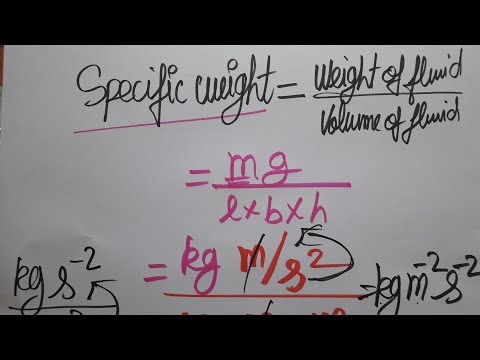The dimensional formula of the volume is [L3] and that of mass is [M]. Similarly the dimensional formula of the density of water is also ML−3 . Thus, the formula of specific gravity is = density of substance/ density of water 4∘C . So, the dimensional formula of specific gravity will be= ML−3ML−3=M0L0 .
Q. What is the SI unit and dimensional formula of angular momentum?
What is Angular Momentum?
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the SI unit and dimensional formula of angular momentum?
- Q. What is the dimensional formula of frequency of vibration?
- Q. Is specific gravity is dimensional variable?
- Q. Is strain a dimensional variable?
- Q. Is density is a dimensional variable?
- Q. Which is a dimensional variable?
- Q. What are the examples of dimensional variables?
- Q. What are the dimensions of variables?
- Q. What is the difference between dimensional values and dimensional variables?
- Q. What are dimensional variables give two examples?
- Q. What are dimensional constants give one example?
- Q. What are dimensional constants with examples?
- Q. What are dimensional constants explain?
- Q. What is called dimensional constant?
- Q. What is the definition of dimensional constant?
- Q. What are the applications of dimensional analysis?
- Q. What is dimensional constant and non dimensional?
| Symbol | The angular momentum is a vector quantity, denoted by /vec{L} |
|---|---|
| Units | It is measured using SI base units: Kg.m2.s-1 |
| Dimensional formula | The dimensional formula is: [M][L]2[T]-1 |
Q. What is the dimensional formula of frequency of vibration?
Therefore, frequency is dimensionally represented as [M0 L0 T1].
Q. Is specific gravity is dimensional variable?
Because it is the ratio of two quantities that have the same dimensions (mass per unit volume), specific gravity has no dimension. Specific gravity (G) is defined as the ratio between the weight of a substance and the…
Q. Is strain a dimensional variable?
Strain has no dimension because it is a ratio of similar physical quantities change in length and original length.
Q. Is density is a dimensional variable?
Therefore ,density is a dimension variable quantity.
Q. Which is a dimensional variable?
Dimensional variables are those physical quantities which have dimensions of the form [M^a L^b T^c]… {where,M,L,T are fundamental physical quantities which are Mass,Length and Time respectively. And a,b,c are any real numbers} … but are variables.
Q. What are the examples of dimensional variables?
Physical quantities which posses dimensions and have variable are called dimensional variables. Examples are length, velocity, and acceleration etc.
Q. What are the dimensions of variables?
Dimensions are named integers that are used to specify the size (or dimensionality ) of one or more variables. Each dimension must have a unique name, but a variable and dimension can share a name.
Q. What is the difference between dimensional values and dimensional variables?
Dimensional variables are those quantities which have dimensions and whose numerical value may change. Dimensional constants are quantities having dimensions but having a constant value, e.g., gravitation constant (G), Planck’s constant (H), Stefan’s constant etc.
Q. What are dimensional variables give two examples?
Physical quantities which posses dimensions and have variable are called dimensional variables. Examples are length, velocity, and acceleration etc. Plank’s constant (h), speed of light in vacuum (c) and Newton’s gravitational constant (G) are taken as three fundamental constants.
Q. What are dimensional constants give one example?
Those constant which have dimension but constant value called dimensional constants, example of these constant like gravitational constant, electric field constant etc there are many dimension constants .
Q. What are dimensional constants with examples?
Those constant which have dimension but constant value called dimensional constants , example of these constant like gravitational constant, electric field constant , efsonal(€) ,etc there are many dimension constants .
Q. What are dimensional constants explain?
Dimensional Constants We understood the concept of finding the dimensional formula of a physical quantity. So, dimensional constants are those quantities whose values are constant, and they possess dimensions. For example, Gravitational constant, Boltzmann constant, Planck’s constant, etc.
Q. What is called dimensional constant?
D. Gravitational constant. Answer Verified. Hint: The physical quantities which have dimensions and have a fixed value are called dimensional constant.
Q. What is the definition of dimensional constant?
[də′men·chən·əl ′kän·stənt] (physics) A physical quantity whose numerical value depends on the units chosen for fundamental quantities but not on the system being considered.
Q. What are the applications of dimensional analysis?
(1) To convert the physical quantity from one system to another. (2) To check the correctness of a physical relation. (3) To obtain relationship among various physical quantities involved. (4) To find dimensions of constant in a physical relation.
Q. What is dimensional constant and non dimensional?
Answer. Speed, velocity, acceleration etc., aredimensional variables. Dimensional constants are quantities havingdimensions but having a constantvalue, e.g., gravitation constant (G), Planck’s constant (H), Stefan’sconstant etc.