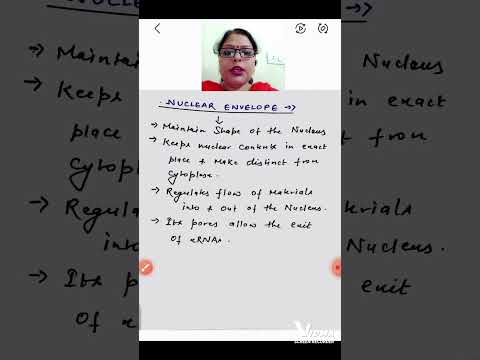
Q. What is the function of the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope keeps the contents of the nucleus, called the nucleoplasm, separate from the cytoplasm of the cell. The all-important genetic material, mainly the DNA is kept separate and relatively safe from the chemical reactions taking place in the cytoplasm.
Q. What is the difference and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells contain many membrane-enclosed, large, complex organelles in the cytoplasm whereas prokaryotic cells do not contain these membrane-bound organelles. Only eukaryotes possess a membrane-bound nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as the mitochondria, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes and ER.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the function of the nuclear envelope?
- Q. What is the difference and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Q. Which structure is common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Q. Which characteristic do most plants have in common?
- Q. Which structure is common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells quizlet?
- Q. Which characteristic is observed in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Q. Which cell organelle is covered by two membranes?
- Q. Which two molecules are used to make cell membranes?
- Q. What cell membrane is made up of?
- Q. What builds cell membranes?
- Q. What 4 types of molecules exist in the plasma membrane?
- Q. What are the 4 major biomolecules give examples?
Q. Which structure is common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The structures that are common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA. All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA.
Q. Which characteristic do most plants have in common?
Summary
- Plants are multicellular eukaryotes. They have organelles called chloroplasts and cell walls made of cellulose.
- Plants also have specialized reproductive organs.
- Almost all plants make food by photosynthesis.
- Life as we know it would not be possible without plants.
Q. Which structure is common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells quizlet?
Which two structures are common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Plasma membrane and cytoplasm. Plasma membrane is the gatekeeper and the cytoplasm holds chemical reactions.
Q. Which characteristic is observed in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have structures in common. All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA.
Q. Which cell organelle is covered by two membranes?
The nucleus, the largest organelle in eukaryotic cells, is surrounded by two membranes, each one a phospholipid bilayer containing many different types of proteins. The inner nuclear membrane defines the nucleus itself.
Q. Which two molecules are used to make cell membranes?
Cell membranes are composed of proteins and lipids. Since they are made up of mostly lipids, only certain substances can move through. Phospholipids are the most abundant type of lipid found in the membrane. Phospholipids are made up of two layers, the outer and inner layers.
Q. What cell membrane is made up of?
With few exceptions, cellular membranes — including plasma membranes and internal membranes — are made of glycerophospholipids, molecules composed of glycerol, a phosphate group, and two fatty acid chains. Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule that functions as the backbone of these membrane lipids.
Q. What builds cell membranes?
The fundamental building blocks of all cell membranes are phospholipids, which are amphipathic molecules, consisting of two hydrophobic fatty acid chains linked to a phosphate-containing hydrophilic head group (see Figure 2.7).
Q. What 4 types of molecules exist in the plasma membrane?
The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group.
Q. What are the 4 major biomolecules give examples?
The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
- polynucleotide chain of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Portion of polynucleotide chain of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
- molecular view of the cell membrane.
- DNA packaging into chromatin and chromosome.