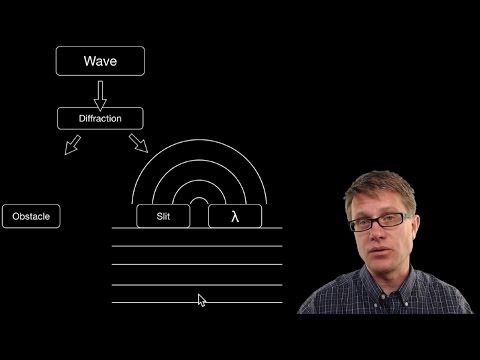
Q. What is the bending of a wave around an object called?
Refraction is the change in direction of waves that occurs when waves travel from one medium to another. Diffraction is the bending of waves around obstacles and openings. The amount of diffraction increases with increasing wavelength.
Q. When a wave bends around a barrier or passes through an opening it is called?
Diffraction. When a wave moves around a barrier or through an opening in a barrier, it bends and spreads out. These wave interactions are called diffraction. Interference. Interference is the interaction between waves that meet.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the bending of a wave around an object called?
- Q. When a wave bends around a barrier or passes through an opening it is called?
- Q. Why can you hear around corners?
- Q. What three properties do all waves have?
- Q. How do you calculate specular reflection?
- Q. What is an example of specular reflection?
- Q. What are the 2 types of reflection?
- Q. What is meant by specular reflection?
- Q. What is regular or specular reflection?
- Q. What does specular mean?
- Q. What does specular mean in blender?
- Q. What is a specular texture?
- Q. What is the definition refraction?
- Q. What does exulted mean?
- Q. What is refraction class 10th?
- Q. What is angle of refraction?
- Q. What does Snell’s law state?
- Q. Why is there no refraction at 0 degrees?
- Q. Is there an angle at which there is no refracted light?
- Q. Does refraction occur at 90 degrees?
Q. Why can you hear around corners?
Sound waves that we can hear have much longer wavelengths than do light waves. As a result, the diffraction of sound waves around a corner is noticeable and we can hear the sound in the “shadow region,” but the diffraction of light waves around a corner is not noticeable.
Q. What three properties do all waves have?
All kinds of waves have the same fundamental properties of reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference, and all waves have a wavelength, frequency, speed and amplitude.
Q. How do you calculate specular reflection?
The reflection vector R is calculated with the following formula:
- R = 2 * (N · L) * N L.
- V = Camera Position – Vertex Position.
- Specular Light = (R · V)n
- Final Color = (Diffuse Light + Ambient Light + Specular Light) * Diffuse Color.
- Next: Normalmapping.
Q. What is an example of specular reflection?
Specular reflection is reflection from a mirror-like surface, where parallel rays all bounce off at the same angle. Examples of specular reflections include a bathroom mirror, the reflections on a lake, and glare on a pair of eyeglasses.
Q. What are the 2 types of reflection?
The reflection of light can be roughly categorized into two types of reflection. Specular reflection is defined as light reflected from a smooth surface at a definite angle, whereas diffuse reflection is produced by rough surfaces that tend to reflect light in all directions (as illustrated in Figure 3).
Q. What is meant by specular reflection?
Specular reflection is a type of surface reflectance often described as a mirror-like reflection of light from the surface. In specular reflection, the incident light is reflected into a single outgoing direction. It is further reflected at a similar angle.
Q. What is regular or specular reflection?
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface. Specular reflection may be contrasted with diffuse reflection, in which light is scattered away from the surface in a range of directions.
Q. What does specular mean?
: of, relating to, or having the qualities of a mirror.
Q. What does specular mean in blender?
Specular shaders create the bright highlights that one would see on a glossy surface, mimicking the reflection of light sources. Unlike diffuse shading, specular reflection is viewpoint dependent.
Q. What is a specular texture?
A specular surface is a highly smooth surface. When the surface is very smooth, the reflected highlight is easy to see. As the surface becomes rougher, the reflected highlights gets broader and dimmer. This is a more “diffused” reflection.
Q. What is the definition refraction?
: the bending of a ray when it passes at an angle from one medium into another in which its speed is different (as when light passes from air into water) refraction.
Q. What does exulted mean?
intransitive verb. 1 : to be extremely joyful : rejoice the team exulted in their victory. 2 obsolete : to leap for joy.
Q. What is refraction class 10th?
• Refraction of light is the phenomenon of change in the path of light in going from one medium to another. • In going from a rarer to a denser medium, the ray of light bends towards normal and in going from a denser to a rarer medium, the ray of light bends away from normal.
Q. What is angle of refraction?
: the angle between a refracted ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to the interface at which refraction occurs.
Q. What does Snell’s law state?
Snell’s law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air.
Q. Why is there no refraction at 0 degrees?
So, the angle of inciden is zero and hence the angle of refraction is also zero. In other words,the ray which is incident normally on the interface between the two different media, propagates un deviated from one medium to other and there is no refraction.
Q. Is there an angle at which there is no refracted light?
when there is an angle of refraction! Imagine the angle of incidence getting larger and larger for the case of n1>n2. Eventually the refracted ray will make an angle of 90° with the surface normal. If the angle of incidence is increased beyond that angle, then refraction does not occur!
Q. Does refraction occur at 90 degrees?
At 90 degree the incidence angle (where the light wave moves sideways along the surface of the media interface) it does not change from one medium to another so refraction does not occur.