Q. What is the electronic structure of potassium?
[Ar] 4s¹
Q. How many protons and electrons are in K+?
19 protons
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the electronic structure of potassium?
- Q. How many protons and electrons are in K+?
- Q. How do you draw a Bohr Rutherford diagram?
- Q. How many shells does K+ have?
- Q. Why is potassium K +?
- Q. Where is potassium used?
- Q. What’s the neutrons for potassium?
- Q. What is the standard notation for potassium?
- Q. What is the ground state of potassium?
- Q. What are the common compounds of potassium?
- Q. Is Potassium a mixture?
- Q. Is potassium negative or positive?
- Q. What is the difference between a potassium atom and a potassium ion?
- Q. What is potassium ion charge?
- Q. Does potassium react with water?
- Q. Is S or S2 bigger?
- Q. Is O 1 or O 2 bigger?
- Q. What is the name for S2?
- Q. How many shells does K have?
- Q. How many electrons are in the outer shell of K+?
- Q. Which elements does potassium bond with?
- Q. Can an atom have 0 valence electrons?
- Q. Why does K have no valence electrons?
- Q. How many valence electrons are in an atom of oxygen?
- Q. Why do valence electrons have the most energy?
- Q. Which Shell has more energy K or L?
- Q. What is the lowest energy level?
- Q. What is highest energy level?
- Q. Which Subshell is lowest in energy?
- Q. Which Shell has highest energy?
- Q. What is the L shell?
- Q. What is K shell and L shell?
- Q. When an electron jumps from L to K shell?
- Q. When an electron revolves in a stationary orbit then?
- Q. When the energy of electron is maximum?
- Q. When an electron drops to a lower energy level?
- Q. What happens when an electron moves to a lower energy level?
- Q. Why is ground state energy negative?
- Q. What happens when an electron returns to ground state?
- Q. Why do excited electrons return to ground state?
- Q. What does the exclusion principle say?
- Q. What is Pauli exclusion principle and its application?
- Q. Why is Pauli exclusion principle important?
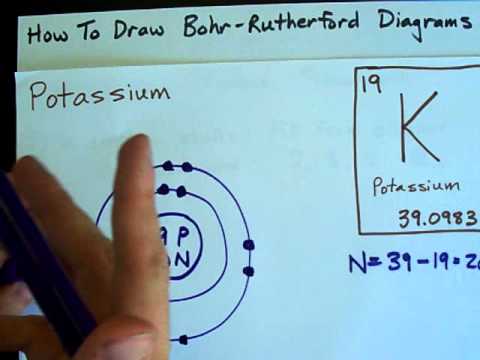
Q. How do you draw a Bohr Rutherford diagram?
Drawing Bohr-Rutherford diagrams is super easy using the following steps:
- Find the number of protons, neutrons and electrons for the atom. The number of protons is the atomic number.
- Set up the diagram. To set up the diagram, you will need a circle in the middle.
- Add in orbitals and electrons.
Q. How many shells does K+ have?
List of elements with electrons per shell
| Z | Element | No. of electrons/shell |
|---|---|---|
| 17 | Chlorine | 2, 8, 7 |
| 18 | Argon | 2, 8, 8 |
| 19 | Potassium | 2, 8, 8, 1 |
| 20 | Calcium | 2, 8, 8, 2 |
Q. Why is potassium K +?
The name derives from the English “potash” or “pot ashes” because it is found in caustic potash (KOH). The symbol K derives from the Latin kalium via the Arabic qali for alkali.
Q. Where is potassium used?
Industrial applications for potassium include soaps, detergents, gold mining, dyes, glass production, gunpowder, and batteries. Potassium also plays a vital role in our bodies. It is used in muscle contraction, fluid and pH balance, bone health, and helps to prevent kidney stones.
Q. What’s the neutrons for potassium?
The element of potassium has the symbol K. The nucleus of an atom of potassium contains 19 protons and 20 neutrons.
Q. What is the standard notation for potassium?
Potassium is a chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin kalium) and atomic number 19.
Q. What is the ground state of potassium?
Potassium atoms have 19 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8. 8.1. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral potassium is [Ar].
Q. What are the common compounds of potassium?
Potassium forms many important compounds. Potassium chloride (KCl) is the most common potassium compound. It is used in fertilizers, as a salt substitute and to produce other chemicals. Potassium hydroxide (KOH) is used to make soaps, detergents and drain cleaners.
Q. Is Potassium a mixture?
Explanation: Potassium metal (K), chlorine gas (Cl), and potassium chloride (KCl) are all homogeneous compounds. Potassium and chlorine is a mixture because the parts are all heterogeneous or separate.
Q. Is potassium negative or positive?
The important ions in the nervous system are sodium and potassium (both have 1 positive charge, +), calcium (has 2 positive charges, ++) and chloride (has a negative charge, -).
Q. What is the difference between a potassium atom and a potassium ion?
Explanation: A potassium atom, K is in its normal elemental state with 1 valence electron in it’s most outer shell. However the potassium ion has lost it’s valence electron and has therefore formed a positive action, K+ . It instead has 19 protons and 18 electrons, yielding a net positive charge.
Q. What is potassium ion charge?
Potassium ions have a charge of 1+, while sulfate ions have a charge of 2−.
Q. Does potassium react with water?
Potassium reacts violently with water to produce half a mole of hydrogen per mole of potassium and water and generates approximately 47 kilocalories per mole of heat. Potassium can be stored in nitrogen gas with no reaction. It reacts with hydrogen at approximately 350 °C (660 °F) to form the hydride.
Q. Is S or S2 bigger?
(ii) Explain why the radius of the S2- ion is larger than the radius of the S atom. The nuclear charge is the same for both species, but the eight valence electrons in the sulfide ion experience a greater amount of electron-electron repulsion than do the six valence electrons in the neutral sulfur atom.
Q. Is O 1 or O 2 bigger?
O+1 ion contains 7 electrons and 8 protons ,O contains 8 electrons and 8 protons ,O-1 ion contains 9 electrons and 8 protons and O-2 ion contains 10 electrons and 8 protons. So O-2 is biggest in size.
Q. What is the name for S2?
Disulfur
| PubChem CID | 5460602 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | disulfur sulfur dimer disulphur 23550-45-0 S2 More… |
| Molecular Weight | 64.14 |
| Dates | Modify 2021-06-26 Create 2004-09-16 |
| Description | Disulfur is a diatomic sulfur. ChEBI |
Q. How many shells does K have?
Each shell consists of one or more subshells, and each subshell consists of one or more atomic orbitals….List of elements with electrons per shell.
| Z | 19 |
|---|---|
| Element | Potassium |
| No. of electrons/shell | 2, 8, 8, 1 |
| Group | 1 |
Q. How many electrons are in the outer shell of K+?
eight
Q. Which elements does potassium bond with?
Potassium metal reacts vigorously with all the halogens to form potassium halides. So, it reacts with fluorine, F2, chlorine, Cl2, bromine, I2, and iodine, I2, to form respectively potassium(I) bromide, KF, potassium(I) chloride, KCl, potassium(I) bromide, KBr, and potassium(I) iodide, KI.
Q. Can an atom have 0 valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the outer electrons that are involved in bonding. Only electrons in the s and p orbitals are valance electrons, so a given atom can have between 0 and 7 valance electrons. Atoms with 0 valence electrons are called noble gases and don t like form bonds.
Q. Why does K have no valence electrons?
Elemental potassium has an [Ar] 4s1 electron configuration. One would say it has one valence electron. If we take that one valence electron away, it makes sense to say that it now has zero valence electrons because “1 – 1 = 0”.
Q. How many valence electrons are in an atom of oxygen?
six valence electrons
Q. Why do valence electrons have the most energy?
So a large amount of energy is required to liberate an electron from an inner most shell rather than an electron from the outermost shell. This is why we say that the electron in the outermost shell has a higher (potential) energy than the inner most shells.
Q. Which Shell has more energy K or L?
L shell has higher energy because according to Bohr’s theory the shell which is closer to nucleus has lower energy and the shell which is away from the nucleus has higher energy. K is closer to nucleus. So it has lower energy than L-shell.
Q. What is the lowest energy level?
At the lowest energy level, the one closest to the atomic center, there is a single 1s orbital that can hold 2 electrons. At the next energy level, there are four orbitals; a 2s, 2p1, 2p2, and a 2p3. Each of these orbitals can hold 2 electrons, so a total of 8 electrons can be found at this level of energy.
Q. What is highest energy level?
valence electrons
Q. Which Subshell is lowest in energy?
In a more realistic model, electrons move in atomic orbitals, or subshells. There are four different orbital shapes: s, p, d, and f. Within each shell, the s subshell is at a lower energy than the p.
Q. Which Shell has highest energy?
Electrons with the highest energy levels exist in the outermost shell of an atom and are relatively loosely bound to the atom. This outermost shell is known as the valance shell and electrons in this shell are called valance electrons.
Q. What is the L shell?
: the second innermost shell of electrons surrounding an atomic nucleus — compare k-shell , m-shell.
Q. What is K shell and L shell?
: the innermost shell of electrons surrounding an atomic nucleus and constituting the lowest available energy level for the electrons — compare l-shell , m-shell.
Q. When an electron jumps from L to K shell?
When an electron jumps from L to K shell i.e. from lower to higher shell energy is released because L is outer shell than K so when electron jumps from higher shell to lower shell energy is released. Thus option B is the correct answer.
Q. When an electron revolves in a stationary orbit then?
☆ when an electron revolves in a stationary orbit then its energy remain constant .
Q. When the energy of electron is maximum?
The electron has minimum energy in the first orbit and its energy increases as n increases i.e. it becomes less negative. The electron can have a maximum energy value of zero when n=∞.
Q. When an electron drops to a lower energy level?
When the electron changes levels, it decreases energy and the atom emits photons. The photon is emitted with the electron moving from a higher energy level to a lower energy level. The energy of the photon is the exact energy that is lost by the electron moving to its lower energy level.
Q. What happens when an electron moves to a lower energy level?
When an electron moves from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, energy is absorbed by the atom. When an electron moves from a higher to a lower energy level, energy is released (often as light).
Q. Why is ground state energy negative?
Explanation: The energy of an electron is zero when the electron has completely left the atom, i.e., when its principal quantum number n = ∞. Thus, all energy states of an electron, including the ground state, have negative energies.
Q. What happens when an electron returns to ground state?
An electron in an excited state can release energy and ‘fall’ to a lower state. When it does, the electron releases a photon of electromagnetic energy. When the electron returns to the ground state, it can no longer release energy but can absorb quanta of energy and move up to excitation states (higher orbitals).
Q. Why do excited electrons return to ground state?
Excited electrons return to ground state to regain its stability in terms of energy and momentum. When electron is exited from its stable situation, by absorbing energy given from outside, first its momentum do increase ( according to nh /2π ) . But electron no longer hold this excess momentum & energy.
Q. What does the exclusion principle say?
the principle that in any system described by quantum mechanics no two identical particles having spin equal to half an odd integer can be in the same quantum state: first postulated for the electrons in atoms.
Q. What is Pauli exclusion principle and its application?
The Pauli exclusion states that no two electrons can have an identical set of quantum numbers. The Pauli principle applies to identical particles with half-integral spin i.e., S = 1/2, 3/2, 5/2 In other words, each electron should have its own singlet state or unique state.
Q. Why is Pauli exclusion principle important?
Why Is the Pauli Exclusion Principle Important? The Pauli exclusion principle informs electron configuration and the way atoms are classified in the periodic table of elements. Ground state, or lowest energy levels in an atom can fill up, forcing any additional electrons to higher energy levels.