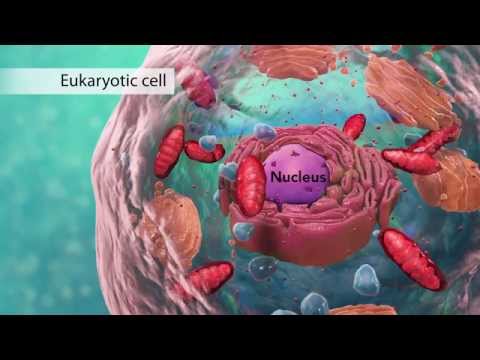
Q. What is the function of nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus controls and regulates the activities of the cell (e.g., growth and metabolism) and carries the genes, structures that contain the hereditary information. Nucleoli are small bodies often seen within the nucleus.
Q. Is the nucleus always in the center of a cell?
The nucleus is not always in the center of the cell. It will be a big dark spot somewhere in the middle of all of the cytoplasm (cytosol). You probably won’t find it near the edge of a cell because that might be a dangerous place for the nucleus to be.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the function of nucleus in a cell?
- Q. Is the nucleus always in the center of a cell?
- Q. What is a nucleus simple definition?
- Q. Why is the nucleus so important?
- Q. What does the nucleus do to keep the cell alive?
- Q. What would happen if the nucleus was removed from a cell?
- Q. How is a nucleus formed?
- Q. What is nucleus with diagram?
- Q. What is inside a nucleus?
- Q. What is the nucleus covered by?
- Q. Who discovered nucleus in cell?
- Q. What are the main things in a nucleus?
- Q. Does the nucleus contain DNA?
- Q. Is RNA found inside and outside the nucleus?
- Q. What are cells without a nucleus called?
- Q. Can cell live without nucleus?
- Q. Which is biggest cell?
- Q. Which is the longest cell in human body?
- Q. What is the smallest cell in the female body?
- Q. What is the biggest cell in the female human body?
- Q. Can you see human eggs?
- Q. Are all eggs female?
- Q. Are eggs one cell?
- Q. What is the largest single cell in the world?
- Q. Do human eggs have yolks?
- Q. Is yolk a cell?
- Q. Is the yolk the baby?
- Q. Are egg yolks good for you?
Q. What is a nucleus simple definition?
1 : a usually round part of most cells that is enclosed in a double membrane, controls the activities of the cell, and contains the chromosomes. 2 : the central part of an atom that comprises nearly all of the atomic mass and that consists of protons and neutrons.
Q. Why is the nucleus so important?
The nucleus is considered to be one of the most important structures of eukaryotic cells as it serves the function of information storage, retrieval and duplication of genetic information. It is a double membrane-bound organelle that harbours the genetic material in the form of chromatin.
Q. What does the nucleus do to keep the cell alive?
This organelle has two major functions: it stores the cell’s hereditary material, or DNA, and it coordinates the cell’s activities, which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein synthesis, and reproduction (cell division). Only the cells of advanced organisms, known as eukaryotes, have a nucleus.
Q. What would happen if the nucleus was removed from a cell?
It is the brain of the cell and controls most of its functions. If the nucleus is removed from the cell then the cell will not be able to function properly, it will not be able to grow. Also, the cell will not know what to do and there would be no cell division. Gradually, the cell may die.
Q. How is a nucleus formed?
The vesicles first fuse to form membranes around individual chromosomes, which then fuse with each other to form a complete single nucleus.
Q. What is nucleus with diagram?
The nucleus is a spherical-shaped organelle that is present in every eukaryotic cell. The Nucleus is the control centre of eukaryotic cells. It is also responsible for the coordination of genes and gene expression. The structure of the nucleus includes nuclear membrane, chromosomes, nucleoplasm, and nucleolus.
Q. What is inside a nucleus?
The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell’s genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Inside the nucleus, chromatin (DNA wrapped around proteins, described further below) is stored in a gel-like substance called nucleoplasm.
Q. What is the nucleus covered by?
nuclear membrane
Q. Who discovered nucleus in cell?
botanist Robert Brown
Q. What are the main things in a nucleus?
The nucleus consists of the following main parts: (1) Nucleolemma or nuclear membrane (karyotheca) (2) Nuclear sap or karyolymph or nucleoplasm (3) Chromatin network or fibres (4) Nucleolus (5) Endosomes.
Q. Does the nucleus contain DNA?
The nucleus contains the cell ‘s DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins. Found within the nucleoplasm, the nucleolus is a condensed region of chromatin where ribosome synthesis occurs. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and is stored within the nucleoplasm.
Q. Is RNA found inside and outside the nucleus?
There are two types of nucleic acids which are polymers found in all living cells. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) is found mainly in the nucleus of the cell, while Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) is found mainly in the cytoplasm of the cell although it is usually synthesized in the nucleus.
Q. What are cells without a nucleus called?
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles.
Q. Can cell live without nucleus?
The nucleus is the control centre of the eukaryotic cell. So without the nucleus, most of the eukaryotic cells will die. The mature red blood cells of humans are devoid of a nucleus, they have a shorter life span.
Q. Which is biggest cell?
The largest cells is an egg cell of ostrich. The longest cell is the nerve cell. The largest cell in the human body is female ovum.
Q. Which is the longest cell in human body?
nerve cell
Q. What is the smallest cell in the female body?
The Cerebellum’s Granule Cell is the smallest cell in the human body that is between 4 micrometers to 4.5 micrometers long. The RBC ‘s size also found roughly 5 micrometers. The largest cell is ovum in the human body. The ovum also called egg cell is the reproductive cell in the female body.
Q. What is the biggest cell in the female human body?
human egg cell
Q. Can you see human eggs?
Egg cells are among the largest cells in the body—each egg is 0.1mm, which seems quite small, but it’s actually visible to the naked eye (1).
Q. Are all eggs female?
A female baby is born with all the eggs that she will ever have. This is estimated to be around two million, but by the time a girl reaches puberty, this number has decreased to about 400,000 eggs stored in her ovaries.
Q. Are eggs one cell?
meals. But, scientifically-speaking, the egg is a single cell laid down by the fernale; when fertilized by the single cell or nucleus of the male sperm, it remains a single cell but then has its full complement of chromosomes and genes.
Q. What is the largest single cell in the world?
Biologists used the world’s largest single-celled organism, an aquatic alga called Caulerpa taxifolia, to study the nature of structure and form in plants. It is a single cell that can grow to a length of six to twelve inches.
Q. Do human eggs have yolks?
Mammalian ova contain only a tiny amount of the nutritive yolk, for nourishing the embryo in the early stages of its development only. In contrast, bird eggs contain enough to supply the chick with nutriment throughout the whole period of incubation.
Q. Is yolk a cell?
Biologists like to argue over the semantics of this, but it is generally accepted that the yolk of an egg is one single, massive cell, thousands of times bigger than typical cells. This is often invisible in the eggs you buy, because they are unfertilized, so the cell has not split and grown.
Q. Is the yolk the baby?
The yolk is the source of food for the embryo and contains all the fat in the egg. The small white spot on the yolk is called the germinal disc. When an egg is fertilized the germinal disc divides and develops into an embryo.
Q. Are egg yolks good for you?
Compared to egg whites, the yolk contains most of an egg’s good stuff, including the bulk of its iron, folate and vitamins. The yolks also contain two nutrients—lutein and zeaxanthin—that support eye and brain health.