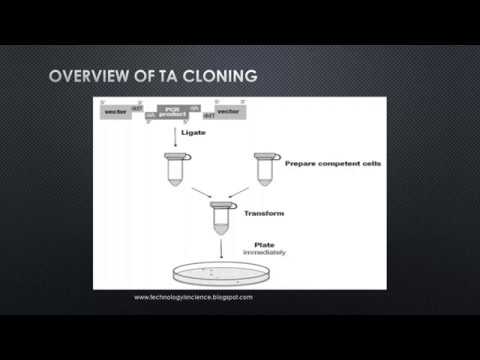
Q. What is TA cloning explain its steps?
TA cloning is one of the simplest and most efficient methods for the cloning of PCR products. The procedure exploits the terminal transferase activity of certain thermophilic DNA polymerases, including Thermus aquaticus (Taq) polymerase.
Q. How do you know if A ligation is successful?
The presence of high molecular weight molecules after incubation will be indicative of successful ligation. If your insert has ligated to the backbone, then you need to cross check with insert release and see that your insert and vector are released in the same size range as you would know.
Table of Contents
Q. How do you test for ligation?
You can check your ligation products by gel electrophoresis or PCR using plasmid primers across the insert but the number of ligation products and their low concentration makes analysis by agarose gel electrophoresis an impractical method.
Q. How much is a vector for ligation?
Typical ligation reactions use 100-200ng of vector DNA.
Q. What is the purpose of PCR?
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was originally developed in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis.
Q. What are the components of PCR?
For PCR there are five chemical components needed, including a DNA template, DNA polymerase enzyme, primers, nucleotides and reaction buffer. The DNA template is that particular DNA sequence which you want copied.
Q. What is a PCR protocol?
Protocols.io also provides an interactive version of this protocol where you can discover and share optimizations with the research community. PCR. The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a powerful and sensitive technique for DNA amplification (1). Taq DNA Polymerase is an enzyme widely used in PCR (2).
Q. What is ligation independent cloning?
Ligation Independent Cloning (LIC) Ligation Independent Cloning (LIC) is a technique developed in the early 1990s as an alternative to restriction enzyme/ligase cloning. Inserts are usually PCR amplified and vectors are made linear either by restriction enzyme digestion or by PCR.