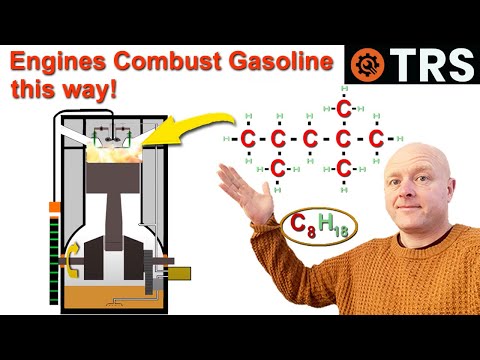
Q. What is chemical composition of gasoline?
Gasoline is a petroleum-derived product comprising a mixture of liquid aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, ranging between C4 and C12 carbon atoms with the boiling range of 30–225°C. It is predominantly a mixture of paraffins, naphthenes, aromatics and olefins.
Q. What is the chemical composition of unleaded gasoline?
Unleaded gasoline contains at least 15 hazardous chemicals including, by volume, benzene (∼5%), toluene (35%), naphthalene (∼1%), trimethylbenzene (∼7%), and MTBE (∼18%, in some states).
Table of Contents
- Q. What is chemical composition of gasoline?
- Q. What is the chemical composition of unleaded gasoline?
- Q. What is the mixture of gasoline?
- Q. What is the main hydrocarbon in gasoline?
- Q. What is the scientific name for gasoline?
- Q. How much gasoline is left in the world?
- Q. What happens if we run out of gasoline?
- Q. Will the world ever run out of gasoline?
- Q. Can we survive without fossil fuels?
- Q. What are 3 problems with using fossil fuels?
- Q. What are the 5 types of fossil fuels?
- Q. What is fuel and its types?
- Q. What are the main sources of fuel?
- Q. What are the two kinds of fuels?
- Q. What are fuels give five examples?
Q. What is the mixture of gasoline?
The typical composition of gasoline hydrocarbons (% volume) is as follows: 4-8% alkanes; 2-5% alkenes; 25-40% isoalkanes; 3-7% cycloalkanes; l-4% cycloalkenes; and 20-50% total aromatics (0.5-2.5% benzene) (IARC 1989).
Q. What is the main hydrocarbon in gasoline?
Simply, “Gasoline contains mainly alkanes (paraffins), alkenes (olefins), and aromatics,” according to Advanced Motor Fuels. The most prevalent hydrocarbons in gasoline, alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with large reserves of energy.
Q. What is the scientific name for gasoline?
Alternative Titles: gas, gasolene, motor gasoline, petrol. Gasoline, also spelled gasolene, also called gas or petrol, mixture of volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbons derived from petroleum and used as fuel for internal-combustion engines. It is also used as a solvent for oils and fats.
Q. How much gasoline is left in the world?
There are 6,923 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of proven gas reserves in the world as of 2017. The world has proven reserves equivalent to 52.3 times its annual consumption. This means it has about 52 years of gas left (at current consumption levels and excluding unproven reserves).
Q. What happens if we run out of gasoline?
By the year 2080, the world’s supply of oil will be in steep decline. It will take more energy to take the petroleum out of the ground than can be gained from the use of the produced oil. This would mean gasoline prices would skyrocket as countries would get low in their reserves of oil.
Q. Will the world ever run out of gasoline?
The truth is, any of the fossil fuels that are usually in the discussion, like oil and natural gas, probably won’t be running out for generations, if ever. Some resources are able to be recycled, and others can be recovered. So as our reserves dwindle down, they’ll just start becoming more expensive to produce.
Q. Can we survive without fossil fuels?
It is not feasible to immediately stop extracting and using fossil fuels. The global economy, human health and livelihoods currently depend heavily on oil, coal and gas. But over time, we need to displace fossil fuels with low-carbon renewable energy sources.
Q. What are 3 problems with using fossil fuels?
Fossil fuels take a toll on the environment. They cause obvious problems such as oil spills and smog filled air. They also cause other, more complicated problems that are not so easy to see. Acid rain, for example, caused partially by sulfur in fossil fuels, damages buildings and harms trees, aquatic life, and insects.
Q. What are the 5 types of fossil fuels?
fossil fuel coal, oil, or natural gas. Fossil fuels formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals.
Q. What is fuel and its types?
Fuel meaning: Meaning of fuel is a substance that is burned to provide nuclear energy, heat or power. Materials like coal, wood, oil, or gas can provide heat when burned. Methanol, Gasoline, Diesel, Propane, Natural gas, Hydrogen are types of fuel. Nuclear energy is produced by burning plutonium.
Q. What are the main sources of fuel?
Primary energy sources take many forms, including nuclear energy, fossil energy — like oil, coal and natural gas — and renewable sources like wind, solar, geothermal and hydropower.
Q. What are the two kinds of fuels?
Fuels can be generally classified into two factors:
- Solid Fuels.
- Liquid Fuels.
- Gaseous Fuels.
Q. What are fuels give five examples?
Wood, coal, LPG, kerosene, diesel etc. Characteristics of ideal fuel: It should have high calorific value. It should burn without giving out any smoke or harmful gases.