AVR Full-Form | What is Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR)
Q. Where is AVR located in a generator?
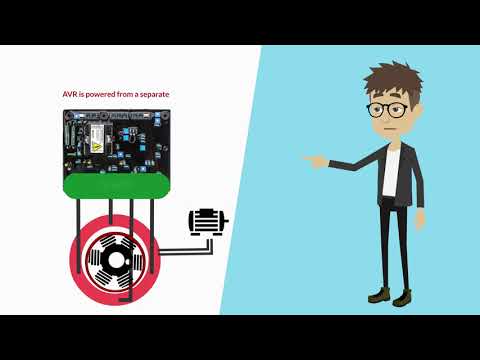
Where is an AVR located in a generator? Normally the generator AVR is located in one of three places. It can be in the main control box of the generator, it can be in the alternators terminal box and it could be (only on very small portable units usually) located under the alternators rear cover.
Table of Contents
- Q. Where is AVR located in a generator?
- Q. What is the price of AVR?
- Q. What does a AVR do?
- Q. What are the types of AVR?
- Q. How do generators regulate voltage?
- Q. What is droop mode?
- Q. Why is droop needed?
- Q. What is power factor mode in AVR?
- Q. How do you adjust the power factor of a generator?
- Q. How does power factor affect voltage regulation?
- Q. How does AVR control reactive power?
- Q. What are the methods of controlling reactive power?
Q. What is the price of AVR?
Questions & Answers on AVR Unit
| Phase | Min Price | Max Price |
|---|---|---|
| Single Phase | Rs 2000/Piece | Rs 14000/Piece |
| Three Phase | Rs 3000/Piece | Rs 956000/Piece |
Q. What does a AVR do?
An automatic voltage regulator (AVR) is an electronic device that maintains a constant voltage level to electrical equipment on the same load. The AVR regulates voltage variations to deliver constant, reliable power supply.
Q. What are the types of AVR?
In general, there are two types of an Automatic Voltage Regulator. One is the Relay Type and the other is the Servo Motor type. A Relay type AVR makes use of electronic circuitry like relays and semi-conductors to regulate the voltage.
Q. How do generators regulate voltage?
As the speed of the engine the generator increases, the voltage produced also increases. The excitation system monitors the generator output and regulates the magnetic field to maintain the desired voltage. As the load on the generator is increased, an increase in current flow causes the voltage to drop.
Q. What is droop mode?
Droop speed control is a control mode used for AC electrical power generators, whereby the power output of a generator reduces as the line frequency increases. It is commonly used as the speed control mode of the governor of a prime mover driving a synchronous generator connected to an electrical grid.
Q. Why is droop needed?
Speed droop is a governor function which reduces the governor reference speed as fuel position (load) increases. All engine controls use the principle of droop to provide stable operation. Without some form of droop, engine-speed regulation would always be unstable. A load increase would cause the engine to slow down.
Q. What is power factor mode in AVR?
It is reported and known that power plants machines in VAr/PF control mode caused/contributed to system voltage collapse. The purpose of the AVR is to support system voltage. If you are in VAR/PF control you will do nothing to prevent a voltage collapse.
Q. How do you adjust the power factor of a generator?
You can improve power factor by adding power factor correction capacitors to your plant distribution system. When apparent power (kVA) is greater than working power (kW), the utility must supply the excess reactive current plus the working current . Power capacitors act as reactive current generators .
Q. How does power factor affect voltage regulation?
The voltage regulation of the transformer is the percentage change in the output voltage from no-load to full-load. And since power factor is a determining factor in the secondary voltage, power factor influences voltage regulation. This means the voltage regulation of a transformer is a dynamic, load-dependent number.
Q. How does AVR control reactive power?
The primary means of generator reactive power control is the generator excitation control using Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR). The purpose of AVR is to hold the terminal voltage magnitude of a synchronous generator at specified level.
Q. What are the methods of controlling reactive power?
The steady state voltage and reactive power control in distribution systems can be properly controlled by coordinating the available voltage and reactive power control equipment, such as on-load tap-changers, substation shunt capacitors and feeder shunt capacitors.