Q. What is phagocytosis and its steps?
The Steps Involved in Phagocytosis. Step 1: Activation of the Phagocyte. Step 2: Chemotaxis of Phagocytes (for wandering macrophages, neutrophils, and eosinophils) Step 3: Attachment of the Phagocyte to the Microbe or Cell. Step 4: Ingestion of the Microbe or Cell by the Phagocyte.
Q. What occurs during phagocytosis quizlet?
Phagocytosis – the process by which particulate matter is engulfed and degraded by a cell. This is in contrast to endocytosis – a process by which soluble macromolecules are taken into a cell. You just studied 84 terms!
Table of Contents
- Q. What is phagocytosis and its steps?
- Q. What occurs during phagocytosis quizlet?
- Q. What are the 7 steps of phagocytosis?
- Q. How do phagocytes work?
- Q. What are the 3 types of phagocytes?
- Q. How do phagocytes fight infection?
- Q. What are the 4 steps of phagocytosis?
- Q. Why is phagocytosis important?
- Q. Which phagocyte is the first to respond to an infection?
- Q. What is a natural killer?
- Q. What are some characteristics of phagocytosis?
- Q. How long is phagocytosis?
- Q. Which cells do not perform phagocytosis?
- Q. What is phagocytosis?
- Q. What is phagocytosis of sperm?
- Q. What increases phagocytosis of sperm?
- Q. What gives sperm motility?
- Q. What is the best medicine for sperm motility?
- Q. Which foods increase sperm motility?
- Q. What is minimum sperm motility?
- Q. How can I check my sperm motility at home?
- Q. Is 80 sperm motility good?
- Q. Can sperm motility change over time?
- Q. How can I get pregnant with low sperm motility?
- Q. Does milk increase sperm count?
- Q. Can I get pregnant with Asthenozoospermia?
- Q. How much sperm is required for getting pregnant?
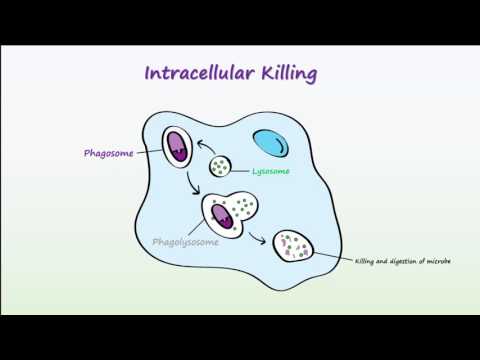
Q. What are the 7 steps of phagocytosis?
- Step 1: Activation of Phagocytic cells and Chemotaxis.
- Step 2: Recognition of invading microbes.
- Step 3: Ingestion and formation of phagosomes.
- Step 4: Formation of phagolysome.
- Step 5: Microbial killing and formation of residual bodies.
- Step 6: Elimination or exocytosis.
Q. How do phagocytes work?
Phagocytes are a type of white blood cell that use phagocytosis to engulf bacteria, foreign particles, and dying cells to protect the body. They bind to pathogens and internalise them in a phagosome, which acidifies and fuses with lysosomes in order to destroy the contents.
Q. What are the 3 types of phagocytes?
The main types of phagocytes are monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, tissue dendritic cells, and mast cells. Other cells, such as epithelial cells and fibroblasts, may also engage in phagocytosis, but lack receptors to detect opsonized pathogens and are not primarily immune system cells.
Q. How do phagocytes fight infection?
Phagocytes surround any pathogens in the blood and engulf them. They are attracted to pathogens and bind to them. The phagocytes membrane surrounds the pathogen and enzymes found inside the cell break down the pathogen in order to destroy it.
Q. What are the 4 steps of phagocytosis?
There are four essential steps in phagocytosis: (1) the plasma membrane entraps the food particle, (2) a vacuole forms within the cell to contain the food particle, (3) lysosomes fuse with the food vacuole, and (4) enzymes of the lysosomes digest the food particle.
Q. Why is phagocytosis important?
Phagocytosis is a critical part of the immune system. Several types of cells of the immune system perform phagocytosis, such as neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, and B lymphocytes. The act of phagocytizing pathogenic or foreign particles allows cells of the immune system to know what they are fighting against.
Q. Which phagocyte is the first to respond to an infection?
If pathogen enters, neutrophils are the first to respond and act by phagocytosing pathogen.
Q. What is a natural killer?
Natural killer (NK) cells are effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system that control several types of tumors and microbial infections by limiting their spread and subsequent tissue damage.
Q. What are some characteristics of phagocytosis?
Phagocyte, type of cell that has the ability to ingest, and sometimes digest, foreign particles, such as bacteria, carbon, dust, or dye. It engulfs foreign bodies by extending its cytoplasm into pseudopods (cytoplasmic extensions like feet), surrounding the foreign particle and forming a vacuole.
Q. How long is phagocytosis?
Phagocytosis of bacteria by human neutrophils takes on average nine minutes to occur. Once inside the phagocyte, the bacterium is trapped in a compartment called a phagosome. Within one minute the phagosome merges with either a lysosome or a granule, to form a phagolysosome.
Q. Which cells do not perform phagocytosis?
So, the correct answer is ‘Basophil’.
Q. What is phagocytosis?
Phagocytosis: The process by which a cell engulfs particles such as bacteria, other microorganisms, aged red blood cells, foreign matter, etc. The principal phagocytes include the neutrophils and monocytes (types of white blood cells). The prefix “phago-” comes from the Greek “phago” meaning “to eat.”
Q. What is phagocytosis of sperm?
Phagocytosis of sperm means breakdown of digestion of the sperm by various enzymes.
Q. What increases phagocytosis of sperm?
IUDs release some toxic substances and increase the number of leukocytes that phagocytes the sperms in order to prevent fertilisation, implantation. Phagocytosis is the process by which one cell engulfs another cell or large particle.
Q. What gives sperm motility?
Sperm motility is the ability of sperm to swim through the female reproductive tract in order to fertilize an egg. The tail of the sperm, the flagellum, is what gives sperm motility. Powered by Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the tail propels sperm towards its target by whipping back and forth.
Q. What is the best medicine for sperm motility?
Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) When men take it in oral form, it triggers the pituitary gland to make more luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulation hormone (FSH). A higher-level of these two hormones can improve sperm count, morphology and motility.
Q. Which foods increase sperm motility?
It can increase the production of testosterone, thereby increasing sperm count as well as sperm motility and quality.
- Foods that can Boost Sperm Count. There are a lot of foods that can boost sperm count and some of them are listed below:
- Eggs.
- Spinach.
- Bananas.
- Maca Roots.
- Asparagus.
- Dark Chocolate.
- Walnuts.
Q. What is minimum sperm motility?
For the sperm to get through the cervical mucus to fertilize a woman’s egg, they need to have progressive motility of at least 25 micrometers a second. Poor sperm motility or asthenozoospermia is diagnosed when less than 32 percent of the sperm are able to move efficiently.
Q. How can I check my sperm motility at home?
Home sperm tests require ejaculation into a collection cup. While procedures vary for transferring semen and completing the test, results are typically available within a few minutes. The tests work by detecting a protein found only in sperm.
Q. Is 80 sperm motility good?
Sperm count: at least 20 million per milliliter (m/mL) Sperm motility, or the ability to move rapidly: 60% to 80% actively moving.
Q. Can sperm motility change over time?
“Motility” is the ability of the sperm to move and “swim” properly toward the egg. Research demonstrates that sperm motility decreases with age; one study of healthy, non-smoking men demonstrated that motility decreased . 8% per year.
Q. How can I get pregnant with low sperm motility?
If the sperm is otherwise healthy, pregnancy with low sperm motility can occur. Using a reproductive technology such as in vitro fertilization or intrauterine insemination (IUI) can help increase the chance of pregnancy. This is because they bypass the need for the sperm to swim on their own.
Q. Does milk increase sperm count?
Yes, milk does a body good. But in the case of sperm, men may want to forego the high-fat stuff. Full-fat dairy foods can negatively impact sperm count and motility. It’s better for your guy to reach for low-fat milk, skim milk or milk alternatives like almond milk or coconut milk.
Q. Can I get pregnant with Asthenozoospermia?
However, it is important to note that if only motility is affected but the quality of sperm is healthy, men with asthenozoospermia can still achieve pregnancy via In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF).
Q. How much sperm is required for getting pregnant?
How many sperm do you need to get pregnant? It takes just one sperm to fertilize a woman’s egg. Keep in mind, though, for each sperm that reaches the egg, there are millions that don’t. On average, each time men ejaculate they release nearly 100 million sperm.