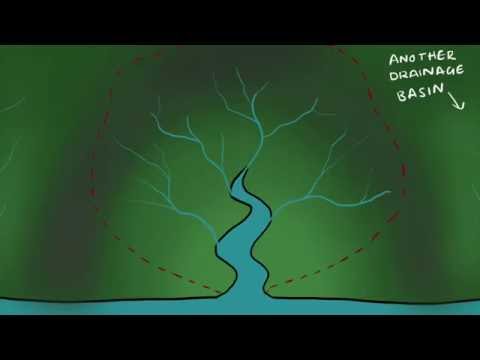
Q. What is drainage and drainage basin?
A drainage basin is a region of land where water from rain or snowmelt drains downhill into a body of water, such as a river, lake, dam, estuary, wetland, sea or ocean. The drainage basin includes both the streams and rivers that convey the water as well as the land surfaces from which water drains into those channels.
Q. What is drainage basin simple definition?
Drainage basins refer to the area of land drained by a major river and its tributaries. All rivers flow from the source (often in the mountains) to the mouth (the sea). The drainage basin is regarded as a closed system because water never leaves. Instead, it is recycled from one state to another.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is drainage and drainage basin?
- Q. What is drainage basin simple definition?
- Q. What is Basin in hydrograph?
- Q. What is the definition of drainage basin in geography?
- Q. What is drainage basin class 9?
- Q. What do drainage basins do?
- Q. What is drainage basin answer?
- Q. What is a drainage basin class 9?
- Q. How does a hydrograph of a drainage basin work?
- Q. How does a hydrograph help in flood prevention?
- Q. Is the drainage basin system an open or closed system?
- Q. How are hydrographs different in small and large catchments?
Q. What is Basin in hydrograph?
A drainage basin is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff , throughflow , and groundwater flow . Drainage basins are divided from each other by topographic barriers called a watershed .A watershed represents all of the stream tributaries that flow to some location along the stream channel.
Q. What is the definition of drainage basin in geography?
Definition: When rain falls on an area of land, the water travels downhill and typically collects into a lake or travels on through a river. In a catchment area water can be collected through rain or drained by rivers or streams. A catchment area can also be known as Drainage Basin.
Q. What is drainage basin class 9?
A drainage basin or river basin is an area that is drained by a single river system. A water division is considered an upland that divides two irrigation systems that are adjacent to each other. In this blog, we discuss drainage class 9 notes in detail.
Q. What do drainage basins do?
A drainage basin is an example of an open system because it is open to inputs from outside, such as precipitation, and is responsible for outputs out of the system, such as output of water into the sea and evaporation of water into the atmosphere.
Q. What is drainage basin answer?
Complete answer:The term drainage basin is used to describe an area of land which collects the precipitation and then drains off into a single point which can be a river, bay, or any other water body.
Q. What is a drainage basin class 9?
Q. How does a hydrograph of a drainage basin work?
A hydrograph shows how a river is affected by a storm. This helps to understand discharge patterns of a particular drainage basin and helps to predict flooding and plan flood prevention measures. Large basins receive more precipitation than smaller basins, therefore they have a larger runoff.
Q. How does a hydrograph help in flood prevention?
A hydrograph shows how a river is affected by a storm. This helps to understand discharge patterns of a particular drainage basin and helps to predict flooding and plan flood prevention measures. As you can see in the graph below, the peak rainfall is the time of highest rainfall.
Q. Is the drainage basin system an open or closed system?
The hydrological (water) cycle is the global circulation of water. It is a closed system. A drainage basin system is one part of the hydrological cycle. It is an open system as it has inputs and outputs. A flood hydrograph shows how a river’s discharge changes in response to a rainfall event.
Q. How are hydrographs different in small and large catchments?
•The peak discharge is less in small catchment. •The time base of the hydrographs from larger basins will be larger than those of corresponding hydrographs from smaller basins. •The duration of the surface runoff from the time of occurrence of the peak will be higher in large catchments.