Q. What is cosolvent effect?
Weakly electrolytes and nonpolar molecules frequently have poor water solubility. Their solubility usually can be increased by the addition of water miscible solvent in which the drug has good solubility. This process is known as cosolvency, and the solvents used to increase solubility are known as cosolvent.
Q. What is the meaning of co solvency?
A cosolvent is a substance that is added to a mixture of two or more separate substances that are typically immiscible, in order to make them mixable. Cosolvents are added to increase the solvent power of the primary substance in the mixture.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is cosolvent effect?
- Q. What is the meaning of co solvency?
- Q. How does cosolvent increase the solubility of poorly soluble drugs?
- Q. What is cosolvent give example?
- Q. How does cosolvent increase solubility?
- Q. Is water a cosolvent?
- Q. What is a co solvent system?
- Q. Which of the cosolvent are used to increase solubility of drug?
- Q. Is acetone a cosolvent?
- Q. Which of the following complexing agent is used to increase the solubility of drug?
- Q. Is ethanol a cosolvent?
- Q. Is glycerol a cosolvent?
- Q. How does cosolvent improve solubility between non-miscible phases?
- Q. What is the effect of cosolvency on drug solubilization?
- Q. What happens when a cosolvent is added to a solvent?
- Q. How is the effectiveness of a cosolvent determined?
Q. How does cosolvent increase the solubility of poorly soluble drugs?
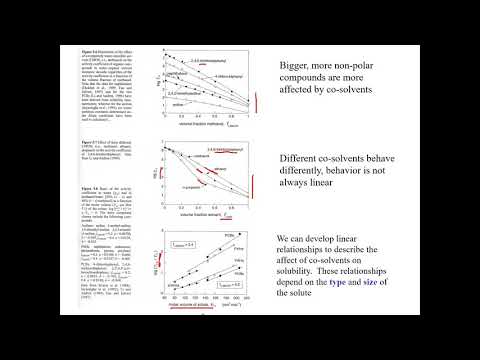
Cosolvents improve solubility between non-miscible phases, as demonstrated by a solute dissolved in organic solvent but insoluble in water (left). A cosolvent miscible in both phases and able to dissolve the solute is added to form a homogeneous solution of water, organic solvent, and compound (right).
Q. What is cosolvent give example?
Answer: Common cosolvents for this purpose are ethanol, propylene glycol, glycerine, glycofural, and polyethylene glycols.
Q. How does cosolvent increase solubility?
This process is known as cosolvency, and the solvents used to increase solubility are known as cosolvent. Cosolvent system works by reducing the interfacial tension between the aqueous solution and hydrophobic solute. It is also commonly referred to as solvent blending.
Q. Is water a cosolvent?
These results demonstrate that the strong water/cosolvent (water–ethanol) attraction is the key. Because of the strong water–cosolvent attraction, the total number of hydrogen bonding with PDEA is decreasing.
Q. What is a co solvent system?
A co solvent system is one in which a water miscible or partially miscible organic solvent is mixed with water to form a modified aqueous solution. The resulting solution will have physical properties that are intermediate to that of the pure organic solvent and water through the reduction of water–water interaction.
Q. Which of the cosolvent are used to increase solubility of drug?
Co-solvent solubilization approach has been used to enhance the solubility of seven antidiabetic drugs: gliclazide, glyburide, glipizide, glimepiride, repaglinide, pioglitazone, and roziglitazone.
Q. Is acetone a cosolvent?
Acetone, ethanol, and methanol were selected as cosolvents. Optimal nanoparticles were achieved with ethanol as a cosolvent, and the formation efficiency of the particles was also higher with ethanol as compared with acetone or methanol.
Q. Which of the following complexing agent is used to increase the solubility of drug?
It has been demonstrated that cyclodextrins can be used as complexing agents for poorly soluble anti-cancer drugs, increasing their solubility and hence drug availability.
Q. Is ethanol a cosolvent?
The results of the study show that ethanol has a role as a cosolvent where the OH (hydroxyl) as the head (polar) is attached to the polar methanol molecule while the CH (hydrocarbon) group as the tail (non-polar) interacts with the non-polar gasoline molecule.
Q. Is glycerol a cosolvent?
Glycerol is a co-solvent for water extraction that has been shown to be highly effective for obtaining polyphenol extracts under atmospheric conditions.
Q. How does cosolvent improve solubility between non-miscible phases?
Cosolvents improve solubility between non-miscible phases, as demonstrated by a solute dissolved in organic solvent but insoluble in water (left). A cosolvent miscible in both phases and able to dissolve the solute is added to form a homogeneous solution of water, organic solvent, and compound (right).
Q. What is the effect of cosolvency on drug solubilization?
The effect of cosolvency on drug solubilization can be great, as evidenced by a 2009 study in which researchers from Panjab University showed the solubility of various anti-diabetic drugs increase by more than 500 times by use of a cosolvent.
Q. What happens when a cosolvent is added to a solvent?
A cosolvent miscible in both phases and able to dissolve the solute is added to form a homogeneous solution of water, organic solvent, and compound (right). In chemistry, cosolvents are substances added to a primary solvent in small amounts to increase the solubility of a poorly-soluble compound.
Q. How is the effectiveness of a cosolvent determined?
The effectiveness of a cosolvent is determined by its solubilization power. This is the maximum rate of dissolution of a solute in mixtures of various compositions. Cosolvents work best in the presence of another solvent that, in conjunction, enhances the dissolution of a solute.