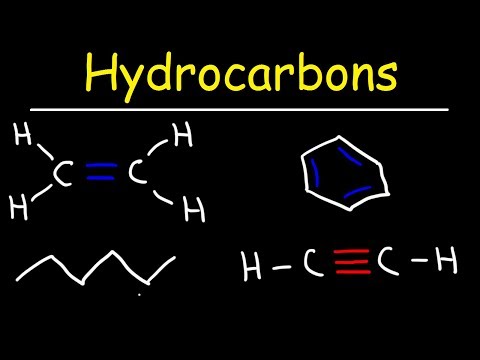
Unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain one or more double bonds are called alkenes. The name of a specific alkene always ends in –ene and has a prefix indicating the number of carbon atoms.
Q. Which compound is an unsaturated hydrocarbon Hexanal?
hexyne
Table of Contents
- Q. Which compound is an unsaturated hydrocarbon Hexanal?
- Q. Which compound is unsaturated hydrocarbon?
- Q. Are alkynes unsaturated?
- Q. What is the formula for unsaturated hydrocarbon?
- Q. What is unsaturated hydrocarbon with example?
- Q. What is meant by unsaturated hydrocarbons?
- Q. What are the properties of unsaturated hydrocarbons?
- Q. Which amongst the following is a unsaturated hydrocarbon?
- Q. Which of the following is unsaturated compounds?
- Q. Which among the following is an example of hydrocarbon?
- Q. What are two organic compounds?
- Q. How do you distinguish between ionic and molecular compounds?
Q. Which compound is unsaturated hydrocarbon?
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atoms….Combustion.
| Number of Carbon | 2 |
|---|---|
| Substance | ethene |
| Type | unsaturated |
| Formula | C2H4 |
| Hcø(kJ/mol) | −1410.8 |
Q. Are alkynes unsaturated?
Like alkenes, alkynes are unsaturated because they are capable of reacting with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to form a corresponding fully saturated alkane. Because alkynes possess two π bonds per molecule, they are said to contain two elements of unsaturation.
Q. What is the formula for unsaturated hydrocarbon?
Their general formula is thus CnH2n–2. Compounds containing double or triple bonds are often referred to collectively as unsaturated compounds. Because of their multiple bonds, alkenes and alkynes are usually more chemically reactive than alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons. Figure 1) joining the two atoms together.
Q. What is unsaturated hydrocarbon with example?
An unsaturated hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon containing at least one double or triple bond. An alkene is a hydrocarbon containing double bonds. Ethene, C2H4, is an example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Other examples of unsaturated compounds are benzene, C6H6, and acetic acid, C2H4O2.
Q. What is meant by unsaturated hydrocarbons?
A hydrocarbon molecule containing one or more double or triple bonds, and can thus absorb more hydrogen atoms.
Q. What are the properties of unsaturated hydrocarbons?
Answers
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons have double or triple bonds and are quite reactive; saturated hydrocarbons have only single bonds and are rather unreactive.
- An alkene has a double bond; an alkane has single bonds only.
- saturated; alkane. unsaturated; alkyne. unsaturated; alkene.
Q. Which amongst the following is a unsaturated hydrocarbon?
The answer is (c) (ii) and (iv) Option (ii and (iv) having double and triple bonds, hence they are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Q. Which of the following is unsaturated compounds?
C4H8 is an alkene with the general formula; CnH2n and thus an unsaturated compound.
Q. Which among the following is an example of hydrocarbon?
Simple hydrocarbons and their variations
| Number of carbon atoms | Alkane (single bond) | Alkene (double bond) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Methane | — |
| 2 | Ethane | Ethene (ethylene) |
| 3 | Propane | Propene (propylene) |
| 4 | Butane | Butene (butylene) |
Q. What are two organic compounds?
Among the numerous types of organic compounds, four major categories are found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Q. How do you distinguish between ionic and molecular compounds?
The difference between Ionic and Molecular Compounds is that the electrons of atoms in ionic compounds are transferred between the elements because of the presence of a difference in electronegativity. However, in the case of molecular compounds, the electrons are only shared but not transferred.