Power basically emanates from position or authority which can influence people both positively and negatively. For simplicity and understanding purposes power is usually classified into following categories: Coercive Power- This kind of power involves the usage of threat to make people do what one desires.
Q. What are the three types of electrical power?
The AC power is mainly classified into three types. They are the apparent power, active power and real power.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the three types of electrical power?
- Q. What are 4 types of electricity?
- Q. What is power and its type?
- Q. What is electrical energy and examples?
- Q. What is electrical unit?
- Q. What are the basics of electrical?
- Q. How many volts are there in one unit?
- Q. How much electricity does a AC use?
- Q. What is unit set with example?
- Q. Is 0 an empty set?
- Q. What is proper set and improper set?
- Q. What is an example of an empty set?
- Q. What kind of set is an empty null set?
- Q. What is the difference between empty set and null set?
- Q. Does an empty set equal an empty set?
- Q. Is an empty set finite or infinite?
- Q. What is the complement of empty or null set?
- Q. What are the 4 operations of sets?
- Q. Why does the empty set exist?
- Q. Does empty set mean no solution?
Q. What are 4 types of electricity?
- Static Electricity. Static Electricity is nothing but the contact between equal amount of protons and electrons (positively and negatively charged subatomic particles).
- Current Electricity. Current Electricity is a flow of electric charge across an electrical field.
- Hydro Electricity.
- Solar Electricity.
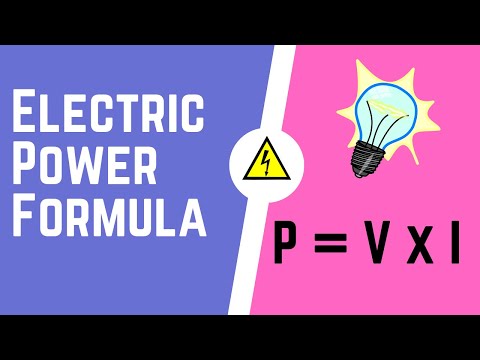
Electric power is the rate, per unit time, at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Electric power is usually produced by electric generators, but can also be supplied by sources such as electric batteries.
Q. What is power and its type?
Q. What is electrical energy and examples?
Examples: A light bulb, the glowing coils on a toaster, the sun, and even headlights on cars. E. Electrical Energy – Energy produced by electrons moving through a substance is known as electrical energy. We mostly see electric energy in batteries and from the outlets in our homes.
Q. What is electrical unit?
A unit (as mentioned on the electricity bills) is represented in kWH or Kilowatt Hour. This is the actual electricity or energy used. If you use 1000 Watts or 1 Kilowatt of power for 1 hour then you consume 1 unit or 1 Kilowatt-Hour (kWh) of electricity.
Q. What are the basics of electrical?
Basic electricity:
- Conductors: electrons flow easily. Low resistance.
- Semi-conductors: electron can be made to flow under certain circumstances. Variable resistance according to formulation and circuit conditions.
- Insulator: electrons flow with great difficulty. High resistance.
Q. How many volts are there in one unit?
So to display the units or multiples of units for either Resistance, Current or Voltage we would use as an example: 1kV = 1 kilo-volt – which is equal to 1,000 Volts. 1mA = 1 milli-amp – which is equal to one thousandths (1/1000) of an Ampere.
Q. How much electricity does a AC use?
2 Star Window AC Electricity Consumption:
| AC Type | Model | Power- Consumption ( Watts/Hr) |
|---|---|---|
| Split AC | l.OTon | 1154 |
| 1.5Ton | 1709 | |
| 2.0Ton | 2210 | |
| Window AC | l.OTon | 1250 |
Q. What is unit set with example?
In mathematics, a singleton, also known as a unit set, is a set with exactly one element. For example, the set {null } is a singleton containing the element null. The term is also used for a 1-tuple (a sequence with one member).
Q. Is 0 an empty set?
One of the most important sets in mathematics is the empty set, 0. This set contains no elements. When one defines a set via some characteristic property, it may be the case that there exist no elements with this property.
Q. What is proper set and improper set?
An improper subset is a subset containing every element of the original set. A proper subset contains some but not all of the elements of the original set. For example, consider a set {1,2,3,4,5,6}. Then {1,2,4} and {1} are the proper subset while {1,2,3,4,5} is an improper subset.
Q. What is an example of an empty set?
Any Set that does not contain any element is called the empty or null or void set. The symbol used to represent an empty set is – {} or φ. Examples: Let W = {d: d > 8, d is the number of days in a week} will also be a void set because there are only 7 days in a week.
Q. What kind of set is an empty null set?
Empty Set: The empty set (or null set) is a set that has no members. Notation: The symbol ∅ is used to represent the empty set, { }. Note: {∅} does not symbolize the empty set; it represents a set that contains an empty set as an element and hence has a cardinality of one.
Q. What is the difference between empty set and null set?
Originally Answered: What is the difference between a null set and an empty set? In the context of measure theory, a null set is a set of measure zero. The empty set is always a null set, but the other null sets depend on which measure you’re using. The empty set is the (unique) set that contains no elements.
Q. Does an empty set equal an empty set?
Every empty set is same in the sense that if you take two empty sets, say ∅1 and ∅2, then they are contained in one another.
Q. Is an empty set finite or infinite?
elements. The empty set is also considered as a finite set, and its cardinal number is 0.
Q. What is the complement of empty or null set?
Example: ∅’ = U The complement of an empty set is the universal set. Set Difference: The relative complement or set difference of sets A and B, denoted A – B, is the set of all elements in A that are not in B.
Q. What are the 4 operations of sets?
Operations on Sets
| Operation | Notation | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Intersection | A∩B | all elements which are in both A and B |
| Union | A∪B | all elements which are in either A or B (or both) |
| Difference | A−B | all elements which are in A but not in B |
| Complement | ˉA (or AC ) | all elements which are not in A |
Q. Why does the empty set exist?
The empty set is a subset of any set. This is because we form subsets of a set X by selecting (or not selecting) elements from X. One option for a subset is to use no elements at all from X. This gives us the empty set.
Q. Does empty set mean no solution?
If an equation has no solutions, its solution set is the empty set or null set–a set with no members, denoted Ø. For example, the solution set to x2 = – 9 is Ø, because no number, when squared, is equal to a negative number. Sometimes we will be given a set of values from which to find a solution–a replacement set.