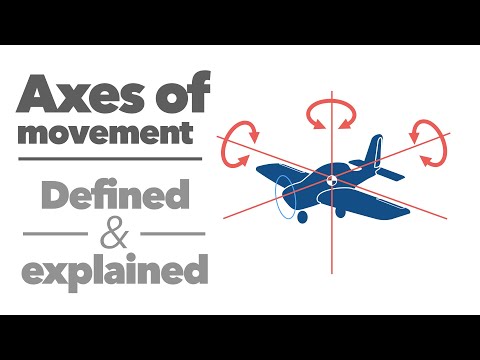
Q. What is called three axis stabilization?
Another method for achieving three-axis stabilization is to use electrically-powered reaction wheels, also called momentum wheels. Massive wheels are mounted in three orthogonal axes aboard the spacecraft. They provide a means to trade angular momentum back and forth between spacecraft and wheels.
Q. What are stabilization techniques in satellite communication?
Three Axis Method In this method, we can stabilize the satellite by using one or more momentum wheels. This method is called as three-axis method. The advantage of this method is that the orientation of the satellite in three axes will be controlled and no need of rotating satellite’s main body.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is called three axis stabilization?
- Q. What are stabilization techniques in satellite communication?
- Q. What do you mean by satellite stabilization?
- Q. How do rockets spin?
- Q. Why do satellites rotate?
- Q. What device stabilizes rockets and planes?
- Q. How is geostationary orbit achieved?
- Q. How does a satellite remain in orbit?
- Q. What are the subsystems of a satellite?
- Q. What is rocket stability?
- Q. How is a satellite stabilized on three axis?
- Q. How does spin and three axis stabilization work?
- Q. How is the attitude of a satellite controlled?
- Q. How is a gyroscopic effect used to stabilize a satellite?
Q. What do you mean by satellite stabilization?
Satellite Stabilization methods are employed for the attitude control system that is necessary for the spacecraft in order to maintain the antenna pointed correctly towards the Earth’s direction. Various methods are employed for the stabilization of satellite.
Q. How do rockets spin?
In flight, the fins of the rocket produce aerodynamic forces. The torques cause the rocket to rotate. Most full scale rockets produce pitch or yaw motions by gimballing, or rotating, the exhaust nozzle. If the thrust vector is not alligned with the roll axis, it produces a torque about the center of gravity.
Q. Why do satellites rotate?
A satellite orbits Earth when its speed is balanced by the pull of Earth’s gravity. Without this balance, the satellite would fly in a straight line off into space or fall back to Earth. It moves in the same direction and at the same rate Earth is spinning.
Q. What device stabilizes rockets and planes?
Fin stabilizer, fin or small wing mounted on a ship or aircraft in such a way as to oppose unwanted rolling motions of the vehicle and thus contribute to its stability. The term also refers to the tail protuberances on bombs, artillery shells, and rockets to maintain the stability of these devices in flight.
Q. How is geostationary orbit achieved?
To attain geosynchronous (and also geostationary) Earth orbits, a spacecraft is first launched into an elliptical orbit with an apoapsis altitude in the neighborhood of 37,000 km. The spacecraft then circularizes the orbit by turning parallel to the equator at apoapsis and firing its rocket engine.
Q. How does a satellite remain in orbit?
Satellites are able to orbit around the planet because they are locked into speeds that are fast enough to defeat the downward pull of gravity. A satellite maintains its orbit by balancing two factors: its velocity (the speed it takes to travel in a straight line) and the gravitational pull that Earth has on it.
Q. What are the subsystems of a satellite?
Introduction to satellite subsystems
- Space segment.
- Application.
- Orbit.
- Launch.
- Ground segment.
- Operations.
- Communications.
Q. What is rocket stability?
The definition for model rocket stability is when the Center-of-Gravity (CG) is in front of the Center-of-Pressure (CP). The further dis- tance the CG is in front of the CP, the more stable the rocket will be. “Stability” for us essentially means to fly a predictable flight path.
Q. How is a satellite stabilized on three axis?
When a satellite is stabilized about these axis then it is called as three axis body stabilization. In this method stability is achieved by mounting three momentum wheels on three mutually perpendicular axis as shown in figure: A momentum wheel is a high speed wheel driven by the motor. It is kept in a sealed evaluated chamber.
Q. How does spin and three axis stabilization work?
Spin stabilization and three-axis stabilization are two methods that are used to orient satellites. With spin stabilization, the entire spacecraft rotates around its own vertical axis, spinning like a top. This keeps the spacecraft’s orientation in space under control.
Q. How is the attitude of a satellite controlled?
In order to control the attitude in space, the satellite has to be properly oriented using momentum wheels and thruster motors in these three axis. The two major methods used are as follow: It is the most commonly used method and employed method where the entire spacecraft is rotated at 30 to 100 rotations per minutes.
Q. How is a gyroscopic effect used to stabilize a satellite?
Once the satellite is in the position and its antenna, solar panels and sensors are oriented, the flywheel is put into motion. Again the gyroscopic effect keeps the satellite oriented with proper attitude. The three axis stabilisation as the name suggest use three axis called as pitch, roll and yaw to achieve attitude control.