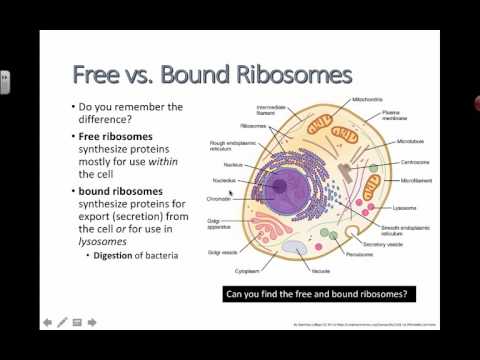
Free ribosomes produce proteins that are used by the cell. This includes proteins that are used for the metabolism of food. The free ribosomes produce enzymes involved in the metabolism of glucose. Bound ribosomes produce proteins that are transported out of the cell.
Q. What is the jelly like stuff inside the cell called?
Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. It is composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules. Some intracellular organelles, such the nucleus and mitochondria, are enclosed by membranes that separate them from the cytoplasm.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the jelly like stuff inside the cell called?
- Q. How proteins are made in a cell?
- Q. Where are free ribosomes made?
- Q. What are the two subunits of a ribosome called?
- Q. What do ribosomes do simple answer?
- Q. How do you explain ribosomes to kids?
- Q. What happens if ribosomes do not function?
- Q. Why are ribosomes like students?
- Q. What part of a school is like a Golgi apparatus?
- Q. What would a ribosome be in a school?
- Q. What part of a school is like rough ER?
- Q. What can a mitochondria be compared to in a school?
Q. How proteins are made in a cell?
Protein from your diet is broken down into individual amino acids which are reassembled by your ribosomes into proteins that your cells need. The information to produce a protein is encoded in the cell’s DNA. When a protein is produced, a copy of the DNA is made (called mRNA) and this copy is transported to a ribosome.
Q. Where are free ribosomes made?
cytosol
Q. What are the two subunits of a ribosome called?
Each ribosome is a complex of proteins and special RNA called ribosomal RNA (rRNA). In both prokayotes and eukaryotes active ribosomes are composed of two subunits called the large and small subunit.
Q. What do ribosomes do simple answer?
Protein Synthesis The main job of the ribosome is to make proteins for the cell. There can be hundreds of proteins that need to be made for the cell, so the ribosome needs specific instructions on how to make each protein. These instructions come from the nucleus in the form of messenger RNA.
Q. How do you explain ribosomes to kids?
A ribosomes is a small organelle involved in the process of making protein, which is called protein synthesis. The ribosome handles translation, which is the second part of protein synthesis. Ribosomes can be found floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Q. What happens if ribosomes do not function?
Without ribosomes to produce proteins, cells simply wouldn’t be able to function properly. They would not be able to repair cellular damage, create hormones, maintain cellular structure, proceed with cell division or pass on genetic information via reproduction.
Q. Why are ribosomes like students?
Ribosomes are like students. Ribosomes are like students because they take instruction from the principal (nucleus). A nuclear membrane is like a hall monitor. The nucleolus is like a classroom because the nucleolus forms ribosomes, like a classroom forms students.
Q. What part of a school is like a Golgi apparatus?
The endoplasmic reticulum is like hallways in a school because they are passage ways for students and staff like the endoplasmic reticulum makes passages for proteins. The Golgi apparatus is like a school bus because a school bus transports kids to school like the Golgi apparatus ships proteins.
Q. What would a ribosome be in a school?
Ribosomes are like teachers in school. Ribosome helps to produce important proteins for a cell and teachers produce educated people. Mitochondrion is like a staff in the school. They act as a powerhouse organelles off the cell getting things done, and the staff do the same, making school run and function.
Q. What part of a school is like rough ER?
school hallways
Q. What can a mitochondria be compared to in a school?
The mitochondria is like a gymnasium. The mitochondria is like a gym because of all of the energy inside. The nucleus is like the principal because it is in charge of everything that goes on within the cell. Mitochondrion is like a staff in the school.