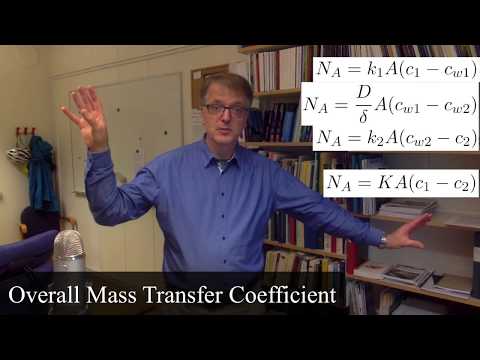
An overall. mass transfer coefficient may be defined in terms of a partial pressure driving force or it may be. defined in terms of a liquid phase concentration driving force. In either case, the coefficient must. account for the entire diffusional resistance in both phases.
Q. What is the significance of film thickness in mass transfer?
Depth Of Penetration Of Solute In Liquid Element3. the Thickness Of Stagnant Film That Offers The Same Resistance To Mass Transfer As Is Actualy Being Offered Under Given Hydrodynamic Conditions.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the significance of film thickness in mass transfer?
- Q. What is a liquid film?
- Q. What is HTU and NTU?
- Q. What is kLa value?
- Q. What is the difference between mass transfer and diffusion?
- Q. Which factors influence the rate of diffusion?
- Q. What is an diffusion?
- Q. Why mass transfer is important for chemical engineers?
- Q. How does mass transfer occur?
- Q. How do you calculate mass transfer?
- Q. What is convective mass transfer?
- Q. What are 4 examples of convection?
- Q. What is the difference between advection and convection?
- Q. Which type of condensation is better?
- Q. What is the difference between film and dropwise condensation?
- Q. Which is a type of condensation heat transfer process?
- Q. How many types of convection are there?
- Q. What is a real life example of convection?
- Q. What is convection definition and example?
- Q. How is convection reduced?
- Q. How is convection created?
- Q. How does convection happen?
Q. What is a liquid film?
The thin liquid film is a phase of small thickness, in which the two interfacial layers overlap to form a unified non-homogeneous structure of specific properties. From: Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2005.
Q. What is HTU and NTU?
The number of transfer units (NTU) required is a measure of the difficulty of the separation. The height of a transfer unit (HTU) is a measure of the separation effectiveness of the particular packings for a particular separation process.
Q. What is kLa value?
The oxygen transfer rate (OTR) and the kLa value are used as decisive parameters for the design of bioreactors. In biotechnological processes, the kLa coefficient indicates the efficiency of oxygen supply to microorganisms in a bioreactor.
Q. What is the difference between mass transfer and diffusion?
Mass transfer is the transport of mass from one place to another. The main difference between mass transfer and diffusion is that mass transfer may or may not involve a concentration gradient whereas diffusion does involve the movement of a solute down a concentration gradient.
Q. Which factors influence the rate of diffusion?
Several factors affect the rate of diffusion of a solute including the mass of the solute, the temperature of the environment, the solvent density, and the distance traveled.
Q. What is an diffusion?
Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules under a concentration gradient. It is an important process occurring in all living beings. Diffusion helps in the movement of substances in and out of the cells. Liquid and gases undergo diffusion as the molecules are able to move randomly.
Q. Why mass transfer is important for chemical engineers?
Knowledge of combined mass, heat, and momentum transfer is crucial to chemical engineering. For a chemical reaction to proceed, there has to be energy and mass transfer, usually supported by forced flow of gases and liquids (momentum transfer).
Q. How does mass transfer occur?
Mass transfer occurs when a species concentration gradient exists between the gas phase and the material (liquid or solid phase). This transport phenomena is from the material toward the gas (desorption) or from the gas into the material (adsorption/absorption) (Lewis and Whitman, 1924).
Q. How do you calculate mass transfer?
[In fact, the mass transfer equation is obtained based on the analogy with the heat transfer equation q = Q/A = h (DT); where DT is the temperature difference driving force for heat flow….
| NA | molar flux of component A, mole/(area.time) |
|---|---|
| ky | mass transfer coefficients in the gas phase |
Q. What is convective mass transfer?
Definition of convective mass transfer: The transport of material between a boundary surface and a moving fluid or between two. immiscible moving fluids separated by a mobile interface.
Q. What are 4 examples of convection?
13 Examples Of Convection In Everyday Life
- Breeze. The formation of sea and land breeze form the classic examples of convection.
- Boiling Water. Convection comes into play while boiling water.
- Blood Circulation in Warm-Blooded Mammals.
- Air-Conditioner.
- Radiator.
- Refrigerator.
- Hot Air Popper.
- Hot Air Balloon.
Q. What is the difference between advection and convection?
Distinction between advection and convection More technically, convection applies to the movement of a fluid (often due to density gradients created by thermal gradients), whereas advection is the movement of some material by the velocity of the fluid.
Q. Which type of condensation is better?
Drop nucleation, growth, and condensation have important practical consequences. Significantly, heat transfer rates in dropwise condensation can be much higher than in filmwise condensation. Thus dropwise condensation is often preferred to filmwise condensation in heat exchangers.
Q. What is the difference between film and dropwise condensation?
DROPWISE CONDENSATION The condensed vapor forms droplet on the surface instead of continuous film. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FILMWISE AND DROPWISE CONDENSATION Heat transfer at in dropwise is 10 times larger than in filmwise . In dropwise a large area of solid surface is directly exposed to vapour .
Q. Which is a type of condensation heat transfer process?
In general, three distinct forms of condensation are observed: Film condensation. Dropwise condensation. Direct contact condensation.
Q. How many types of convection are there?
two types
Q. What is a real life example of convection?
This hot water rises and cooler water moves down to replace it, causing a circular motion. radiator – A radiator puts warm air out at the top and draws in cooler air at the bottom. steaming cup of hot tea – The steam you see when drinking a cup of hot tea indicates that heat is being transferred into the air.
Q. What is convection definition and example?
Convection is the movement of heat because of the movement of warm matter. For example, atmospheric circulation moves warm air to cool places, causing wind. Wind, in turn, can enter and cool a room if the window is open.
Q. How is convection reduced?
If the double glazing is made with air between the glass then convection is minimised because there is little room for the air to move. The material also prevents air circulating inside the cavity, therefore reducing heat loss by convection. Heat loss through the roof can be reduced by laying loft insulation.
Q. How is convection created?
Convection currents are the result of differential heating. Lighter (less dense), warm material rises while heavier (more dense) cool material sinks. It is this movement that creates circulation patterns known as convection currents in the atmosphere, in water, and in the mantle of Earth.
Q. How does convection happen?
Convection occurs when particles with a lot of heat energy in a liquid or gas move and take the place of particles with less heat energy. Heat energy is transferred from hot places to cooler places by convection. Liquids and gases expand when they are heated. The denser cold liquid or gas falls into the warm areas.