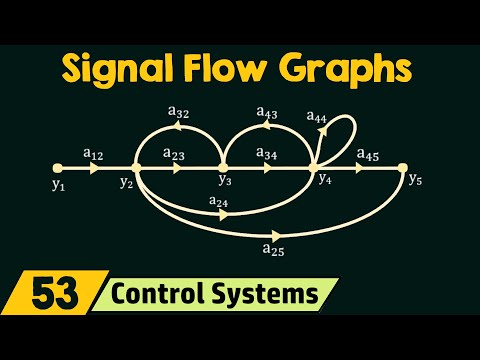
Q. What is meant by signal flow graph?
“A signal-flow graph is a diagram that represents a set of simultaneous algebraic equations. When applying the signal flow graph method to analysis of control systems, we must first transform linear differential equations into algebraic equations in [the Laplace transform variable] s..”
Q. What are the properties of signal flow graphs?
Properties of Signal Flow Graph The signal from a node to other flows through the branch in the direction of arrowhead. The graphical method is valid only for linear time-invariant systems. The signal flowing through a branch is multiplied by the gain or transmittance of that branch.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is meant by signal flow graph?
- Q. What are the properties of signal flow graphs?
- Q. What is the importance of signal flow graph in control system engineering?
- Q. What is the benefits of signal flow graph?
- Q. How do you calculate signal flow from a graph?
- Q. What is the difference between block diagram and signal flow graph?
- Q. How does signal flow work?
- Q. How do you draw a signal flow graph from a differential equation?
- Q. Which node has only outgoing branches?
- Q. What is signal flow graph in DSP?
- Q. Is signal flow graph unique?
- Q. Who invented signal flow graph?
- Q. What is IIR filter in DSP?
- Q. What is windowing technique in DSP?
- Q. What are the types of IIR filters?
- Q. Is Butterworth IIR or FIR?
- Q. Which is better FIR or IIR?
- Q. Is the filter FIR or IIR?
- Q. Is the system FIR or IIR?
- Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of FIR filter?
- Q. Where is FIR filter used?
- Q. How is FIR and IIR difference?
- Q. What is the difference between analog and digital filters?
- Q. What are the types of filters?
- Q. What are the difference analog and digital filters?
- Q. Which filter is better analog or digital?
- Q. Is FIR filter analog or digital?
- Q. Are analog filters still used?
Q. What is the importance of signal flow graph in control system engineering?
Signal flow diagrams help us to identify structures called “loops” in a system, which can be analyzed individually to determine the complete response of the system. An example of a signal flow diagram.
Q. What is the benefits of signal flow graph?
Advantage: the availability of a flow graph gain formula, also called Mason’s gain formula. A signal-flow graph consists of a network in which nodes are connected by directed branches. It depicts the flow of signals from one point of a system to another and gives the relationships among the signals.
Q. How do you calculate signal flow from a graph?
Signal flow graph is a graphical representation of algebraic equations….Let us consider the following signal flow graph to identify these nodes.
- The nodes present in this signal flow graph are y1, y2, y3 and y4.
- y1 and y4 are the input node and output node respectively.
- y2 and y3 are mixed nodes.
Q. What is the difference between block diagram and signal flow graph?
Differing from a purely abstract mathematical representation, a block diagram has the advantage of indicating more realistically the signal flows of the actual system. 4. In a block diagram all system variables are linked to each other through functional blocks.
Q. How does signal flow work?
Signal flow is the order of operations a sound goes through. When you record an instrument, the sound goes through different stages before you hear it through the speakers. Signal flow is the list of steps that sound goes through in order for you to hear it. It’s kind of like riding a train.
Q. How do you draw a signal flow graph from a differential equation?
Given a system differential equation it is possible to derive a signal flow graph directly, but it is more convenient to go first derive the transfer function, and then go from the transfer function to the state space model, and then from the state space model to the signal flow graph.
Q. Which node has only outgoing branches?
The node having only outgoing branches is called input or source node. In Fig. 5.7, x 1 is the input or source node. The node having only incoming branches is called sink node or output node.
Q. What is signal flow graph in DSP?
A signal flow graph is a network of directed branches that connect at nodes. As examples, OSB Figures 6.8 and 6.9 depict the general form of signal flow graphs. In a signal flow graph, the value carried by a specific branch is equal to the value of its originating node. Nodes in signal flow graphs represent variables.
Q. Is signal flow graph unique?
The signal flow graph representation of a LTI system is not unique. For any given rational system function, equivalent sets of difference equations and network structures (flow graphs) exist.
Q. Who invented signal flow graph?
A signal-flow graph or signal-flowgraph, invented by Claude Shannon, but often called a Mason graph after Samuel Jefferson Mason who coined the term, is a specialized flow graph, a directed graph in which nodes represent system variables, and branches represent functional connections between pairs of nodes.
Q. What is IIR filter in DSP?
IIR filters are one of two primary types of digital filters used in Digital Signal Processing (DSP) applications (the other type being FIR). “IIR” means “Infinite Impulse Response.”
Q. What is windowing technique in DSP?
Windowing is the process of taking a small subset of a larger dataset, for processing and analysis. A naive approach, the rectangular window, involves simply truncating the dataset before and after the window, while not modifying the contents of the window at all.
Q. What are the types of IIR filters?
Digital IIR filter designs come from the classical analog designs and include the following filter types:
- Butterworth filters.
- Chebyshev filters.
- Chebyshev II filters, also known as inverse Chebyshev and Type II Chebyshev filters.
- Elliptic filters, also known as Cauer filters.
- Bessel filters.
Q. Is Butterworth IIR or FIR?
For example, Butterworth and Chebyshev filters can be implemented in FIR, but you may need a large number of taps to get the desired response. So we generally use prototypes other than the s domain polynomials as prototypes for FIR filters.
Q. Which is better FIR or IIR?
The advantage of IIR filters over FIR filters is that IIR filters usually require fewer coefficients to execute similar filtering operations, that IIR filters work faster, and require less memory space. FIR filters are better suited for applications that require a linear phase response.
Q. Is the filter FIR or IIR?
The crucial difference between FIR and IIR filters is that the FIR filter provides an impulse response of a finite period. As against IIR is a type of filter that generates impulse response of infinite duration for a dynamic system. Here we are talking about finite and infinite impulse response.
Q. Is the system FIR or IIR?
The easiest way to determine whether a filter is IIR or FIR is to identify its pole locations. For FIR filters, there is a rule for this that is based on the structure of the impulse response: If the system is causal (i.e. it is zero for all n<0), then it is FIR if all of its poles are located at the origin (z=0).
Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of FIR filter?
Advantages and disadvantages of FIR filters
- FIR filter are always stable.
- It is simple.
- FIR filter is having linear phase response.
- It is easy to optimize.
- Noncausal.
- Round of noise error is minimum.
- Both recursive, as well as nonrecursive filter, can be designed using FIR designing techniques.
Q. Where is FIR filter used?
Finite impulse response (FIR) filters are widely used in communication [1], consumer electronics, audio [2], and other signal processing applications [3]. One of the important applications of FIR filters is as a Hilbert transformer.
Q. How is FIR and IIR difference?
IIR filters consist of zeros and poles, and require less memory than FIR filters, whereas FIR only consists of zeros. IIR filters can become difficult to implement, and also delay and distort adjustments can alter the poles & zeroes, which make the filters unstable, whereas FIR filters remain stable.
Q. What is the difference between analog and digital filters?
The main difference between the two methods is that a digital filter circuit has to sample the analogue signal and convert it into a set of binary numbers. In contrast, analogue filters do not have to do this type of conversion and the signal remains in its pure analogue form throughout the filtering process.
Q. What are the types of filters?
Filters can be active or passive, and the four main types of filters are low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and notch/band-reject (though there are also all-pass filters).
Q. What are the difference analog and digital filters?
Analog filtering involves physical hardware that alters analog signals before they are passed off to other components to be processed. Digital filtering involves passing analog data to a processor that then runs code to digitally filter the data.
Q. Which filter is better analog or digital?
Analog filters are fairly simple but increase in complexity if you desire a more precise roll-off; that is, making the filtered result more precisely “step-like” at roll-off requires successively more components. Digital filters can be more precise in filtering, but the signal must be digital.
Q. Is FIR filter analog or digital?
FIR filters can be discrete-time or continuous-time, and digital or analog.
Q. Are analog filters still used?
Today, it is often preferred to carry out filtering in the digital domain where complex algorithms are much easier to implement, but analogue filters do still find applications, especially for low-order simple filtering tasks and are often still the norm at higher frequencies where digital technology is still …