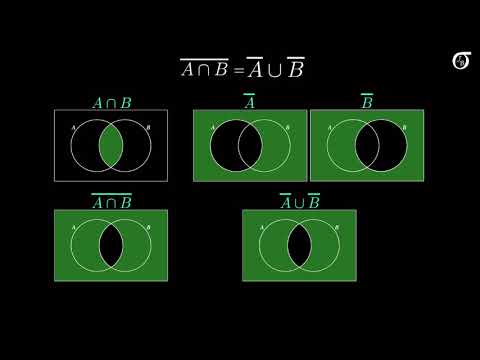
DeMorgan’s laws. Axioms of probability. Event: subset of the sample space. If a set A is comprised of some (but not all) of the elements of B, say A is a subset of B and write A ⊂ B. Similarly, B ⊃ A means A is a subset of B (or B is a superset of A).
Q. Which of the following is De Morgan law?
De Morgans law : The complement of the union of two sets is the intersection of their complements and the complement of the intersection of two sets is the union of their complements. These are called De Morgan’s laws. These are named after the mathematician De Morgan.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which of the following is De Morgan law?
- Q. What are DeMorgan’s theorems prove algebraically the DeMorgan’s Theorem?
- Q. How do you find the controllable canonical form?
- Q. What is canonical structure?
- Q. How do you create a transfer function?
- Q. What is S in transfer function?
- Q. Which type of the control system is more sensitive?
- Q. What is gain in transfer function?
Q. What are DeMorgan’s theorems prove algebraically the DeMorgan’s Theorem?
DeMorgan’s Theorem Statement: The complement of the sum of two or more variables is equal to the product of the complements of the variables. If X and Y are the two logical variables, then according to the De Morgan’s Theorem we can write: (X + Y)’ = X’.
Q. How do you find the controllable canonical form?
Controllable Canonical Form (CCF) We start by multiplying by Z(s)/Z(s) and then solving for Y(s) and U(s) in terms of Z(s). We also convert back to a differential equation.
Q. What is canonical structure?
Canonical structures: When a single molecule is represented in more than one form with comparable energies due to the resonance ,then these different forms are called as resonating structures or canonical forms.
Q. How do you create a transfer function?
To find the transfer function, first write an equation for X(s) and Y(s), and then take the inverse Laplace Transform. Recall that multiplication by “s” in the Laplace domain is equivalent to differentiation in the time domain.
Q. What is S in transfer function?
The transfer function defines the relation between the output and the input of a dynamic system, written in complex form (s variable). For a dynamic system with an input u(t) and an output y(t), the transfer function H(s) is the ratio between the complex representation (s variable) of the output Y(s) and input U(s).
Q. Which type of the control system is more sensitive?
In general, ‘G’ and ‘H’ are functions of frequency. So, feedback will increase the sensitivity of the system gain in one frequency range and decrease in the other frequency range. Therefore, we have to choose the values of ‘GH’ in such a way that the system is insensitive or less sensitive to parameter variations.
Q. What is gain in transfer function?
The transfer function gain is a parameter that connects the steady-state conditions and stability with the transfer function. It is the ratio of what you receive from the system as output to what you input to the system, under steady-state condition.