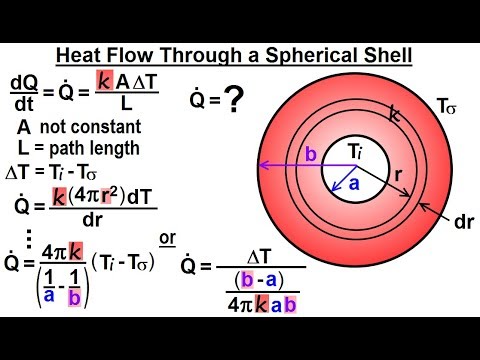
Q. What is spherical shell example?
Example: A sphere of radius 5cm is dropped into a cylindrical vessel partly filled with water. The diameter of the vessel is 10cm.
Q. Why is there no charge inside a conducting sphere?
Electric Field Of Charged Solid Sphere Because, in electrostatic condition , there is no electric field inside a conductor. As there is no electric field inside a conductor , if we assume any hypothetical surface inside a conductor , the net flux φ will be zero. Thus, the net charge inside a conductor Σq = 0.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is spherical shell example?
- Q. Why is there no charge inside a conducting sphere?
- Q. What is the thickness of the sphere?
- Q. Can electric field inside a conductor be non zero?
- Q. Why electric field inside a shell is zero?
- Q. Can electric field be negative?
- Q. Why is my electric field negative?
- Q. How electric field is created?
- Q. What is the symbol for electric field?
- Q. Is electric field real?
- Q. Do electric fields carry energy?
- Q. Who invented electric field?
- Q. Do we know electricity?
- Q. How do you calculate electric field energy?
- Q. Where is electrostatic energy stored?
- Q. Do electromagnetic waves carry charge?
- Q. Is current an electromagnetic wave?
- Q. Is sound an electromagnetic wave?
- Q. Why sound is not electromagnetic wave?
- Q. What is the cause of any sound wave?
Q. What is the thickness of the sphere?
the diameter and the thickness of a hollow metals sphere are 12 cm and 0.01 m respectively. the density of the metal is 8.88 gm per centimetre cube.
Q. Can electric field inside a conductor be non zero?
Can the electric field inside a conductor be non zero? The answer is NO. Electric field inside a conductor is always zero.
Q. Why electric field inside a shell is zero?
It follows that: The electric field immediately above the surface of a conductor is directed normal to that surface. Now, the gaussian surface encloses no charge, since all of the charge lies on the shell, so it follows from Gauss’ law, and symmetry, that the electric field inside the shell is zero.
Q. Can electric field be negative?
An electric field can never be negative. An electric field is a force experienced by the charge divided by the magnitude of the charge.
Q. Why is my electric field negative?
Electric field is not negative. It is a vector and thus has negative and positive directions. An electron being negatively charged experiences a force against the direction of the field. For a positive charge, the force is along the field.
Q. How electric field is created?
Electric fields originate from electric charges, or from time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field is defined mathematically as a vector field that associates to each point in space the (electrostatic or Coulomb) force per unit of charge exerted on an infinitesimal positive test charge at rest at that point.
Q. What is the symbol for electric field?
Symbols for physical quantities and their international units
| symbol | quantity | symbol |
|---|---|---|
| E, E | electric field | N/C, V/m |
| ΦE | electric flux | N m2/C, V m |
| U, UE | potential energy, electric potential energy | J |
| V, VE | voltage, potential, electric potential | V |
Q. Is electric field real?
The correct statement is that electric fields and magnetic fields are both fundamental, both are real, and both are part of one unified entity: the electromagnetic field.
Q. Do electric fields carry energy?
Electromagnetic waves bring energy into a system by virtue of their electric and magnetic fields. These fields can exert forces and move charges in the system and, thus, do work on them. Once created, the fields carry energy away from a source.
Q. Who invented electric field?
Michael Faraday
Q. Do we know electricity?
First we must realize that “electricity” does not exist. There is no single thing named “electricity.” We must accept the fact that, while several different things do exist inside wires, people wrongly call all of them by a single name. So never ask “what is electricity”.
Q. How do you calculate electric field energy?
U = ½ε0E2(A*d). (A*d) is the volume between the plates of the capacitor. Inside this volume the electric field is approximately constant and outside of this volume the electric field is approximately zero. We interpret uE = ½ε0E2 as the energy density, i.e. the energy per unit volume, in the electric field.
Q. Where is electrostatic energy stored?
Assuming the conductors are not free to move, potential energy is stored in the electric field associated with the surface charges (Section 5.22).
Q. Do electromagnetic waves carry charge?
There is no electric charge “in” electromagnetic waves.
Q. Is current an electromagnetic wave?
Electric current is the movement of electric charge through a conductor. Electromagnetic waves are created by moving electric charges, but once created, they can propagate through a vacuum. Photons are the smallest packets of energy that propagate as electromagnetic waves.
Q. Is sound an electromagnetic wave?
Electromagnetic wave is a by-product of both electric and magnetic field. It does not require presence of any medium and can travel through vacuum. Whereas mechanical waves requires the presence of medium. That’s why Sound is a mechanical wave and not an Electromagnetic wave.
Q. Why sound is not electromagnetic wave?
Sound can travel through air because air is made of molecules. Electromagnetic waves are not like sound waves because they do not need molecules to travel. This means that electromagnetic waves can travel through air, solid objects and even space. This is how astronauts on spacewalks use radios to communicate.
Q. What is the cause of any sound wave?
Sound is caused by the simple but rapid mechanical vibrations of various elastic bodies. These when moved or struck so as to vibrate, communicate the same kind of vibrations to the auditory nerve of the ear, and are then appreciated by the mind.