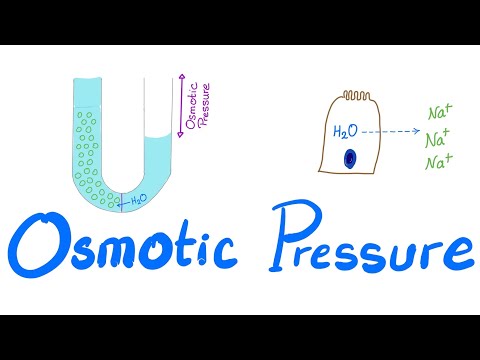
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis.
Q. How is Van t Hoff factor related to degree of ionization?
For weak electrolytes, van’t Hoff factor ‘i’ is a measure of the degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte. Higher is the value of the van’t Hoff factor, higher will be the degree of dissociation. Here n is the number of ions produced by the complete dissociation of 1 mole of substance.
Table of Contents
- Q. How is Van t Hoff factor related to degree of ionization?
- Q. What is osmotic pressure law?
- Q. What is osmotic pressure example?
- Q. What happens if osmotic pressure is high?
- Q. What happens when osmotic pressure increases?
- Q. What is a good example of osmosis?
- Q. Is Sweating an example of osmosis?
- Q. Which best describes the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
- Q. What are some examples of osmosis and diffusion?
- Q. What is the main function of osmosis?
- Q. Why is Osmosis important in real life?
- Q. What are three examples of diffusion from real life?
- Q. Where does osmosis occur in our body?
- Q. What is the principle of reverse osmosis?
- Q. What type of transport is osmosis?
- Q. What is osmosis with diagram?
- Q. How do you calculate osmosis?
Q. What is osmotic pressure law?
van’t Hoff’s Boyle’s Law of Solution: At constant temperature, the osmotic pressure (π) of a dilute solution is directly proportional to its molar concentration (C) or inversely proportional to volume (V) of the solution.
Q. What is osmotic pressure example?
An excellent example of a semipermeable membrane is that inside the shell of an egg. After shell removal is accomplished with acetic acid, the membrane around the egg can be used to demonstrate osmosis. Karo syrup is essentially pure sugar, with very little water in it, so its osmotic pressure is very low.
Q. What happens if osmotic pressure is high?
role in. … loss of electrolytes (salt), the osmotic pressure of the extracellular fluids becomes higher than in the cells. Since water passes from a region of lower to a region of higher osmotic pressure, water flows out of the cells into the extracellular fluid, tending to lower its osmotic pressure and increase…
Q. What happens when osmotic pressure increases?
Osmotic (Hydrostatic) Pressure The volume on the side with the solute increases until the number of water molecules on both sides is equal. Increasing the concentration of solute reduces the space available for water molecules, which reduces their numbers.
Q. What is a good example of osmosis?
An example of osmosis occurs when a sugar solution and water, top, are separated by a semipermeable membrane. The solution’s large sugar molecules cannot pass through the membrane into the water. Small water molecules move through the membrane until equilibrium is established, bottom.
Q. Is Sweating an example of osmosis?
Your sweat glands use osmosis. Your body doesn’t pump water to your skin in the form of sweat. Instead it deposits a little bit of salt inside one of you sweat glands.
Q. Which best describes the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Osmosis: Osmosis is the movement of solvent particles across a semipermeable membrane from a dilute solution into a concentrated solution. Diffusion: Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. The overall effect is to equalize concentration throughout the medium.
Q. What are some examples of osmosis and diffusion?
Examples
- Examples of Osmosis: Examples include red blood cells swelling up when exposed to freshwater and plant root hairs taking up water.
- Examples of Diffusion: Examples of diffusion include the scent of perfume filling a whole room and the movement of small molecules across a cell membrane.
Q. What is the main function of osmosis?
The main function of osmosis is equilibrium. Water will move from a dilute region to a concentrated region until the water concentration in both…
Q. Why is Osmosis important in real life?
Osmosis has a number of life-preserving functions: it assists plants in receiving water, it helps in the preservation of fruit and meat, and is even used in kidney dialysis. In addition, osmosis can be reversed to remove salt and other impurities from water.
Q. What are three examples of diffusion from real life?
Here are a few notable examples.
- Balloons. Ever notice how helium balloons slowly lose their lift?
- Food Coloring. A drop of food coloring in a glass of watercolors the water through diffusion.
- Perfume.
- Soda.
- Tea.
- Breathing.
- Calcium.
- Kidneys.
Q. Where does osmosis occur in our body?
Where Does It Happen? Osmosis occurs in both the small and large intestines, with the majority of osmosis occurring in the large intestine. As your body processes food, it moves from the esophagus to the stomach and then to the small intestine.
Q. What is the principle of reverse osmosis?
The equilibrium point of this water column height in terms of water pressure against the membrane is called osmotic pressure. If a force is applied to this column of water, the direction of water flow through the membrane can be reversed. This is the basis of the term reverse osmosis.
Q. What type of transport is osmosis?
Osmosis is a type of simple diffusion in which water molecules diffuse through a selectively permeable membrane from areas of high water concentration to areas of lower water concentration.
Q. What is osmosis with diagram?
Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a partially permeable membrane from a dilute solution (high concentration of water) to a concentrated solution (low concentration of water). In the diagram, the concentration of sugar is initially higher on the right side of the membrane.
Q. How do you calculate osmosis?
Osmotic pressure causes water to move into the solution with the highest concentration. The equation for osmotic pressure is pi=iMRT. The higher the concentration (M) or the temperature (T) of a solution, the higher the osmotic pressure.