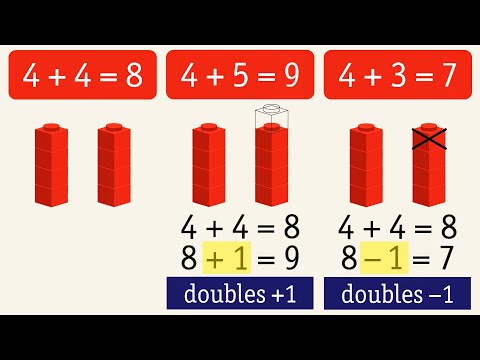
Q. What is double minus one?
Doubles minus 1 is a strategy used to add two consecutive numbers that is, when they are next to each other. We simply add the bigger number twice or double it and then, subtract 1 from it, to get the final result. Here, for example, consecutive number 7 and 8 have been added using the doubles minus one strategy.
Q. What is a doubles plus one fact?
Double Plus 1 Addition Facts “Double plus one” facts are based on knowing doubles first, then just counting on one. This allows students to answer questions in which two adjacent numbers, such as 4 and 5, are added: Double 4 = 8, so 4 + 5 = 8 + 1 = 9.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is double minus one?
- Q. What is a doubles plus one fact?
- Q. What is a double 0 in math?
- Q. What’s a Double O Seven?
- Q. What is a double zero in math?
- Q. Is a double zero distinct?
- Q. What’s a simple zero?
- Q. What is a simple root?
- Q. How do you find a simple pole?
- Q. How do you find the zeros of infinity?
- Q. How many open loop zeros are at infinity?
- Q. Is infinity a pole?
- Q. What is pole and zero in control?
- Q. What is Omega N in control system?
- Q. What is the meaning of poles?
- Q. What is a dominant pole?
- Q. What does mean by dominating zero?
- Q. Why is root locus used?
- Q. What are the disadvantages of root locus method?
- Q. What is root locus in Matlab?
- Q. What is Sgrid Matlab?
- Q. What is Matlab Sisotool?
- Q. Is root locus open loop or closed-loop?
Q. What is a double 0 in math?
A double zero results from a function having a repeated root, for example: roots derived from factors of the form (x-a)^2. We already know that roots occur where the graph touches/cuts the x axis, so if a factor is of some squared form then the corresponding y values of the function would be positive.
Q. What’s a Double O Seven?
007 is a nickname given to surgeons who tend to kill their patients, originating from James Bond’s code number, which means “License to kill.”
Q. What is a double zero in math?
Strategic Advice: A double zero occurs in a polynomial when a factor is repeated, or in other words, squared. For example, the factor (x – a) produces a simple zero at x = a, while (x – b)2 produces a double zero at x = b.
Q. Is a double zero distinct?
A double zero is when a graph intersects the x-axis but does not cross over it; the graph approaches the x-axis and once it touches it, it immediately turns back in the opposite direction. Two distinct zeroes results when a graph crosses over the x-axis at two different points.
Q. What’s a simple zero?
Simple zero and simple pole are terms used for zeroes and poles of order. Degree is sometimes used synonymously to order. This characterization of zeros and poles implies that zeros and poles are isolated, that is, every zero or pole has a neighbourhood that does not contain any other zero and pole.
Q. What is a simple root?
simple root (plural simple roots) (algebra) A root of a polynomial equation which has multiplicity one.
Q. How do you find a simple pole?
dk−1 dzk−1 ( (z − z0)kf(z) )/ / /z=z0 . In particular, if f(z) has a simple pole at z0 then the residue is given by simply evaluating the non-polar part: (z−z0)f(z), at z = z0 (or by taking a limit if we have an indeterminate form).
Q. How do you find the zeros of infinity?
1 Answer. It’s actually quite straightforward: positive powers of s (or, in discrete-time, z), correspond to poles at infinity. Negative powers give you zeros at infinity. Clearly, lims→∞H(s)=∞, hence you have a pole at infinity (and a zero at s=0).
Q. How many open loop zeros are at infinity?
2 zeros
Q. Is infinity a pole?
Poles at infinity are obtained when the order of the numerator is higher than the order of the denominator. There will be n finite zeros and m finite poles and, as s->infinity, the m poles will cancel m of the numerator zeros leaving (n-m) zeros, therefore G(s) -> infinity and there will be (n-m) poles at infinity.
Q. What is pole and zero in control?
Poles and Zeros of a transfer function are the frequencies for which the value of the denominator and numerator of transfer function becomes zero respectively. The values of the poles and the zeros of a system determine whether the system is stable, and how well the system performs.
Q. What is Omega N in control system?
The frequency of the oscillation is ωd and the time constant of exponential decay is 1/ζωn. Where, ωd, is referred as damped frequency of the oscillation, and ωn is natural frequency of the oscillation. The term ζ affects that damping a lot and hence this term is called damping ratio.
Q. What is the meaning of poles?
Definition of pole (Entry 3 of 5) 1 : either extremity of an axis of a sphere and especially of the earth’s axis. 2a : either of two related opposites. b : a point of guidance or attraction.
Q. What is a dominant pole?
The dominant pole approximation is a method for approximating a (more complicated) high order system with a (simpler) system of lower order if the location of the real part of some of the system poles are sufficiently close to the origin compared to the other poles.
Q. What does mean by dominating zero?
If the denominator is of higher degree, the denominator dominates and the limit is zero. The denominator will eventually get larger than the numerator and drive the quotient towards zero.
Q. Why is root locus used?
The root locus plot indicates how the closed loop poles of a system vary with a system parameter (typically a gain, K). We can choose a value of ‘s’ on this locus that will give us good results.
Q. What are the disadvantages of root locus method?
The limitations of root locus method for tuning PID controllers are: Not perform well on a nonlinear system. Loses significance at high frequencies or high degrees of damping. The designs are susceptible to noise .
Q. What is root locus in Matlab?
The root locus returns the closed-loop pole trajectories as a function of the feedback gain k (assuming negative feedback). Root loci are used to study the effects of varying feedback gains on closed-loop pole locations. The poles on the root locus plot are denoted by x and the zeros are denoted by o .
Q. What is Sgrid Matlab?
sgrid(zeta,wn) creates the grid over the plot if the current axis contains a continuous s-plane root locus diagram or pole-zero map. Alternatively, you can select Grid from the context menu to generate the same s-plane grid. sgrid(___,’new’) clears the current axes first and sets hold on .
Q. What is Matlab Sisotool?
‘SISOTOOL’ is one of the latest features in the Control System Toolbox in Matlab that enables software-based controller design for single-input-single-output (SISO) systems.
Q. Is root locus open loop or closed-loop?
– The Root Locus Plot is a plot of the roots of the characteristic equation of the closed-loop system for all values of a system parameter, usually the gain; however, any other variable of the open- loop transfer function may be used.