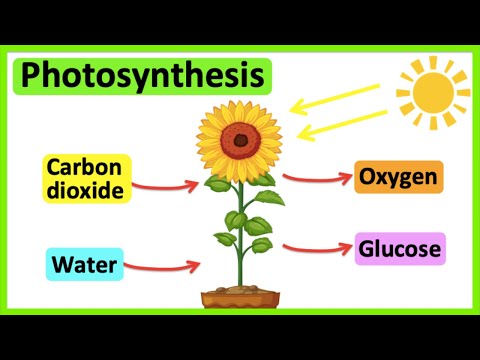
Q. What is photosynthesis done by?
Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis. The process is carried out by plants, algae, and some types of bacteria, which capture energy from sunlight to produce oxygen (O2) and chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar).
Q. Is photosynthesis performed by consumers?
This process is called photosynthesis, and it takes place in the chloroplasts, tiny green structures found in the green parts of plants. Animals that eat plants directly are called primary consumers.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is photosynthesis done by?
- Q. Is photosynthesis performed by consumers?
- Q. What organisms perform photosynthesis?
- Q. Who occurs photosynthesis?
- Q. Where is glucose found naturally?
- Q. What is glucose needed for?
- Q. Is glucose and sugar the same?
- Q. What is the healthiest sugar substitute?
- Q. Why was Stevia banned?
- Q. What is the safest sweetener?
- Q. Why is sucralose bad for you?
- Q. Why is Coke Zero bad for you?
- Q. Which is better stevia or monk fruit?
- Q. Does Monk Fruit raise insulin?
- Q. Does monk fruit make you gain weight?
- Q. Is monk fruit good for you?
- Q. Why does monk fruit have erythritol?
- Q. What is the best monk fruit?
- Q. Why does monk fruit taste cold?
- Q. Does monk fruit dissolve like sugar?
Q. What organisms perform photosynthesis?
Plants, algae, and a group of bacteria called cyanobacteria are the only organisms capable of performing photosynthesis (Figure 1). Because they use light to manufacture their own food, they are called photoautotrophs (literally, “self-feeders using light”).
Q. Who occurs photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis takes place inside plant cells in small objects called chloroplasts . Chloroplasts contain a green substance called chlorophyll . This absorbs the light energy needed to make photosynthesis happen. Plants and algae can only carry out photosynthesis in the light.
Q. Where is glucose found naturally?
Glucose is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. In animals, glucose is released from the breakdown of glycogen in a process known as glycogenolysis.
Q. What is glucose needed for?
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main sugar found in blood. The body gets glucose from the food we eat. This sugar is an important source of energy and provides nutrients to the body’s organs, muscles and nervous system.
Q. Is glucose and sugar the same?
Sugar vs. glucose. There are different kinds of sugars, but the type the body uses most is glucose. Other sugars, like fructose from fruit or lactose from milk, are converted into glucose and used for energy.
Q. What is the healthiest sugar substitute?
Stevia is probably the healthiest option, followed by xylitol, erythritol, and yacon syrup. Natural sugars like maple syrup, molasses, and honey are less harmful than regular sugar and even have health benefits.
Q. Why was Stevia banned?
Though widely available throughout the world, in 1991 stevia was banned in the U.S. due to early studies that suggested the sweetener may cause cancer. In December 2008, the FDA accepted this argument, declared stevia GRAS, and allowed its use in mainstream U.S. food production.
Q. What is the safest sweetener?
The best and safest sugar substitutes are erythritol, xylitol, stevia leaf extracts, and neotame—with some caveats: Erythritol: Large amounts (more than about 40 or 50 grams or 10 or 12 teaspoons) of this sugar alcohol sometimes cause nausea, but smaller amounts are fine.
Q. Why is sucralose bad for you?
Sucralose and the microbiome Research in rodents shows that sucralose upsets the microbiome balance, and that can lead to increased inflammation. “We know long-term inflammation can contribute to a variety of problems, including obesity and diabetes,” says Patton.
Q. Why is Coke Zero bad for you?
Further research is needed to determine the exact effects of Coke Zero and other diet beverages on your health. Coke Zero and other diet sodas are linked to alterations in the gut microbiome and an increased risk of osteoporosis and heart and kidney disease.
Q. Which is better stevia or monk fruit?
In terms of taste, stevia is 200-300 times sweeter than regular table sugar. Stevia’s advantage over regular table sugar or artificial sweeteners are similar to the advantages of monk fruit – zero calories, zero carbs, zero sugars.
Q. Does Monk Fruit raise insulin?
People with diabetes have to be careful about their sweeteners — many raise blood sugar, or glucose, levels and cause spikes of the hormone insulin. However, natural sweeteners, such as stevia, monk fruit, and erythritol, tend to raise blood glucose levels less and contain fewer calories than sugar.
Q. Does monk fruit make you gain weight?
Currently, no research has examined how monk fruit sweeteners affect weight. However, there is substantial evidence that substituting foods and beverages sweetened with low-calorie sweeteners for their full-sugar counterparts can play a role in weight loss or weight management.
Q. Is monk fruit good for you?
They’re safe for children, pregnant women, and breast-feeding women. According to a 2009 study , monk fruit gets its sweetness from antioxidant mogrosides. The study found monk fruit extract has the potential to be a low-glycemic natural sweetener. A 2013 study concluded mogrosides may help reduce oxidative stress.
Q. Why does monk fruit have erythritol?
Monk fruit contains natural sugars, mainly fructose and glucose. Because this extract may be 100–250 times sweeter than table sugar, many manufacturers mix monk fruit sweetener with other natural products, such as inulin or erythritol, to reduce the intensity of the sweetness.
Q. What is the best monk fruit?
The Best Monk Fruit Sweeteners
| Rank | Product |
|---|---|
| 1. | It’s Just – 100% Monkfruit Extract Powder |
| 2. | Smart 138 Monk Drops |
| 3. | Purisure Monk Fruit Extract |
| 4. | NOW Foods Monk Fruit Liquid Organic |
Q. Why does monk fruit taste cold?
The cooling effect is a chemical reaction that happens when undissolved erythritol makes contact with the saliva in your mouth. The reason it feels like it is getting cold in your mouth is that it actually is. The erythritol is actually taking heat from your mouth when it is dissolving.
Q. Does monk fruit dissolve like sugar?
It has a course sugar-like consistency and is light beige in color. It does have a slight aftertaste but I found it more pleasant than some other sweeteners I’ve tried. It’s relatively quick dissolving and one packet made a cup of coffee overly sweet by my standards. Its heat stable so you can cook with it.