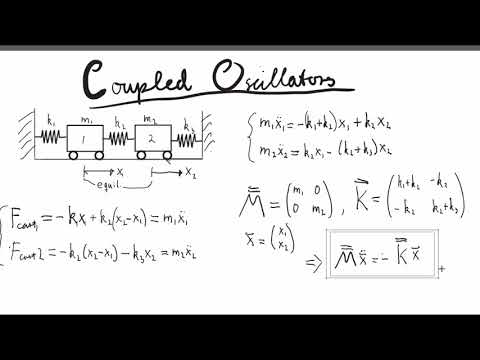
Q. What is coupled oscillator?
Coupled Oscillations occur when two or more oscillating systems are connected in such a manner as to allow motion energy to be exchanged between them. Coupled oscillators occur in nature (e.g., the moon and earth orbiting each other) or can be found in man-made devices (such as with the pacemaker).
Q. What are normal mode in coupled oscillation?
A normal mode of an oscillating system is the motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is coupled oscillator?
- Q. What are normal mode in coupled oscillation?
- Q. What is normal mode in coupled pendulum?
- Q. Why is Hamiltonian better than Lagrangian?
- Q. What is a coupled harmonic oscillator?
- Q. What is coupled pendula?
- Q. What are the natural frequencies of coupled oscillator?
- Q. What is resonance in coupled pendulum?
- Q. What is difference between Lagrange and Hamiltonian?
- Q. What is the relationship between Hamiltonian and Lagrangian?
- Q. Why is coupled oscillator important?
- Q. Where does the motion take place in a coupled oscillator?
- Q. Can a harmonic oscillator behave like a sine wave?
- Q. What makes a protein a coupled oscillator?
- Q. Where does the force of a harmonic oscillator originate?
Q. What is normal mode in coupled pendulum?
Te two boxed equations are the two normal modes of the coupled pendulum system. In a normal mode, all the particles oscillate at the same frequency (but not necessarily the same amplitude or phase).
Q. Why is Hamiltonian better than Lagrangian?
(ii) Claim: The Hamiltonian approach is superior because it leads to first-order equations of motion that are better for numerical integration, not the second-order equations of the Lagrangian approach.
Q. What is a coupled harmonic oscillator?
Coupled oscillators are oscillators connected in such a way that energy can be transferred between them. The motion of coupled oscillators can be complex, and does not have to be periodic. The atoms oscillate around their equilibrium positions, and the interaction between the atoms is responsible for the coupling.
Q. What is coupled pendula?
Two pendulums that can exchange energy are called coupled pendulums. The gravitational force acting on the pendulums creates rotational stiff- ness that drives each pendulum to return to its rest position. This cou- pling also produces an additional rotational stiffness that causes the spring.
Q. What are the natural frequencies of coupled oscillator?
There is a resonance at their natural frequency, ω0, when the oscillators oscillate in phase and a resonance at the frequency ω = √ω20 + 2kc/m when the oscillators are 180° out of phase. These oscillations are referred to individually as the symmetric and antisymmetric modes or collectively as the normal modes.
Q. What is resonance in coupled pendulum?
Every pendulum has a natural or resonant frequency, which is the number of times it swings back and forth per second. The resonant frequency depends on the pendulum’s length. Longer pendulums have lower frequencies. As soon as the second pendulum starts to swing, it starts pulling back on the first pendulum.
Q. What is difference between Lagrange and Hamiltonian?
Lagrangian mechanics can be defined as a reformulation of classical mechanics. The key difference between Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics is that Lagrangian mechanics describe the difference between kinetic and potential energies, whereas Hamiltonian mechanics describe the sum of kinetic and potential energies.
Q. What is the relationship between Hamiltonian and Lagrangian?
What is the relation between the Hamiltonian and Lagrangian in GR to Newtonian mechanics? The Lagrangian and Hamiltonian in Classical mechanics are given by L=T−V and H=T+V respectively. Usual notation for kinetic and potential energy is used.
Q. Why is coupled oscillator important?
Many important physics systems involved coupled oscillators. Coupled oscillators are oscillators connected in such a way that energy can be transferred between them. The atoms oscillate around their equilibrium positions, and the interaction between the atoms is responsible for the coupling.
Q. Where does the motion take place in a coupled oscillator?
The motion can only take place in one dimension, along the axes of the springs. Solution: We are asked to find the normal modes of coupled harmonic oscillators.
Q. Can a harmonic oscillator behave like a sine wave?
So we can see that the harmonic oscillator behaves like a sine wave. Simple enough – anyone who has ever observed a spring can tell you that this is indeed its behavior. However, if we want to model real systems, sometimes a single spring isn’t enough. For example, let’s consider the case of the structure of a protein.
Q. What makes a protein a coupled oscillator?
We can represent this chemical bond as a spring, which means that the protein as a whole is just a collection of springs that are coupled to each other. In other words, each spring no longer oscillates independently – its motion depends also on the springs it is coupled to, and vice versa.
Q. Where does the force of a harmonic oscillator originate?
A harmonic oscillator stems from a restoring force, or a force that is negatively proportional to some measurable quantity: where is the proportional factor and is the measurable quantity.