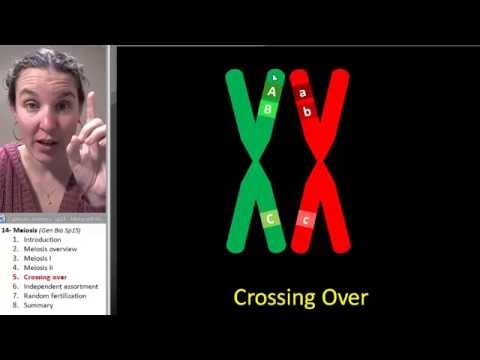
Q. What is the benefit of chromosomes crossing over?
A benefit of crossing over is that it maintains genetic diversity within a population, allowing for millions of different genetic combinations to be passed from parents to offspring. Genetic variability is very important to the long-term survival of a species.
Q. What is the benefit of crossing over and recombination?
The process of recombination helps in promoting genetic variation in the gene pool.
Q. What are the advantages of independent assortment and crossing over?
Independent assortment produces new combinations of alleles. In meiosis I, crossing over during prophase and independent assortment during anaphase creates sets of chromosomes with new combinations of alleles. Genetic variation is also introduced by random fertilization of the gametes produced by meiosis.
Q. Does crossing over cause genetic variation?
Crossing Over Crossing over results in a shuffling of genetic material and is an important cause of the genetic variation seen among offspring.
Q. What is crossing over very short answer?
Crossing over is a process that produces new combinations (recombinations) of genes by interchanging and exchanging of corresponding segments between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
Q. What is crossing over what is its significance?
Crossing over is the process of exchange of genetic material or segments between non-sister chromatids of two homologous chromosomes. Crossing over occurs due to the interchange of sections of homologous chromosomes. Significance : 1.
Q. What happens during crossing over and what is the significance amoeba sisters?
What happens during crossing over and what is the significance? They exchange DNA causing them to be even more diverse. Meiosis does PMAT twice! That means there is a prophase 1 and a prophase 2.
Q. What is Terminalization in crossing over?
: the movement of transverse bonds between paired chromosomes in meiosis from their points of origin toward the ends of the chromosomes.
Q. What is crossing over diagram?
Crossing over is essential for the normal segregation of chromosomes during meiosis. In the diagram, genes B and b are crossed over with each other, making the resulting recombinants after meiosis Ab, AB, ab, and aB.
Q. Which is a true statement of crossing over?
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which results in new allelic combinations in the daughter cells.
Q. What is crossing over class11?
Crossing over is the exchange of chromosomes between the non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Genetic material of the plant and animal cell are arranged in a compact thread-like structure known as chromosome, inside the nucleus. The chromatids of one chromosome are known as sister chromatids.
Q. Is crossing over directly proportional to temperature?
Primarily, frequency of crossing over is dependent upon the distance between the linked genes, but a number of genetic, environmental and physiological factors also affect it. These are: Temperature : High and low temperature increase the frequency of crossing over.
Q. Why are temperature and volume directly proportional?
Combined and ideal gas laws If temperature and pressure are kept constant, then the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the number of molecules of gas. If the temperature and volume remain constant, then the pressure of the gas changes is directly proportional to the number of molecules of gas present.
Q. Are temperature and moles directly proportional?
At constant temperature and pressure the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas. At constant temperature and volume the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas.
Q. Is P and V directly proportional?
Boyle’s law states that pressure (P) and volume (V) are inversely proportional. Charles’ law states that volume (V) and temperature (T) are directly proportional. Gay-Lussac’s law states that pressure (P) and temperature (T) are directly proportional.
Q. What does N stand for in PTVn?
number of moles
Q. What is P in PV nRT?
In the formula P V = N R T {/displaystyle PV=NRT/,} : P is the pressure of the gas. In SI units, this is measured in Pascals, or Newtons of force per square meter of area.
Q. What is r in PV nRT?
PV = nRT. The factor “R” in the ideal gas law equation is known as the “gas constant”. R = PV. nT. The pressure times the volume of a gas divided by the number of moles and temperature of the gas is always equal to a constant number.