Fermi Level in n-type Semiconductor When pentavalent impurity is added to pure semiconductor, it results in n-type semiconductor. The fifth electron of donor atom is loosely bounded. By small thermal energy or by applying electric field, this electron can be easily excited from the valence band to the conduction band.
Q. What is the use of Fermi level in semiconductors?
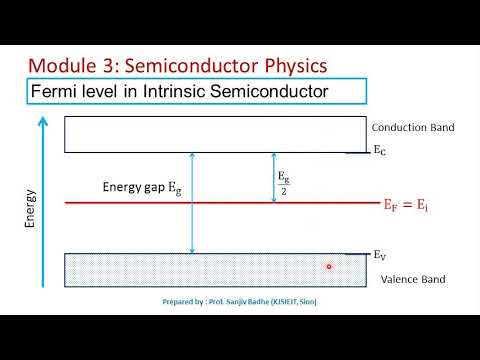
It determines the population at different energy levels. It also determines how easily can the material conductor electricity. As your Fermi level approaches your conduction band energy, it will be easier for the electrons from the valence band to travel to the conduction band.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the use of Fermi level in semiconductors?
- Q. What is the Fermi level for N type semiconductor?
- Q. What is n type and p type semiconductor?
- Q. How do you know if a semiconductor is N or P type?
- Q. Which type of impurity is indium?
- Q. What are the properties of indium?
- Q. Why is indium important?
- Q. Is hydrogen a donor or acceptor?
- Q. Is alcohol a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor?
- Q. Which of the following is a hydrogen bond donor?
Q. What is the Fermi level for N type semiconductor?
From the energy level diagram of the n-type semiconductor, it’s clear that the Fermi level is present near the conduction band and far away from the valence band. In the case of n-type semiconductor, the Fermi level is present just below the conduction band.
Q. What is n type and p type semiconductor?
P-type semiconductors are created by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with an electron acceptor element during manufacture. The term p-type refers to the positive charge of a hole. As opposed to n-type semiconductors, p-type semiconductors have a larger hole concentration than electron concentration.
Q. How do you know if a semiconductor is N or P type?
If the dopant has more electrons in the outer shell than the semiconductor material, it’s going to be n-type, and with less electrons in the outer shell, it’s p-type.
Q. Which type of impurity is indium?
trivalent compound
Q. What are the properties of indium?
Indium is a soft, ductile, manleable, lustrous metallic metal. Its colour is silvery white and it has a face-centered tetragonal structure. It is liquid over a wide range of temperatures, like gallium that belongs to its same group. Both indium and gallium are able to wet glass.
Q. Why is indium important?
Most indium is used to make indium tin oxide (ITO), which is an important part of touch screens, flatscreen TVs and solar panels. This is because it conducts electricity, bonds strongly to glass and is transparent. Indium nitride, phosphide and antimonide are semiconductors used in transistors and microchips.
Q. Is hydrogen a donor or acceptor?
In the diagram at left below, the oxygen atom of the hydroxy group is called the hydrogen bond donor, because it is “donating” its hydrogen to the nitrogen. The nitrogen atom is called the hydrogen bond acceptor, because it is “accepting” the hydrogen from the oxygen.
Q. Is alcohol a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor?
Water and alcohols may serve as both donors and acceptors, whereas ethers, aldehydes, ketones and esters can function only as acceptors. Similarly, primary and secondary amines are both donors and acceptors, but tertiary amines function only as acceptors. 1.
Q. Which of the following is a hydrogen bond donor?
In this hydrogen bond between water and ammonia, water is the hydrogen bond donor (shown in red) and ammonia is the hydrogen bond acceptor. In this hydrogen bond between water and ammonia, ammonia is the hydrogen bond donor (shown in red) and water is the hydrogen bond acceptor.