Q. What is the average mass of an element?
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as daltons, D). The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope.
Q. What is the average atomic mass an average of?
The average atomic mass (sometimes called atomic weight) of an element is the weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. Average masses are generally expressed in unified atomic mass units (u), where 1 u is equal to exactly one-twelfth the mass of a neutral atom of carbon-12.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the average mass of an element?
- Q. What is the average atomic mass an average of?
- Q. How do you find the average mass of an isotope?
- Q. How do isotopes relate to the average atomic mass?
- Q. What is the difference between isotopic mass and atomic mass?
- Q. Why do isotopes have different masses?
- Q. Do Isotopes have the same atomic mass?
- Q. Why do isotopes occur?
- Q. Are isotopes dangerous?
- Q. What are examples of radioactive isotopes?
- Q. Is Dalton’s theory still accepted today?
- Q. What was wrong with Dalton?
- Q. Which atomic theory is accepted today?
- Q. Who invented electron?
- Q. Is atomic theory proven?
- Q. Is Dalton’s theory correct?
- Q. Who proved Dalton’s theory wrong?
- Q. Which concept in Dalton’s theory has been modified?
- Q. What are the 4 parts of Dalton’s atomic theory?
- Q. What are Daltons 5 principles?
- Q. What are the 5 main ideas of Dalton’s theory?
- Q. How many atoms are in our body?
- Q. What did Rutherford’s model explain?
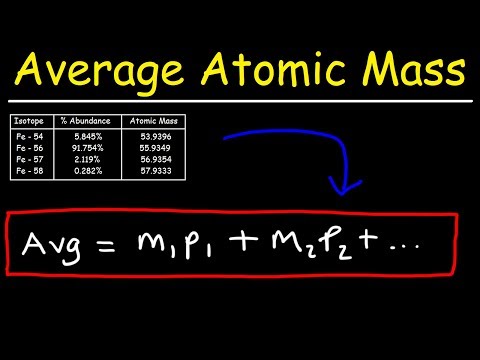
Q. How do you find the average mass of an isotope?
To calculate the average atomic mass, multiply the fraction by the mass number for each isotope, then add them together. Whenever we do mass calculations involving elements or compounds (combinations of elements), we always use average atomic masses.
Q. How do isotopes relate to the average atomic mass?
Every isotope (at least, the ones that occur naturally) contributes to the average atomic mass, which appears in the element’s box on most periodic tables. You must find the total mass (500 + 1200 = 1700) and divide it by the total number of people (30) so the average is 56.67.
Q. What is the difference between isotopic mass and atomic mass?
While atomic mass is an absolute mass, relative isotopic mass is a dimensionless number with no units. This loss of units results from the use of a scaling ratio with respect to a carbon-12 standard, and the word “relative” in the term “relative isotopic mass” refers to this scaling relative to carbon-12.
Q. Why do isotopes have different masses?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons but the same number of protons and electrons. The difference in the number of neutrons between the various isotopes of an element means that the various isotopes have different masses.
Q. Do Isotopes have the same atomic mass?
Isotopes are atoms with different atomic masses which have the same atomic number. The atoms of different isotopes are atoms of the same chemical element; they differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Q. Why do isotopes occur?
Isotopes can either form spontaneously (naturally) through radioactive decay of a nucleus (i.e., emission of energy in the form of alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons, and photons) or artificially by bombarding a stable nucleus with charged particles via accelerators or neutrons in a nuclear reactors.
Q. Are isotopes dangerous?
Exposure to radiation generally is considered harmful to the human body, but radioisotopes are highly valuable in medicine, particularly in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Radioisotopes typically have short half-lives and typically decay before their emitted radioactivity can cause damage to the patient’s body.
Q. What are examples of radioactive isotopes?
Radioactive isotopes of radium, thorium, and uranium, for example, are found naturally in rocks and soil. Uranium and thorium also occur in trace amounts in water. Radon, generated by the radioactive decay of radium, is present in air.
Q. Is Dalton’s theory still accepted today?
Dalton’s atomic theory was accepted by many scientists almost immediately. Most of it is still accepted today. However, scientists now know that atoms are not the smallest particles of matter.
Q. What was wrong with Dalton?
Drawbacks of Dalton’s Atomic Theory The indivisibility of an atom was proved wrong: an atom can be further subdivided into protons, neutrons and electrons. However an atom is the smallest particle that takes part in chemical reactions. According to Dalton, the atoms of same element are similar in all respects.
Q. Which atomic theory is accepted today?
Dalton’s atomic theory
Q. Who invented electron?
Thomson Joseph John Thomson
Q. Is atomic theory proven?
Dalton’s theory has not proven to be correct under all circumstances. The first rule was proven incorrect when scientists divided atoms in a process called nuclear fission. The second rule was proven incorrect by the discovery that not all atoms of the same element have the same mass; there are different isotopes.
Q. Is Dalton’s theory correct?
For more on isotopes, you can watch this video on atomic number, mass number, and isotopes. Despite these caveats, Dalton’s atomic theory is still mostly true, and it forms the framework of modern chemistry. Scientists have even developed the technology to see the world on an atomic level!
Q. Who proved Dalton’s theory wrong?
Atomic Theory. In 1897, English physicist J. J. Thomson (1856–1940) disproved Dalton’s idea that atoms are indivisible. When elements were excited by an electrical current, atoms break down into two parts.
Q. Which concept in Dalton’s theory has been modified?
Which concept in Dalton’s atomic theory has been modified? Atoms cannot be divided.
Q. What are the 4 parts of Dalton’s atomic theory?
Terms in this set (4)
- All matter is composed of… atoms.
- all atoms of the same elements have…… The same properties.
- Compounds are formed when. atoms of two different elements join together.
- A chemical reaction is. A rearrangement of atoms.
Q. What are Daltons 5 principles?
Terms in this set (5) Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. Number 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. Number 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple.
Q. What are the 5 main ideas of Dalton’s theory?
Dalton’s Atomic Theory All atoms of an element are identical. The atoms of different elements vary in size and mass. Compounds are produced through different whole-number combinations of atoms. A chemical reaction results in the rearrangement of atoms in the reactant and product compounds.
Q. How many atoms are in our body?
Short Answer. There are approximately 7 x 1027 atoms in the average human body. This is the estimate for a 70 kg adult human male. Generally, a smaller person would contain fewer atoms; a larger person would contain more atoms.
Q. What did Rutherford’s model explain?
Rutherford’s model shows that an atom is mostly empty space, with electrons orbiting a fixed, positively charged nucleus in set, predictable paths. This model of an atom was developed by Ernest Rutherford, a New Zealand native working at the University of Manchester in England in the early 1900s.