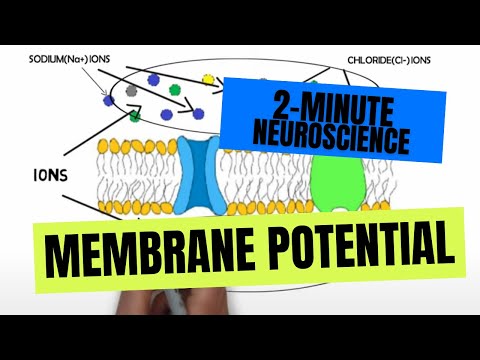
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. Almost all plasma membranes have an electrical potential across them, with the inside usually negative with respect to the outside.
Q. What is a membrane potential a voltage or electrical charge across the plasma membrane?
Membrane potential refers to the difference in electrical charge across the neuronal membrane, between the inside of the cell and the extracellular fluid surrounding the neuron.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is a membrane potential a voltage or electrical charge across the plasma membrane?
- Q. What is a membrane potential quizlet?
- Q. What is a membrane potential Chapter 3?
- Q. Why is the membrane potential negative?
- Q. What increases membrane potential?
- Q. What is a decrease in membrane potential?
- Q. How can membrane potential be reduced?
- Q. What does hypokalemia do to resting membrane?
- Q. What are signs of hypokalemia?
- Q. How does low potassium make you feel?
- Q. Can low potassium cause a heart attack?
- Q. Can low potassium cause sleep problems?
- Q. What does low potassium do to your heart?
- Q. Should you take potassium at night or in the morning?
- Q. Which vitamin deficiency causes lack of sleep?
- Q. What vitamin helps you to sleep?
- Q. What is the best vitamin for lack of sleep?
Q. What is a membrane potential quizlet?
membrane potential. -The potential inside a cell membrane measured relative to the fluid just outside; it is negative under resting conditions and becomes positive during an action potential. -the difference in electrical polarization or charge between two sides of a membrane or cell wall.
Q. What is a membrane potential Chapter 3?
membrane potential. separation of oppositely charged particles across a membrane. steady state. rate of active transport is equal to and depends on the rate of Na+ diffusion into the cell. Only $3.99/month.
Q. Why is the membrane potential negative?
The resting membrane potential is a result of different concentrations inside and outside the cell. The negative charge within the cell is created by the cell membrane being more permeable to potassium ion movement than sodium ion movement.
Q. What increases membrane potential?
The outward synaptic current will increase as the membrane potential is made less negative (depolarized) and decrease as the potential is made more negative (hyperpolarized). An increased permeability to K+ can bring the membrane potential close to the Nernst potential for K+ and thus hyperpolarize the cell.
Q. What is a decrease in membrane potential?
Changes in membrane potential involve either depolarization (i.e., a decrease in transmembrane potential) or hyperpolarization (an increase in the potential difference across the membrane).
Q. How can membrane potential be reduced?
A set of voltage-gated potassium channels open, allowing potassium to rush out of the cell down its electrochemical gradient. These events rapidly decrease the membrane potential, bringing it back towards its normal resting state.
Q. What does hypokalemia do to resting membrane?
Serum hypokalemia causes hyperpolarization of the RMP (the RMP becomes more negative) due to the altered K+ gradient. As a result, a greater than normal stimulus is required for depolarization of the membrane in order to initiate an action potential (the cells become less excitable).
Q. What are signs of hypokalemia?
What are the signs and symptoms of hypokalemia (low potassium)?
- Weakness and fatigue (most common)
- Muscle cramps and pain (severe cases)
- Worsening diabetes control or polyuria.
- Palpitations.
- Psychological symptoms (eg, psychosis, delirium, hallucinations, depression)
Q. How does low potassium make you feel?
Common signs and symptoms of potassium deficiency include weakness and fatigue, muscle cramps, muscle aches and stiffness, tingles and numbness, heart palpitations, breathing difficulties, digestive symptoms and mood changes.
Q. Can low potassium cause a heart attack?
If potassium levels in the blood get too low, you can develop an abnormal heart rhythm or even have a heart attack or sudden cardiac arrest.
Q. Can low potassium cause sleep problems?
An imbalance of potassium can cause many different side effects including anxiety and new research suggests a potential for sleep disturbances. If you have low levels of potassium, you may experience an increase in your anxiety symptoms.
Q. What does low potassium do to your heart?
Potassium plays an important role in regulating the contractions of all muscles, including the heart muscle. Very low levels of potassium in the body can lead to irregular heart rhythms, including sinus bradycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.
Q. Should you take potassium at night or in the morning?
You should check with your doctor before changing your diet. It is best to take this medicine with a meal or bedtime snack, or within 30 minutes after meals. Swallow the extended-release tablet whole. Do not break, crush, chew, or suck it.
Q. Which vitamin deficiency causes lack of sleep?
Being deficient in vitamin D can lead to a host of sleep issues, including sleep disruption, insomnia, and overall poor sleep quality. “A deficiency in Vitamin D has been associated with many changes in sleep such as fewer sleeping hours, and sleep that is less restful and restorative,” said Dr.
Q. What vitamin helps you to sleep?
Omega-3, Vitamin D A study in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine found the combination of omega-3s and vitamin D from fatty fish like salmon improved sleep in participants. Researchers think it’s because of the effect of those nutrients on regulating serotonin.
Q. What is the best vitamin for lack of sleep?
Best Vitamins and Supplements for a Good Night’s Sleep
- Vitamin C. The first thing that comes to mind when you think of vitamin C might be that it’s a great boost for your immune system.
- Vitamin D. Intuitively, you might vitamin D would wake you up, not help put you to sleep.
- Magnesium.
- Iron.
- Calcium.