1. Current is basically the rate of flow of electric charge per unit time whereas current density is the current flowing per unit area. 2. Current is a scalar quantity whereas current density is a vector quantity.
Q. Is force scalar quantity?
Since force has a direction it can be regarded as a vector quantity. Hence force is not a scalar quantity. It is a vector quantity.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is force scalar quantity?
- Q. What is current density calculate its formula?
- Q. What is the relation between current density and electric field?
- Q. How is electric current different from water current?
- Q. Is pipes as electricity to wires?
- Q. Is 110V AC or DC?
- Q. Why do us use 110V?
- Q. What are the examples of vector quantity?
- Q. Is angular momentum is a vector quantity?
- Q. Is Vector a current?
- Q. Is force a vector quantity?
- Q. Why is force not a scalar quantity?
- Q. Is temperature a scalar or vector?
- Q. Is temperature a vector value?
- Q. Is Half Life a scalar or vector quantity?
- Q. Is density scalar or vector?
- Q. Is density a vector quantity?
- Q. What is scalar and vector with examples?
- Q. Is Angle a vector quantity?
- Q. Is upthrust a vector quantity?
- Q. Is amplitude a vector quantity?
- Q. What is the quantity of vector?
- Q. Is distance a vector quantity?
- Q. Which is the following is not a vector quantity?
- Q. Can a scalar quantity be negative?
- Q. Is M SA a scalar or a vector?
- Q. What is the symbol of scalar quantity?
- Q. Is MS SA a vector?
- Q. Is M S 2 vector or scalar?
- Q. Is 20 degrees Celsius scalar or vector?
- Q. Is M S 2 a vector?
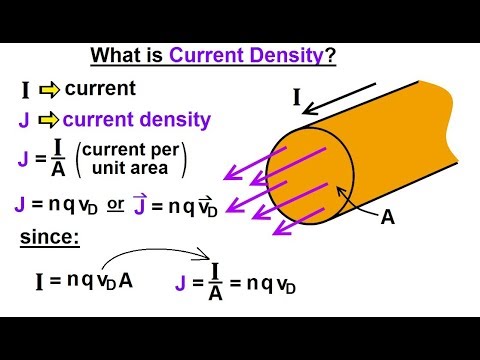
Q. What is current density calculate its formula?
The SI unit of current is the ampère [A]. An ampère is a coulomb per second. The ampère is one of the seven base units of the International System of Units….Summary.
| J, J = | current density [A/m2] as a vector or its scalar magnitude |
|---|---|
| ρ = | charge density [C/m3] |
| v = | drift velocity [m/s] |
| A = | area [m2] |
Q. What is the relation between current density and electric field?
For an amazingly wide range of materials, an empirical rule called Ohm’s law gives the following relation between current density and applied electric field: J = σ E . In other words, the current density is directly proportional to the electric field.
Q. How is electric current different from water current?
Electric current is the rate at which electric charge flows past a point on the electric circuit. Water current is the rate at which water flows past a point on the water circuit.
Q. Is pipes as electricity to wires?
The water pipe analogy can be carried even further. Electrical current in a wire behaves similarly to the flow of water in a pipe. The electrical potential is like the water pressure; thick wires can allow more electrons to go through like a thick pipe could allow more water to go through.
Q. Is 110V AC or DC?
Typically, either 110-volt AC (110V) or 220-volt AC (220V) is used. Most countries use 50Hz (50 Hertz or 50 cycles per second) as their AC frequency. Only a handful use 60Hz. The standard in the United States is 120V and 60Hz AC electricity.
Q. Why do us use 110V?
Once AC was widely accepted as being superior to DC for power distribution, 110V became the standard for AC distribution presumably because it used the “safer” Voltage level of the DC system. After metal filament lamps became feasible, 220V became common in Europe because of the lower distribution costs.
Scalar quantities are defined by a magnitude with no applicable direction. In contrast, vector quantities must have both magnitude and direction of action. Some common scalar quantities are distance, speed, mass, and time. Some common vector quantities are force, velocity, displacement, and acceleration.
Q. What are the examples of vector quantity?
Physical quantities specified completely by giving a number of units (magnitude) and a direction are called vector quantities. Examples of vector quantities include displacement, velocity, position, force, and torque.
Q. Is angular momentum is a vector quantity?
Angular momentum and angular velocity have both magnitude and direction and, therefore, are vector quantities. The axis of rotation of a rotating wheel is the only place that has a fixed direction. The direction of angular momentum and velocity can be determined along this axis.
Q. Is Vector a current?
Note: Current is a vector because it has a magnitude and a direction. Since current doesn’t obey it and it follows algebraic addition, currents are scalar.
Q. Is force a vector quantity?
(Introduction to Mechanics) vector quantities are quantities that possess both magnitude and direction. A force has both magnitude and direction, therefore: Force is a vector quantity; its units are newtons, N. Forces can cause motion; alternatively forces can act to keep (an) object(s) at rest.
Q. Why is force not a scalar quantity?
It has a magnitude and a direction. The direction towards which the force is applied is known as the direction of the force and the application of force is the point where force is applied. Since force has a direction it can be regarded as a vector quantity. Hence force is not a scalar quantity.
Q. Is temperature a scalar or vector?
Temperature is most definitely a scalar quantity. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the atoms in a mass. There is definitely a value (which may be interpreted as a magnitude), but it lacks a direction. Therefore it cannot meet the requirements of being considered a vector.
Q. Is temperature a vector value?
An example of a scalar quantity is temperature: the temperature at a given point is a single number. Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity.
Q. Is Half Life a scalar or vector quantity?
Half life is a scalar quantity.
Q. Is density scalar or vector?
Most recent answer since density is a scalar quantity. it does not inherently shows the direction. thus different in density between two points in flow filed is expresses as scalar density field or density gradient at point at given instant of time. Thus density can be expressed as vector using scalar density field.
Q. Is density a vector quantity?
Current density is a vector quantity because it’s a product of charge density and velocity, here charge density is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity, which makes current density also a vector quantity.
Q. What is scalar and vector with examples?
Scalars and vectors are differentiated depending on their definition. A scalar quantity is defined as the physical quantity that has only magnitude, for example, mass and electric charge….Difference Between Scalar and Vector.
| Vector | Scalar | |
|---|---|---|
| Example | Velocity and Acceleration | Mass and Temperature |
Q. Is Angle a vector quantity?
Actually angle is dimensionless vector quantity. It has magnitude and direction both. We can measure angle in clockwise and anticlockwise about its rotational behaviour. Hence its true to say that angle is “vector” quantity.
Q. Is upthrust a vector quantity?
“Upthrust” is an example of a force. Is upthrust a scalar or vector quantity? Vector because it is a force.
Q. Is amplitude a vector quantity?
A vector quantity is one that requires a one-dimensional list of numbers to describe it, or to put it another way its only attributes are its size and its direction. So amplitude is strictly speaking a scalar.
Q. What is the quantity of vector?
Vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. It is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude. Although a vector has magnitude and direction, it does not have position.
Q. Is distance a vector quantity?
Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to “how much ground an object has covered” during its motion. Displacement is a vector quantity that refers to “how far out of place an object is”; it is the object’s overall change in position.
Q. Which is the following is not a vector quantity?
Answer: Speed is not a vector quantity. It has only magnitude and no direction and hence it is a scalar quantity.
Q. Can a scalar quantity be negative?
Complete answer: Now, as the real numbers include both, positive numbers as well as negative numbers, a scalar can be negative. Now, in physics, the magnitude of a physical quantity is expressed by some magnitude or say numerical value and a unit. Energy can take both, positive as well as negative values.
Q. Is M SA a scalar or a vector?
Scalars are quantities that are fully described by a magnitude (or numerical value) alone. Vectors are quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction….Scalars and Vectors.
| Quantity | Category |
|---|---|
| a. 5 m | See Answer This is a scalar; there is no direction listed for it. |
Q. What is the symbol of scalar quantity?
symbol ψ
Q. Is MS SA a vector?
A vector quantity is described with a direction and a scalar is not. Scalar quantities are path dependent quantities and vector quantities are not. The quantity 9.8 m/s/s is an acceleration value and as such is a vector quantity.
Q. Is M S 2 vector or scalar?
Since acceleration describes a velocity change over time, the acceleration unit includes the unit for velocity (m/s) over another time period (s). Therefore, the unit for acceleration is m/s/s or more commonly m/s2. Acceleration is also a vector and would include the direction that the velocity is changing.
Q. Is 20 degrees Celsius scalar or vector?
Vector Components Any vector directed at an angle to the horizontal can be broken down into its two components….Answers to Review.
| Quantity | Category |
|---|---|
| a. 5 m | SCALAR |
| b. 30 m/sec, East | VECTOR |
| c. 5 mi., North | VECTOR |
| d. 20 degrees Celsius | SCALAR |
Q. Is M S 2 a vector?
, or less commonly, as m/s/s. As acceleration, the unit is interpreted physically as change in velocity or speed per time interval, i.e. metre per second per second and is treated as a vector quantity.