Q. What is beta decay in terms of quarks?
The emission of beta radiation provides evidence that neutrons and protons are made up of quarks. Beta ( ) decay is the release of an electron by the change of a neutron to a proton.
Q. How do you explain beta decay?
Beta decay occurs when, in a nucleus with too many protons or too many neutrons, one of the protons or neutrons is transformed into the other. In beta minus decay, a neutron decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino: n Æ p + e – +.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is beta decay in terms of quarks?
- Q. How do you explain beta decay?
- Q. How do quarks decay?
- Q. What happens when quarks decay?
- Q. What is released in beta plus decay?
- Q. What do top quarks decay into?
- Q. What is beta decay class 12?
- Q. How are quarks involved in beta decay of a proton?
- Q. What makes up the charge of beta decay?
- Q. What kind of quantum number does beta decay conserve?
- Q. How are neutrons and protons composed of quarks?
Q. How do quarks decay?
Up and down quarks can decay into each other by emission of a W boson (this is the origin of beta decay due to the fact that the W can, depending on its type, decay into electrons, positrons and electron (anti-)neutrinos, ). The current understanding of quarks is, that they are a fundamental particle.
Q. What happens when quarks decay?
In a beta decay, a neutron (made of one up quark and two down quarks) can transform into a proton (made of two up quarks and one down quark), an electron, and an electron antineutrino. This reaction can happen in a neutron within an atom or a free-floating neutron. Let’s look at a process called beta decay.
Q. What is released in beta plus decay?
Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino (νe). Positron emission is mediated by the weak force.
Q. What do top quarks decay into?
W boson
The top quark will decay almost instantaneously to a W boson and a down-type quark “x” with the probabilities given by the CKM matrix elements |Vtx|2. The main decay happens into a W boson and a b quark with a probability of 99.9%.
Q. What is beta decay class 12?
Beta decay is a radioactive decay in which a beta ray is emitted from an atomic nucleus. During beta decay, the proton in the nucleus is transformed into a neutron and vice versa. If a proton is converted to neutron, it is known as β+ decay.
Q. How are quarks involved in beta decay of a proton?
A proton consists of two up quarks and a down quark ( p = uud ). In positron ( β+) decay, an up quark changes to a down quark, with the release of a positron and a neutrino. The overall result us that a proton becomes a neutron: A neutron consists of two down quarks and a up quark ( n = ddu ).
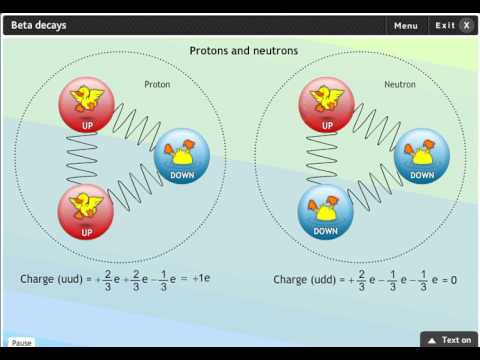
Q. What makes up the charge of beta decay?
Beta ( (beta^-)) decay is the release of an electron by the change of a neutron to a proton. The neutron (charge = 0) is made up of one up quark (charge = (frac {2} {3})) and two down quarks (charge = (2 times frac {1} {3}=frac {2} {3})).
Q. What kind of quantum number does beta decay conserve?
Beta decay conserves a quantum number known as the lepton number, or the number of electrons and their associated neutrinos (other leptons are the muon and tau particles).
Q. How are neutrons and protons composed of quarks?
The emission of beta radiation provides evidence that neutrons and protons are made up of quarks. Beta ( (beta^-)) decay is the release of an electron by the change of a neutron to a proton. The neutron (charge = 0) is made up of one up quark (charge = (frac {2} {3})) and two down quarks (charge = (2 times frac {1} {3}=frac {2} {3})).