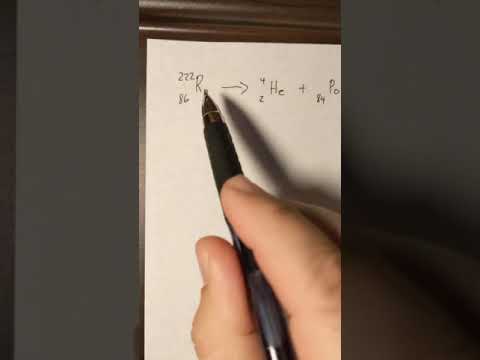It is chemically inert, but radioactive. Radon decays into radioactive polonium and alpha particles. This emitted radiation made radon useful in cancer therapy. Radon was used in some hospitals to treat tumours by sealing the gas in minute tubes, and implanting these into the tumour, treating the disease in situ.
Q. Why does radon-222 build up in basements?
Radon gas accumulates in basements because of low ventilation. Heating and air-conditioning, natural air movement, the “stack effect,” as well as diffusion of radon gas through the floors and walls distribute radon throughout the house.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why does radon-222 build up in basements?
- Q. What products result from radon-222 emissions?
- Q. What is the alpha decay of Rn 222?
- Q. Where is Radon-222 found?
- Q. How is radon 222 created?
- Q. Can you filter radon out of water?
- Q. How can radon 222 be prevented from entering homes?
- Q. Which radioisotope is used for diagnosing thyroid disorders?
- Q. What is the difference between a therapeutic and a diagnostic radioisotope?
- Q. Where were radioisotopes first used in medicine?
- Q. What are the 3 Uses of Isotopes?
Q. What products result from radon-222 emissions?
Polonium-218 and lead-214 are decay products of radon-222.
Q. What is the alpha decay of Rn 222?
polonium-218
Q. Where is Radon-222 found?
Since uranium is essentially ubiquitous (being or seeming to be everywhere at the same time) in the earth’s crust, radium-226 and radon-222 are present in almost all rock and all soil and water. The amount of radon in the soil depends on soil chemistry, which varies from one house to the next.
Q. How is radon 222 created?
Radon-222 is formed naturally during a chain of radioactive decay. The decay series begins with uranium-238, and among the substances formed is radium-226, which decays directly to radon-222. The uranium is widely distributed in rocks and soils throughout the earth’s crust.
Q. Can you filter radon out of water?
Radon can be removed from water by using one of two methods: Aeration treatment – spraying water or mixing it with air and then venting the air from the water before use, or. GAC treatment – filtering water through granular activated carbon. Radon attaches to the carbon and leaves the water free of radon.
Q. How can radon 222 be prevented from entering homes?
More Ways to Take Action
- Stop smoking and discourage smoking in your home.
- Increase air flow in your house by opening windows and using fans and vents to circulate air.
- Seal cracks in floors and walls with plaster, caulk, or other materials designed for this purpose.
Q. Which radioisotope is used for diagnosing thyroid disorders?
An exceptionally useful radioactive isotope is iodine-131, which has a half-life of eight days. It is employed in medicine to monitor thyroid gland functioning, to treat goitre and thyroid cancer, and to locate tumours of the brain and of the liver.
Q. What is the difference between a therapeutic and a diagnostic radioisotope?
Radioisotopes typically have short half-lives and typically decay before their emitted radioactivity can cause damage to the patient’s body. Therapeutic applications of radioisotopes typically are intended to destroy the targeted cells. Today diagnostic and therapeutic procedures using radioactive isotopes are routine.
Q. Where were radioisotopes first used in medicine?
People suffering from polycythemia vera, a rare disease characterized by an over-abundance of red blood cells, were treated with doses of radio-pharmaceuticals. It was the first disease to be controlled with radioisotopes. In 1940, a pioneering treatment procedure debuted to treat leukemia.
Q. What are the 3 Uses of Isotopes?
Radioactive isotopes find uses in agriculture, food industry, pest control, archeology and medicine. Radiocarbon dating, which measures the age of carbon-bearing items, uses a radioactive isotope known as carbon-14. In medicine, gamma rays emitted by radioactive elements are used to detect tumors inside the human body.