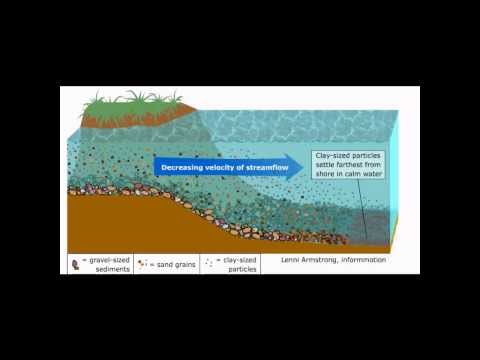
Q. What is river sediment called?
Water can wash sediment, such as gravel or pebbles, down from a creek, into a river, and eventually to that river’s delta. Deltas, river banks, and the bottom of waterfalls are common areas where sediment accumulates. Sediment created and deposited by glaciers is called moraine.
Q. What is the name given to fine clay in a river?
Alluvial deposit, Material deposited by rivers. It consists of silt, sand, clay, and gravel, as well as much organic matter.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is river sediment called?
- Q. What is the name given to fine clay in a river?
- Q. What sediment does a river carry with its flow?
- Q. Why do rivers silt up?
- Q. Is silt or sand smaller?
- Q. Is Clay smaller than sand?
- Q. Why is clay so slippery?
- Q. What is clay size?
- Q. What sieve size is clay?
- Q. What are the standard sieve sizes?
- Q. What size is a 200 sieve?
- Q. Is sieve a size chart?
- Q. Is sieve an 8?
- Q. Is percent finer the same as percent passing?
- Q. What size is 150 mesh?
- Q. What size is 50 mesh?
- Q. What is the smallest mesh size?
- Q. How do I choose mesh size?
- Q. What size is 40 mesh?
- Q. Can a mesh be too fine?
- Q. What is mesh count?
- Q. What is mesh no?
- Q. What Micron is 150 mesh?
- Q. Is 100 micron smaller than 200 micron?
- Q. How do you convert mesh to Micron?
- Q. How many microns is a human hair?
- Q. What is bigger 1 micron or 5 micron?
- Q. How many microns is dust?
- Q. What is the smallest micron you can see?
Q. What sediment does a river carry with its flow?
For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification.
Q. Why do rivers silt up?
When a river “bursts its banks” after heavy rain, flood water spreads out across the floodplain and, because this water hardly moves, finer silt and clay are deposited – often making good farmland! When a river reaches a lake or the sea, it quickly deposits much of its sediment.
Q. Is silt or sand smaller?
Grain size criteria In the Udden–Wentworth scale (due to Krumbein), silt particles range between 0.0039 and 0.0625 mm, larger than clay but smaller than sand particles.
Q. Is Clay smaller than sand?
The particles that make up soil are categorized into three groups by size – sand, silt, and clay. Sand particles are the largest and clay particles the smallest.
Q. Why is clay so slippery?
Clay feels sticky when wet. Water drains very slowly through clay soil. Therefore, clay soil remains saturated after a heavy rain. When this happens, there is little air in the soil, and plant roots cannot find oxygen..
Q. What is clay size?
Clay particles are very small less than 0.002 mm. Clay is a fine-grained natural rock or soil material that combines one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Answer verified by Toppr.
Q. What sieve size is clay?
Soil particles vary greatly in size, and soil scientists classify soil particles into sand, silt, and clay. Starting with the finest, clay particles are smaller than 0.002 mm in diameter. Some clay particles are so small that ordinary microscopes do not show them. Silt particles are from 0.002 to 0.05 mm in diameter.
Q. What are the standard sieve sizes?
Particle Size Conversion
| Sieve Designation | Nominal Sieve Opening | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Mesh | mm |
| 9.51mm | 3/8 in. | 9.51 |
| 8.00mm | 5/16 in. | 8.00 |
| 6.73mm | 0.265 in. | 6.73 |
Q. What size is a 200 sieve?
200) sieve. Gravel: Material passing a 75-mm (3-inch) sieve and retained on a 4.75-mm (No. 4) sieve.
Q. Is sieve a size chart?
Sieve mesh sizes are based on dimensions of the mesh size opening, or on the number of openings per linear inch….ISO Test Sieves.
| ASTM E11 | ISO 565/3310-1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Alternate | Size |
| 4.00mm | No.5 | 4.00mm |
| 3.55mm | – | 3.55mm |
| 3.35mm | No.6 | 3.35mm |
Q. Is sieve an 8?
8in (203mm) diameter ASTM E11 Test Sieve is constructed with a No….
| ASTM E11 Opening Size | No.8 (2.36mm) |
|---|---|
| Stacked Frame Height | 2-1/8in |
| Overall Frame Height | 2-5/8in |
| Material | All Stainless Steel |
| Backing Cloth Included | No |
Q. Is percent finer the same as percent passing?
This means that 18.2% of the material passed through that sieve, and 81.8% (which is 100% – 18.2%, which you can see in the “Cumulative Retained” column) was “caught”, or retained, by that sieve. “% Finer” represents the percentage of material of the total sample (100%) that will pass through the current sieve.
Q. What size is 150 mesh?
Mesh Size
| US Mesh | Micron | Inches |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 149 um | 0.0059 |
| 120 | 125 um | 0.0049 |
| 140 | 105 um | 0.0041 |
| 150 | 89 um | 0.0035 |
Q. What size is 50 mesh?
Mesh and Micron Sizes
| US Mesh* | Microns | Inches |
|---|---|---|
| 35 | 500 | 0.0197 |
| 40 | 400 | 0.0165 |
| 45 | 354 | 0.0138 |
| 50 | 297 | 0.0117 |
Q. What is the smallest mesh size?
A -6 mesh powder has particles that measure less than 3360 microns. A powder that is -325 mesh has particles that measure less than 44 micron. As you can see, the larger the mesh number the smaller the particle size of the powder. You would know that this powder passed though a 325 mesh screen.
Q. How do I choose mesh size?
Choosing a suitable mesh size
- Perform chosen analysis for several different mesh sizes.
- Notice where high deformations or high stresses occur, perhaps it is worth to refine mesh in those regions.
- Collect data from analysis of each mesh: outcome, number of nodes in the model, computing time.
Q. What size is 40 mesh?
Mesh Size Comparison Chart
| Mesh Number | Inches | Microns |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 0.0232 | 595 |
| 35 | 0.0197 | 500 |
| 40 | 0.0165 | 400 |
| 45 | 0.0138 | 354 |
Q. Can a mesh be too fine?
If the mesh is too fine that can cause problems with single precision numerics. This is especially the case where you have a large range of mesh sizes, such as very fine mesh to resolve near-wall behaviour but coarse mesh in the distance. This is easily fixed by going to double precision numerics in most cases.
Q. What is mesh count?
What is mesh count? Well, mesh count is a measure of how many threads of polyester (used to be silk, centuries ago, hence ‘silkscreening’) cross each other per square inch of the screen. For example, a 110 mesh screen would have 110 threads crossing per square inch.
Q. What is mesh no?
Filters. A measure of fineness of a mesh: the numerical value indicates the number of openings per linear inch. The smaller the mesh number, the larger particles can pass through the mesh. noun.
Q. What Micron is 150 mesh?
Micron to Mesh Conversion Table
| Micron (µm) | US Mesh | Tyler Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| 150 | 100 | 100 |
| 125 | 120 | 115 |
| 106 | 140 | 150 |
| 90 | 170 | 170 |
Q. Is 100 micron smaller than 200 micron?
100 micron is finer then the 600 micron. They measure the holes in the mesh in microns, so the higher the number the larger the holes. 015700” holes and 200 micron mesh has . 007850” holes.
Q. How do you convert mesh to Micron?
The chart below roughly converts between U.S. Mesh, microns, and fractions of an inch. There is no simple formula to convert between microns and wire mesh because it would have to account for changing wire diameter….U.S. Mesh vs. Micron.
| U.S. Mesh | Microns | Inches |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 1680 | 0.0661 |
| 14 | 1410 | 0.0555 |
| 16 | 1190 | 0.0469 |
| 18 | 1000 | 0.0394 |
Q. How many microns is a human hair?
70 microns
Q. What is bigger 1 micron or 5 micron?
For example, a 20-micron filter has larger openings than a 5-micron filter. Bacteria range in size from 0.2 to 2 microns in width or diameter and from 1 to 10 microns in length for the nonspherical specie, so a 1-micron filter will remove most bacteria and cysts.
Q. How many microns is dust?
5 microns
Q. What is the smallest micron you can see?
Particle Sizes One micron is equal to one-millionth of a meter, or 1/26,000 of an inch. On average, the human eye cannot see particles that are smaller than 50 to 60 microns.