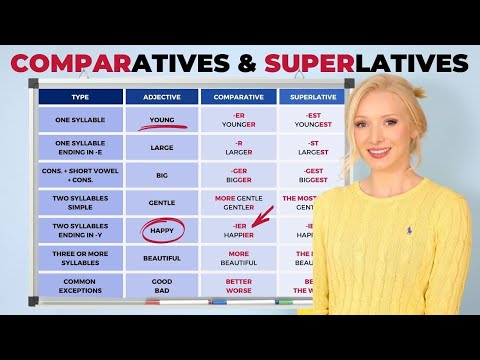
Q. What is the comparative and superlative of high?
Comparative. higher. Superlative. highest. The comparative form of high; more high.
Q. What is the comparative adjective of high?
A comparative adjective is used to show who (or what) has a quality to the greater or lesser degree. (“Higher” is a comparative adjective. “High” is the positive (or normal) degree.)
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the comparative and superlative of high?
- Q. What is the comparative adjective of high?
- Q. What type of word is biggest?
- Q. How do we compare two things?
- Q. What are similar words called?
- Q. How do you use the word juxtapose?
- Q. What is another word for juxtapose?
- Q. What does juxtapose mean in literature?
- Q. What are 5 examples of repetition?
- Q. What does metaphor mean?
- Q. What is the definition of pathetic fallacy?
- Q. What are the major features of pathetic fallacy?
- Q. Why is it called the pathetic fallacy?
- Q. Is time of day pathetic fallacy?
- Q. Is fog pathetic fallacy?
Q. What type of word is biggest?
adjective
Q. How do we compare two things?
Ways of comparing things – thesaurus
- than. conjunction. used when making comparisons.
- relatively. adverb. in comparison with someone or something similar.
- whereas. conjunction.
- compared with/to. phrase.
- relatively speaking. phrase.
- by/in contrast. phrase.
- next to. phrase.
- the… the…
Q. What are similar words called?
Synonyms are words that are similar to another word or have a related meaning.
Q. How do you use the word juxtapose?
Juxtapose sentence example
- By looking at my old diary, I can juxtapose my past with my current life.
- It is interesting to juxtapose the lifestyle of today’s teenage generation with their grandparents’ generation.
- It is easy to juxtapose things that are complete opposites.
Q. What is another word for juxtapose?
Some common synonyms of juxtaposed are adjacent, adjoining, and contiguous. While all these words mean “being in close proximity,” juxtaposed means placed side by side especially so as to permit comparison and contrast.
Q. What does juxtapose mean in literature?
Generally speaking, juxtaposition refers to a stark contrast between two people or things. In literature, juxtaposition is a literary device used to create deliberate differences for the reader to compare and contrast.
Q. What are 5 examples of repetition?
Examples of Repetition: Let it snow, let it snow, let it snow. “Oh, woeful, oh woeful, woeful, woeful day! “And miles to go before I sleep, and miles to go before I sleep.”
Q. What does metaphor mean?
A metaphor is a figure of speech that describes an object or action in a way that isn’t literally true, but helps explain an idea or make a comparison.
Q. What is the definition of pathetic fallacy?
Pathetic fallacy, poetic practice of attributing human emotion or responses to nature, inanimate objects, or animals. …
Q. What are the major features of pathetic fallacy?
Pathetic fallacy is always about giving emotions to something something non-human. Personification is giving any human attribute to an object. For example, ‘The wind whispered through the trees. ‘ or ‘The flowers danced in the breeze.
Q. Why is it called the pathetic fallacy?
The term “pathetic fallacy” was coined by a British writer named John Ruskin, who defined it as “emotional falseness.” Ruskin originally used the term to criticize what he saw as the sentimental attitude of 18th century Romantic poets toward nature.
Q. Is time of day pathetic fallacy?
Pathetic Fallacy is when inanimate parts of nature are given human attributes. For example, this is pathetic fallacy: The sky angrily roared it’s fury. Having a scene set in a time of day is not, in and of itself, pathetic fallacy.
Q. Is fog pathetic fallacy?
I mentioned in the first lesson that the use of fog in A Christmas Carol was similar to a technique called pathetic fallacy. This is when the writer deliberately creates a natural environment that matches the mood or situation of the character. Therefore, Dickens covers the world in fog.