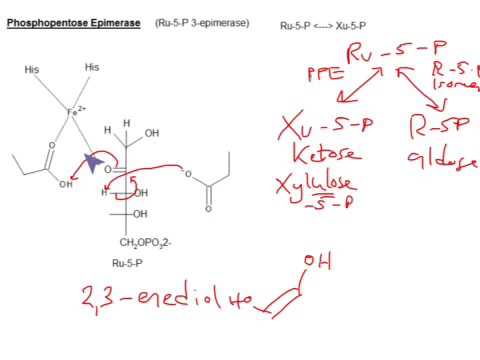
Q. What is the function of ribulose 5-phosphate Epimerase?
In enzymology, a L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase (EC 5.1. 3.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of ribulose 5-phosphate and xylulose 5-phosphate in the oxidative phase of the Pentose phosphate pathway.
Q. What is the first reaction of the pentose phosphate pathway?
The first of the three reactions linking the pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis is the formation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and sedohep-tulose 7-phosphate from two pentoses. The donor of the two-carbon unit in this reaction is xylulose 5-phosphate, an epimer of ribulose 5-phosphate.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the function of ribulose 5-phosphate Epimerase?
- Q. What is the first reaction of the pentose phosphate pathway?
- Q. What is the role of Transaldolase in HMP pathway?
- Q. What is Ribulose phosphate synthesized from?
- Q. When glucose conversion to pyruvate is routed through the pentose phosphate pathway what is the amount of ATP produced per glucose?
- Q. What kind of enzyme catalyzes the reaction of ribose 5 p Ribulose 5 P?
- Q. What is the end product of pentose phosphate pathway?
- Q. Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate?
- Q. Where does the PPP take place?
- Q. What type of enzyme is transaldolase?
- Q. What is ribulose monophosphate pathway?
- Q. What is the difference between ribose and ribulose?
- Q. Which is an important reaction in the metabolism of amino acids?
- Q. What kind of reactions can a ketone undergo?
- Q. What is the reaction of bismuth triflate with β amino ketones?
- Q. How does iodine catalyze the synthesis of β amino ketones?
Q. What is the role of Transaldolase in HMP pathway?
The nearly ubiquitous enzyme transaldolase is a part of the pentose phosphate pathway and transfers a dihydroxyacetone group from donor compounds (fructose 6-phosphate or sedoheptulose 7-phosphate) to aldehyde acceptor compounds.
Q. What is Ribulose phosphate synthesized from?
pentose-phosphate
It is formed by phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, and it can be acted upon by phosphopentose isomerase and phosphopentose epimerase. In plants, Ribulose 5-phosphate produced from the pentose-phosphate pathway is converted into Ribulose-1-5-bisphosphate by the enzyme phosphoribokinase.
Q. When glucose conversion to pyruvate is routed through the pentose phosphate pathway what is the amount of ATP produced per glucose?
1 ATP
Entner–Doudoroff Pathway (ED) The yield of ATP for this pathway is 1 ATP per glucose molecule.
Q. What kind of enzyme catalyzes the reaction of ribose 5 p Ribulose 5 P?
PRPP Synthetase Overactivity (Superactivity) PRPS catalyzes the transfer of the pyrophosphate group of ATP to ribose 5-phosphate to form PRPP. PRPP, an important regulator of de novo purine synthesis pathways, is a substrate in the initial step of the de novo pathway and for purine salvage reactions (Figure 38.2).
Q. What is the end product of pentose phosphate pathway?
The pentose phosphate pathway takes place in the cytosol of the cell, the same location as glycolysis. The two most important products from this process are the ribose-5-phosphate sugar used to make DNA and RNA, and the NADPH molecules which help with building other molecules.
Q. Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate?
Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) is a biotin-containing enzyme that catalyses the HCO3−- and MgATP-dependent carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate. This is a very important anaplerotic reaction, replenishing oxaloacetate withdrawn from the Krebs cycle for various pivotal biochemical pathways.
Q. Where does the PPP take place?
cytoplasm
In mammals, the PPP occurs exclusively in the cytoplasm. In humans, it is found to be most active in the liver, mammary glands, and adrenal cortex. The PPP is one of the three main ways the body creates molecules with reducing power, accounting for approximately 60% of NADPH production in humans.
Q. What type of enzyme is transaldolase?
Crystallographic structure of human transaldolase. Transaldolase is an enzyme (EC 2.2. 1.2) of the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway. In humans, transaldolase is encoded by the TALDO1 gene.
Q. What is ribulose monophosphate pathway?
The ribulose monophosphate (RuMP) pathway, involving 3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthase (HPS) and 6-phospho-3-hexuloisomerase (PHI), is now recognized as a widespread prokaryotic pathway for formaldehyde fixation and detoxification.
Q. What is the difference between ribose and ribulose?
What is the difference between Ribose and Ribulose? Ribose is an aldose sugar- containing an aldehyde group (- CHO). Ribulose contains a ketone group (-C=O) and is referred to as a ketose sugar.
Q. Which is an important reaction in the metabolism of amino acids?
Important reactions in amino acid metabolism. 1) Decarboxylation means a removal of the carboxyl group – biogenic amines are formed. 2) Transamination means an exchange of amino group with 2-oxoacid – 2-oxoacids are formed. 3) Oxidative deamination means an oxidative removal of amino group – 2-oxoacids are formed.
Q. What kind of reactions can a ketone undergo?
Lesson Summary. Ketones are a common compound that can undergo several different types of reactions. A ketone is a carbon connected to two other carbons and double bonded to an oxygen. Addition reactions occur by adding an electronegative atom to the carbon.
Q. What is the reaction of bismuth triflate with β amino ketones?
Bismuth triflate catalyzes the Mannich-type three component reaction of a variety of aldehydes and anilines (leading in situ to aldimines) with silyl enol ethers. The reaction proceeds rapidly and affords the corresponding protected β-amino ketones in high yields.
Q. How does iodine catalyze the synthesis of β amino ketones?
Iodine efficiently catalyzes the three-component coupling of aromatic aldehydes, enolizable ketones or keto esters, and acetonitrile in the presence of acetyl chloride at room temperature to afford β-acetamido ketones in good yields. B. Das, K. Ravinder Reddy, R. Ramu, P. Thirupathi, B. Ravikanth, Synlett, 2006, 1756-1758.