Q. What is the difference between lipoprotein and apoprotein?
The main difference between lipoprotein and apolipoprotein is that lipoprotein is an assembly of molecules whose function is to transport hydrophobic lipids in watery media including water and extracellular fluid whereas apolipoprotein is a protein bound to lipids in order to form lipoproteins.
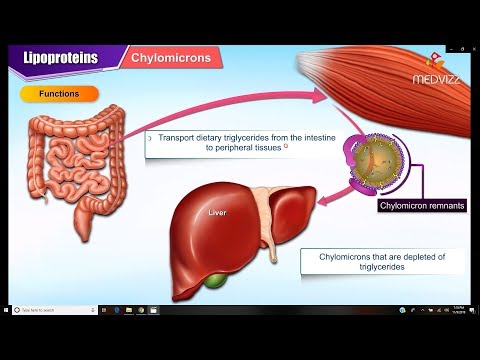
Q. What is the difference between chylomicron and lipoprotein?
Chylomicrons are large triglyceride-rich lipoproteins produced in enterocytes from dietary lipids—namely, fatty acids, and cholesterol. Chylomicrons are composed of a main central lipid core that consists primarily of triglycerides, however like other lipoproteins, they carry esterified cholesterol and phospholipids.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the difference between lipoprotein and apoprotein?
- Q. What is the difference between chylomicron and lipoprotein?
- Q. What is a lipoprotein analysis?
- Q. Is lipoprotein and phospholipid same?
- Q. What is the clinical significance of lipoproteins and apolipoproteins?
- Q. What is the major apoprotein comprising LDL?
- Q. What is the difference between chylomicrons and VLDL?
- Q. What is LDL C and LDL P?
- Q. What’s the difference between an apolipoprotein and a lipoprotein?
- Q. Where does the synthesis of apolipoproteins take place?
- Q. Which is better HDL or low density lipoprotein?
- Q. Which is the most abundant apolipoprotein in the liver?
Q. What is a lipoprotein analysis?
Lipoprotein (a) testing measures the amount of a specific particle, known as lipoprotein (a), in the blood. An elevated level of lipoprotein (a) is linked to a higher risk of health problems like heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
Q. Is lipoprotein and phospholipid same?
Lipoproteins are special particles made up of droplets of fats surrounded by a single layer of phospholipid molecules. Phospholipids are molecules of fats which are attached to a phosphorus-containing group. They are distinctive in being amphipathic, which means they have both polar and non-polar ends.
Q. What is the clinical significance of lipoproteins and apolipoproteins?
Apolipoproteins (apo) play very important roles in the synthesis and catabolism of plasma lipoproteins, in lipid transport, and as activators of certain enzymes associated with lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. They are also involved in various metabolic states or diseases.
Q. What is the major apoprotein comprising LDL?
ApoB
ApoB is the major apoprotein of LDL, but also comprises about 35% of the protein of VLDL.
Q. What is the difference between chylomicrons and VLDL?
Chylomicrons are synthesized in the small intestine, and transport exogenous dietary products while VLDL synthesizes in the liver and transport endogenous dietary products. This is the key difference between chylomicrons and VLDL.
Q. What is LDL C and LDL P?
LDL-C is a measurement of the cholesterol mass within LDL-particles. Thus, LDL-C is a surrogate measure that only provides an estimate of LDL levels. Studies indicate that the risk for atherosclerosis is more related to the number of LDL particles (LDL-P) than the total amount of cholesterol within these particles.
Q. What’s the difference between an apolipoprotein and a lipoprotein?
Lipoproteins are complex, water-soluble macromolecules which are composed of a hydrophobic lipid component and one or more specific hydrophilic proteins. Apolipoproteins are protein molecules which form complexes with lipids to form the lipoprotein.
Q. Where does the synthesis of apolipoproteins take place?
Therefore, the main function of an apolipoprotein is to serve as a structural component of a lipoprotein, transporting lipids through the blood and lymph. Significantly, the synthesis of apolipoproteins occurs in the intestine and in the liver.
Q. Which is better HDL or low density lipoprotein?
More importantly, a higher level of HDL in the blood lowers the risk of atherosclerosis; hence, HDL is known as ‘good lipoprotein’. LDL (low density lipoprotein) – contains 25% protein, 46-50% cholesterol, 21-22% phospholipid, 8-10% triglycerides and cholesterol esters. It carries fat molecules throughout the body.
Q. Which is the most abundant apolipoprotein in the liver?
ApoA – IV is the prominent apolipoprotein in chylomicrons and thus, synthesized primarily in the intestines and the liver. It is abundantly found in the plasma. Its functions are similar to apoA I and II and facilitates transportation of lipids (triglycerides) Apo B is of two main types; apoB – 100 and apoB – 48.