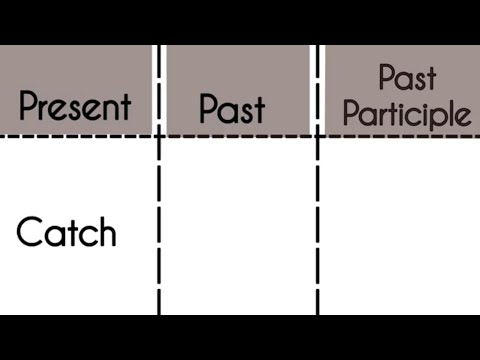
Q. What is the 3rd form of catch?
Conjugation of verb ‘Catch’
| Base Form (Infinitive): | To Catch |
|---|---|
| Past Simple: | Caught |
| Past Participle: | Caught |
| 3rd Person Singular: | Catches |
| Present Participle/Gerund: | Catching |
Q. What is the 2 and 3 form of catch?
Verb Forms of Catch
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the 3rd form of catch?
- Q. What is the 2 and 3 form of catch?
- Q. What is the past tense and past participle of write?
- Q. Do drunks tell the truth?
- Q. Why do I drink until I black out?
- Q. What is alcoholic dementia?
- Q. Do alcoholics get dementia?
- Q. What is considered heavy drinking?
- Q. Can the brain heal itself from alcohol?
- Q. How many brain cells are killed by alcohol?
- Q. What happens to your mind when you stop drinking?
| (Base) 1st | (Past) 2nd | (Past Participle) 3rd |
|---|---|---|
| Catch | Caught | Caught |
| Get list of more Verb Forms. | ||
Q. What is the past tense and past participle of write?
The present tense – base verb. The present participle….11 Past participle forms.
| Present tense form | Past tense | Past participle |
|---|---|---|
| write | wrote | written |
Q. Do drunks tell the truth?
‘ Alcohol can most definitely act as a truth serum — something that allows people to say what is truly on their mind.” At the same time, Vranich said that alcohol often caused people to have a shorter fuse and perceive negativity in a more exaggerated way — which could have been what happened with Gibson.
Q. Why do I drink until I black out?
Alcohol-related blackouts are gaps in a person’s memory for events that occurred while they were intoxicated. These gaps happen when a person drinks enough alcohol to temporarily block the transfer of memories from short-term to long-term storage—known as memory consolidation—in a brain area called the hippocampus.
Q. What is alcoholic dementia?
Alcohol-related ‘dementia’ is a type of alcohol-related brain damage (ARBD). If a person has alcohol-related ‘dementia’ they will struggle with day-to-day tasks. This is because of the damage to their brain, caused by regularly drinking too much alcohol over many years.
Q. Do alcoholics get dementia?
Alcoholism can damage your brain and increase the risk of dementia. Here’s what you need to know about the risk, and how to reduce it. Excessive drinking may cause brain damage and increase the risk of Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
Q. What is considered heavy drinking?
For men, heavy drinking is typically defined as consuming 15 drinks or more per week. For women, heavy drinking is typically defined as consuming 8 drinks or more per week.
Q. Can the brain heal itself from alcohol?
Alcohol related brain damage and recovery. Results from a study show the brain is able to repair itself remarkably quickly when chronic alcohol abusers become abstinent. The study found that grey matter which had shrunk due to alcohol abuse began returning within two weeks after the patient stopped drinking.
Q. How many brain cells are killed by alcohol?
Alcohol doesn’t kill brain cells, but it does have both short- and long-term effects on your brain, even in moderate amounts. Going out for happy hour a few nights a month likely won’t cause any long-term damage. But if you find yourself drinking heavily or binge drinking often, consider reaching out for help.
Q. What happens to your mind when you stop drinking?
When you stop drinking, your brain no longer has to block GABA functions. So, your brain begins to return to its normal state. The second biological event is the level of neurotransmitter glutamate goes down. It may be a slight amount, but it does go down.