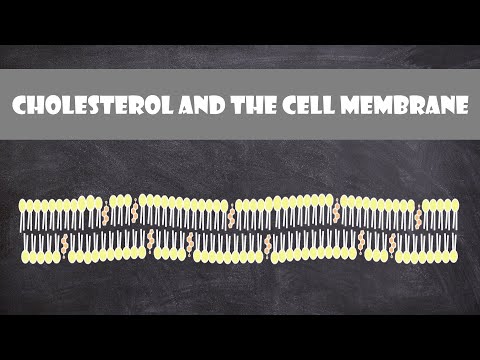
Q. What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane quizlet?
Cholesterol helps regulate the fluidity of a cell membrane by limiting lateral movement of the phospholipids.
Q. What is the function of the cholesterol molecules in a cell membrane A They make it thicker B they make it porous c they make it more fluid D they make it less flexible?
Cholesterol molecules are important in maintaining the consistency of the cell membrane. They are made up of four rings of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are hydrophobic and are found among the hydrophobic tails in the lipid bilayer. They keep phospholipid tails from coming into contact and solidifying.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane quizlet?
- Q. What is the function of the cholesterol molecules in a cell membrane A They make it thicker B they make it porous c they make it more fluid D they make it less flexible?
- Q. How do molecules of cholesterol affect the structure of cell membrane?
- Q. Where is cholesterol found in the cell membrane?
- Q. What is the role of each molecule in the cell membrane?
- Q. What are Leptomeninges?
- Q. What is the purpose of Leptomeninx?
- Q. What is the role of meninges?
- Q. Why is it called Leptomening?
- Q. What does Pleocytosis mean?
- Q. What is the sac around the brain called?
- Q. What is the membrane around the brain called?
- Q. What 4 Things protect the brain?
Q. How do molecules of cholesterol affect the structure of cell membrane?
Depending on the temperature, cholesterol has distinct effects on membrane fluidity. At high temperatures, cholesterol interferes with the movement of the phospholipid fatty acid chains, making the outer part of the membrane less fluid and reducing its permeability to small molecules.
Q. Where is cholesterol found in the cell membrane?
Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer. Cholesterol, another lipid composed of four fused carbon rings, is found alongside phospholipids in the core of the membrane.
Q. What is the role of each molecule in the cell membrane?
Phospholipids form the basic structure of a cell membrane, called the lipid bilayer. Scattered in the lipid bilayer are cholesterol molecules, which help to keep the membrane fluid consistent. Membrane proteins are important for transporting substances across the cell membrane.
Q. What are Leptomeninges?
Leptomeninges: The two innermost layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord. The two layers are called the arachnoid mater and pia mater.
Q. What is the purpose of Leptomeninx?
Meningeal Anatomy Leptomeninx is the term used when the pia mater and arachnoid are considered together as a functional unit and contraposed to pachymeninx (from the Greek packys, meaning thick), designates the finer meningeal coverings.
Q. What is the role of meninges?
Meninges, singular meninx, three membranous envelopes—pia mater, arachnoid, and dura mater—that surround the brain and spinal cord. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.
Q. Why is it called Leptomening?
Leptomeninges. The arachnoid and pia mater together are sometimes called the leptomeninges, literally “thin meninges” (Greek: λεπτός “leptos”—”thin”). Because the arachnoid is connected to the pia by cob-web like strands, it is structurally continuous with the pia, hence the name pia-arachnoid or leptomeninges.
Q. What does Pleocytosis mean?
Medical Definition of pleocytosis : an abnormal increase in the number of cells (as lymphocytes) in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Q. What is the sac around the brain called?
Dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. The dura surrounds the brain and the spinal cord.
Q. What is the membrane around the brain called?
Three layers of membranes known as meninges protect the brain and spinal cord. The delicate inner layer is the pia mater. The middle layer is the arachnoid, a web-like structure filled with fluid that cushions the brain.
Q. What 4 Things protect the brain?
The brain is protected by the skull (cranium), cerebrospinal fluid and 3 protective membranes (Meninges). The spinal cord is protected similarly but with vertebrae instead of the cranium.