The main difference between homeobox homeotic and hox genes is that homeobox is a specific DNA sequence found within homeotic genes while homeotic genes are the genes responsible for the regulation of the patterns of anatomical development in animals, plants, fungi, and some unicellular eukaryotes, and Hox genes are a …
Q. What are Hox genes and why are they so important?
The Hox genes are a set of transcription factor genes that exhibit an unusual property: They provide a glimpse of one way in which gene expression is translated into the many different forms that animals (metazoans) exhibit.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are Hox genes and why are they so important?
- Q. What is the role of homeotic genes?
- Q. Do plants have Hox genes?
- Q. Are Hox genes only in vertebrates?
- Q. What is Pseudogenization?
- Q. What does Hox stand for?
- Q. What are Homeodomains?
- Q. What is a homeobox and what is its significance?
- Q. What does the presence of homeobox genes in fruit flies and mice indicate about their evolution?
- Q. What can small changes in Hox genes tell us?
- Q. What type of factors can influence gene expression?
- Q. How does genetic regulation influence a developing embryo?
- Q. What is differential gene expression?
- Q. How does development of the pancreas illustrate differential gene expression?
- Q. What role do histones serve in the expression of genes?
- Q. Which of the following defines histones?
- Q. What turns genes on and off?
Q. What is the role of homeotic genes?
Homeotic gene, any of a group of genes that control the pattern of body formation during early embryonic development of organisms. These genes encode proteins called transcription factors that direct cells to form various parts of the body.
Q. Do plants have Hox genes?
Homeobox genes are found in plants, fungi, and animals, and even in slime molds (Dictyostelium). Although now several prokaryotic genomes have been sequenced, no true homeobox gene has been found in these organisms.
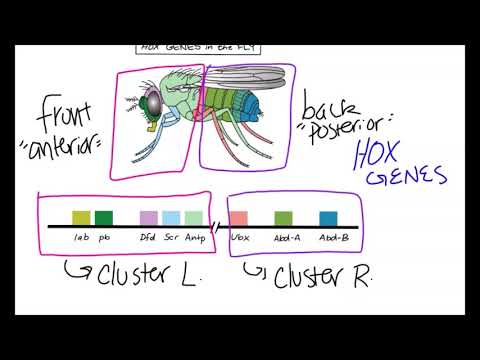
Q. Are Hox genes only in vertebrates?
The protein product of each Hox gene is a transcription factor. Each Hox gene contains a well-conserved DNA sequence known as the homeobox, of which the term “Hox” was originally a contraction….Vertebrates.
| Cluster | Human Chromosome | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| [email protected] | chromosome 2 | HOXD1, HOXD3, HOXD4, HOXD8, HOXD9, HOXD10, HOXD11, HOXD12, HOXD13 |
Q. What is Pseudogenization?
Pseudogenization is an evolutionary phenomenon where- by a gene loses its function by disruption to its regulatory or. coding sequence. Such loss of function is generally thought. to be detrimental to an organism and selectively disadvan-
Q. What does Hox stand for?
1 : hamstring. 2 : to pester by following : harass, annoy.
Q. What are Homeodomains?
The DNA sequence that encodes the homeodomain is called the “homeobox” and homeobox-containing genes are known as “hox genes.” The homeodomain is very highly conserved and consists of three helical regions folded into a tight globular structure that binds a 5′-TAAT-3′ core motif. …
Q. What is a homeobox and what is its significance?
What is a homeobox, and what is its significance? A homeobox is a DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, found within genes that are involved in the regulation of patterns of anatomical development (morphogenesis) in animals, fungi and plants.
Q. What does the presence of homeobox genes in fruit flies and mice indicate about their evolution?
The presence of homeobox genes in fruit flies and mice indicates a common evolutionary ancestor.
Q. What can small changes in Hox genes tell us?
For example, Hox genes help lay out the basic body forms of many animals, including humans, flies, and worms. They set up the head-to-tail organization. Small changes in such powerful regulatory genes, or changes in the genes turned on by them, could represent a major source of evolutionary change.
Q. What type of factors can influence gene expression?
Environmental factors such as diet, temperature, oxygen levels, humidity, light cycles, and the presence of mutagens can all impact which of an animal’s genes are expressed, which ultimately affects the animal’s phenotype.
Q. How does genetic regulation influence a developing embryo?
This process of gene expression is regulated by cues from both within and outside cells, and the interplay between these cues and the genome affects essentially all processes that occur during embryonic development and adult life. …
Q. What is differential gene expression?
Differential gene expression, commonly abbreviated as DG or DGE analysis refers to the analysis and interpretation of differences in abundance of gene transcripts within a transcriptome (Conesa et al., 2016).
Q. How does development of the pancreas illustrate differential gene expression?
How does development in the pancreas illustrate differential gene expression? Progenitor cells in the pancreas divide to give rise to daughter cells that differentiate as either exocrine or endocrine cells.
Q. What role do histones serve in the expression of genes?
A histone is a protein that provides structural support to a chromosome. In order for very long DNA molecules to fit into the cell nucleus, they wrap around complexes of histone proteins, giving the chromosome a more compact shape. Some variants of histones are associated with the regulation of gene expression.
Q. Which of the following defines histones?
A type of protein found in chromosomes. Histones bind to DNA, help give chromosomes their shape, and help control the activity of genes.
Q. What turns genes on and off?
Each cell expresses, or turns on, only a fraction of its genes at any given time. The rest of the genes are repressed, or turned off. The process of turning genes on and off is known as gene regulation. Signals from the environment or from other cells activate proteins called transcription factors.