2. Air bags in cars are designed with impulse, or momentum change principles. When a driver gets into an accident their momentum carries them forward into the steering wheel. By putting an airbag in the car, a smaller force is exerted over a longer period of time to change the momentum of the driver to a stop.
Q. What is impulse momentum change theorem?
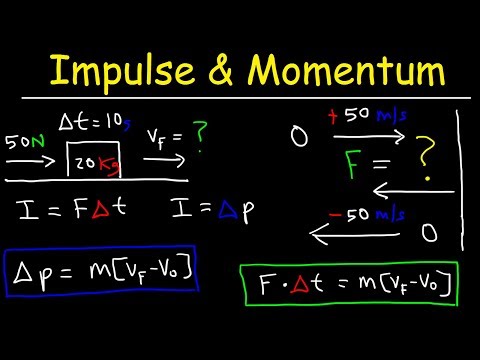
The impulse-momentum theorem states that the impulse applied to an object will be equal to the change in its momentum. Δ→tF=m(vf)−m(vi) Notice that we have calculated the change in momentum as the initial momentum (mivi) subtracted from the final momentum (mfvf).
Table of Contents
- Q. What is impulse momentum change theorem?
- Q. What do impulse momentum theorem states?
- Q. Why is the impulse momentum theorem important?
- Q. What is the relationship between impulse and change in momentum?
- Q. Does a moving body have momentum?
- Q. What is the difference between momentum and acceleration?
- Q. Does direction matter measuring momentum?
Q. What do impulse momentum theorem states?
The Impulse-Momentum Theorem states that the net impulse acting on the object is also equal to the change in the momentum of the object.
Q. Why is the impulse momentum theorem important?
Because of the impulse-momentum theorem, we can make a direct connection between how a force acts on an object over time and the motion of the object. One of the reasons why impulse is important and useful is that in the real world, forces are often not constant.
Q. What is the relationship between impulse and change in momentum?
The impulse experienced by the object equals the change in momentum of the object. In equation form, F • t = m • Δ v. In a collision, objects experience an impulse; the impulse causes and is equal to the change in momentum.
Q. Does a moving body have momentum?
If an object is in motion (on the move) then it has momentum. Momentum can be defined as “mass in motion.” All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum – it has its mass in motion. Momentum depends upon the variables mass and velocity.
Q. What is the difference between momentum and acceleration?
The key difference between acceleration and momentum is that acceleration refers to the rate of change in velocity of a moving object, whereas the momentum of an object is the product of the mass of the object and its velocity.
Q. Does direction matter measuring momentum?
Two objects with the same mass will always have the same momentum. Direction does not matter when you are measuring momentum. T 8. Momentum can be transferred from one object to another.