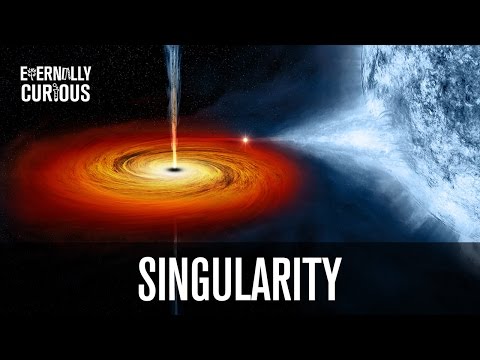
In both cases the singularity was a single point where the curvature of space time are infinite. Therefore, the main difference is that a black hole singularity is the end of space time (and pulls matter in) and the big bang singularity is the beginning of space time (where matter and space were made ‘real’).
Q. Does a singularity have infinite mass?
The singularity is a point where volume goes to zero, not where mass goes to infinity. It is a point with zero volume, but which still holds mass, due to the extreme stretching of space by gravity. The density is infinite, but the mass is still finite.
Table of Contents
Q. What exactly is a singularity?
A singularity means a point where some property is infinite. For example, at the center of a black hole, according to classical theory, the density is infinite (because a finite mass is compressed to a zero volume). Hence it is a singularity.
Q. Can a wormhole be created?
A wormhole is effectively just a tunnel that connects two places in the Universe. So far scientists have simulated this process, but are nowhere near creating a gravitational wormhole, as it would require us to create huge amounts of gravitational energy – something we don’t yet know how to do.
Q. Are black holes and white holes connected?
White holes may simply be the opposite end of black holes, connected by theoretical tunnels of space-time called (of course) wormholes. So the matter and energy falling into a black hole would eventually beam out of a white hole, somewhere in this or another universe.
Q. What if space was white?
You see, if the Universe appeared to be white instead of black, it would mean that it’s infinitely old, infinitely big and static at the same time. That might seem like a long time, but remember, even light has its speed limit. We can only see stars that are less than 14 billion light years away from us.