Lagrangian approach: Identify (or label) a material of the fluid; track (or follow) it as it moves, and monitor change in its properties. The properties may be velocity, temperature, density, mass, or concentration, etc in the flow field. Lagrangian approach is also called “particle based approach”.
Q. How do you know if your Lagrangian?
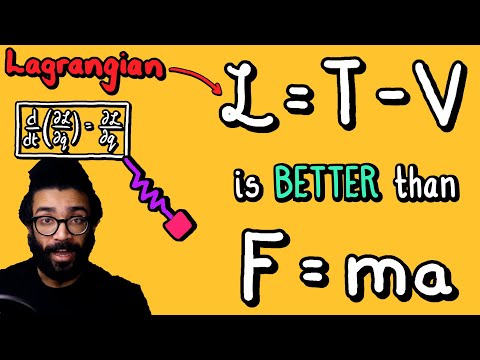
The Lagrangian is L = T −V = m ˙y2/2−mgy, so eq. (6.22) gives ¨y = −g, which is simply the F = ma equation (divided through by m), as expected.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you know if your Lagrangian?
- Q. What does the Lagrangian represent?
- Q. Why do you use Lagrangian formulation over Newtonian formulation What are the advantages?
- Q. What is the difference between Newtonian and Lagrangian mechanics?
- Q. What is Eulerian description of fluid flow?
- Q. What are the types of fluid flow?
- Q. Which equation must be perfunctorily satisfied while dealing with fluid flow problems?
- Q. Why does Rayleigh’s method have limitations?
- Q. Which method is most preferable in fluid mechanics?
- Q. Can the flow inside a nozzle be steady and uniform?
- Q. What is the difference between steady and unsteady flow?
- Q. What is the difference between uniform and nonuniform flow?
- Q. Which one of the following is a major loss?
Q. What does the Lagrangian represent?
Lagrangian function, also called Lagrangian, quantity that characterizes the state of a physical system. In mechanics, the Lagrangian function is just the kinetic energy (energy of motion) minus the potential energy (energy of position).
Q. Why do you use Lagrangian formulation over Newtonian formulation What are the advantages?
One of the attractive aspects of Lagrangian mechanics is that it can solve systems much easier and quicker than would be by doing the way of Newtonian mechanics. In Newtonian mechanics for example, one must explicitly account for constraints. However, constraints can be bypassed in Lagrangian mechanics.
Q. What is the difference between Newtonian and Lagrangian mechanics?
Lagrangian mechanics can be derived from Principle of Least Action, or from Newtonian mechanics. The more the constraints, the simpler the Lagrangian equations, but the more complex the Newtonian become. Lagrangian mechanics is not very suited for non-ideal or non-holonomic systems, such as systems with friction.
Q. What is Eulerian description of fluid flow?
The Eulerian Description is one in which a control volume is defined, within which fluid flow properties of interest are expressed as fields. In the Eulerian description of fluid flow, individual fluid particles are not identified. Instead, a control volume is defined, as shown in the diagram.
Q. What are the types of fluid flow?
The different types of fluid flow are:
- Steady and Unsteady Flow.
- Uniform and Non-Uniform Flow.
- Laminar and Turbulent Flow.
- Compressible and Incompressible Flow.
- Rotational and Irrotational Flow.
- One, Two and Three -dimensional Flow.
Q. Which equation must be perfunctorily satisfied while dealing with fluid flow problems?
Which equation must be perfunctorily satisfied while dealing with fluid flow problems? Explanation: Continuity equation must be perfunctorily satisfied while dealing with fluid flow problems. 10. Convective acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity due to change of velocity with respect to time.
Q. Why does Rayleigh’s method have limitations?
Why does Rayleigh’s method have limitations? Explanation: The main limitation of the Rayleigh’s method is that it has exponential relationship between the variables. It makes it more complex for solving. Since, more variables with exponents will lead to a confusion in the solving process.
Q. Which method is most preferable in fluid mechanics?
Eulerian method
Q. Can the flow inside a nozzle be steady and uniform?
Can the flow inside a nozzle be steady and uniform? Explanation: According to the continuity equation, ρAV =constant, where ρ= density, A= cross-sectional area of flow, V = velocity of flow. For a nozzle, the area gradually decreases towards it’s exit. Hence, it’ll always be an unsteady flow.
Q. What is the difference between steady and unsteady flow?
steady: A steady flow is one in which the conditions (velocity, pressure and cross- section) may differ from point to point but DO NOT change with time. unsteady: If at any point in the fluid, the conditions change with time, the flow is described as unsteady.
Q. What is the difference between uniform and nonuniform flow?
But when the size and shape of cross section are constant along the length of channels under consideration, the flow is said to be uniform. A non-uniform flow is one in which velocity is not constant at a given instant. A flow in which quantity of liquid flowing per second is not constant, is called unsteady flow.
Q. Which one of the following is a major loss?
1. Which one of the following is a major loss? Explanation: The major loss for the flflow through the pipes is due to the frictional resistance between adjacent fluid layers sliding over each other. All other losses are considered to be minor losses.