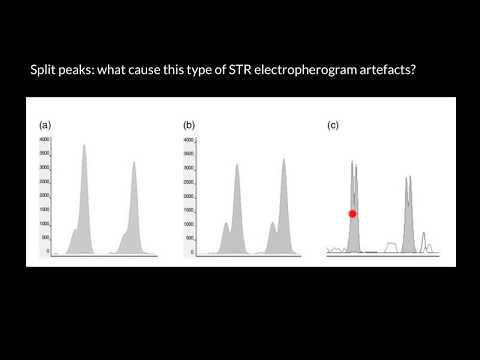
Peak splitting is when a Gaussian peak gets a shoulder or a twin They have the same base, are unexpected and can be caused by a number of factors The splitting can affect all peaks or just one, and different effects can be attributed to different causes
Q. What is n1 rule?
The (n+1) Rule, an empirical rule used to predict the multiplicity and, in conjunction with Pascal’s triangle, splitting pattern of peaks in 1H and 13C NMR spectra, states that if a given nucleus is coupled (see spin coupling) to n number of nuclei that are equivalent (see equivalent ligands), the multiplicity of the
Table of Contents
- Q. What is n1 rule?
- Q. What is splitting of signals?
- Q. What is meant by spin-spin splitting?
- Q. What does J-coupling mean?
- Q. What is shielding and Deshielding?
- Q. What is a quantum spin?
- Q. What is a spin 1 particle?
- Q. What is a spin 1/2 particle?
- Q. Why the spin of electron is half?
- Q. What is a spin 0 particle?
- Q. Can you have negative spin?
- Q. Do electrons actually spin?
- Q. Can you change the spin of an electron?
- Q. Do protons actually spin?
- Q. Are there electrons in space?
- Q. Is empty space really empty?
- Q. Is empty space possible?
- Q. Why is 99 empty space?
- Q. Why can’t we walk through walls?
- Q. What keeps space empty?
- Q. Will the universe ever end?
Q. What is splitting of signals?
The source of signal splitting is a phenomenon called spin-spin coupling, a term that describes the magnetic interactions between neighboring, non-equivalent NMR-active nuclei In our trichloromethane example, the Ha and Hb protons are spin-coupled to each other
Q. What is meant by spin-spin splitting?
In chemical compound: Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy … atoms through a process termed spin-spin splitting Each set of equivalent hydrogens on a given carbon is split into an n+1 multiplet by adjacent hydrogen atoms that are nonequivalent to the hydrogens of the given carbon
Q. What does J-coupling mean?
A J-coupling is an interaction between nuclei containing spin J-couplings are also known as scalar couplings This interaction is mediated through bonds, in contrast to dipole interactions, which are mediated through space The J-coupling typically reduces in magnitude the more bonds exist between the coupled nuclei
Q. What is shielding and Deshielding?
What is Deshielding? Downfield The Nucleus feels stronger magnetic field Deshielding is the opposite of shielding When we say that an atom is deshielded, we mean that “A nucleus whose chemical shift has been increased due to removal of electron density, magnetic induction, or other effects”
Q. What is a quantum spin?
“Spin is the total angular momentum, or intrinsic angular momentum, of a body In quantum mechanics, angular momenta are discrete, quantized in units of Planck’s constant divided by 4 pi Niels Bohr proposed that angular momentum is quantized in this to explain the line spectrum of hydrogen
Q. What is a spin 1 particle?
Electrons, protons, and neutrons are all spin 1/2 particles Photons are spin 1 particles, and certain exotic particles, such as pions, possess spin zero Most particles with spin possess a magnetic moment
Q. What is a spin 1/2 particle?
The spin number describes how many symmetrical facets a particle has in one full rotation; a spin of ½ means that the particle must be fully rotated twice (through 720°) before it has the same configuration as when it started Particles having net spin ½ include the proton, neutron, electron, neutrino, and quarks
Q. Why the spin of electron is half?
A rotation of say 90° along the x-axis then gives an electron with only 50% chance of being up along z, if that property then gets measured So obviously the electron changes under rotation In other words, the 360° rotation changes the sign of the wave pattern, indicating that the particle has half-integral spin
Q. What is a spin 0 particle?
Spin 0 means that the particle has spherical symmetry, without any preferred axis The spin value tells after which angle of rotation the wave function returns to itself: 2π / spin = angle
Q. Can you have negative spin?
Going back to your question, spin has two quantum numbers, one for the magnitude of the intrinsic angular momentum, and another one for the projection over the Z axis The former can not be negative, as it is the quantization of the size of the vector The latter can be both positive and negative
Q. Do electrons actually spin?
The electron is truly an elementary particle, so, unlike the Earth, it cannot spin Again, spinning occurs when the particles that make up an object revolve around an axis that passes through the object An electron has no smaller particles composing it, so an electron simply cannot spin
Q. Can you change the spin of an electron?
The spin of an electron cannot be observed continuously without altering it, so it has to be measured before and after an attempt to manipulate its quantum state This measurement reveals whether the spin is up or down, but the surrounding magnetic environment can also take effect at any time
Q. Do protons actually spin?
Protons always have “spin” The direction and strength of a proton’s spin determines its magnetic and electrical properties Changes to the proton’s spin also alter its structure
Q. Are there electrons in space?
Atoms are not mostly empty space because there is no such thing as purely empty space Atoms are filled with electrons It’s true that a large percentage of the atom’s mass is concentrated in its tiny nucleus, but that does not imply that the rest of the atom is empty
Q. Is empty space really empty?
And as in the rest of physics, its nature has turned out to be mind-bendingly weird: Empty space is not really empty because nothing contains something, seething with energy and particles that flit into and out of existence Physicists have known that much for decades, ever since the birth of quantum mechanics
Q. Is empty space possible?
Quantum mechanics tells us that there is no such thing as empty space Even the most perfect vacuum is actually filled by a roiling cloud of particles and antiparticles, which flare into existence and almost instantaneously fade back into nothingness
Q. Why is 99 empty space?
Atoms make up everything, but they also exist very, very far apart – and atoms themselves are more void than they are matter Every atom has a nucleus surrounded by electrons Every human on planet Earth is made up of millions and millions of atoms which all are 99% empty space
Q. Why can’t we walk through walls?
Here’s The Reason You Can’t Actually Walk Through Walls, According to Science You’ve probably heard that the atoms that make up your body and all other normal matter in the Universe are mostly empty space Solid enough the elements in our atoms can’t just pass through the empty spaces of other atoms, and vice versa
Q. What keeps space empty?
Space is not empty A point in outer space is filled with gas, dust, a wind of charged particles from the stars, light from stars, cosmic rays, radiation left over from the Big Bang, gravity, electric and magnetic fields, and neutrinos from nuclear reactions
Q. Will the universe ever end?
Eventually, 100 trillion years from now, all star formation will cease, ending the Stelliferous Era that’s be running since not long after our universe first formed Much later, in the so-called Degenerate Era, galaxies will be gone, too Stellar remnants will fall apart