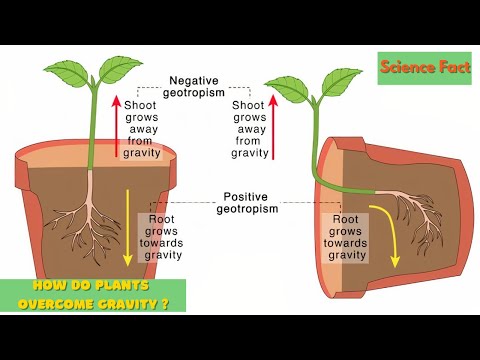
Q. What is the growth of roots of plants towards Earth called?
tropisms
Q. What are the types of tropism?
Forms of tropism include phototropism (response to light), geotropism (response to gravity), chemotropism (response to particular substances), hydrotropism (response to water), thigmotropism (response to mechanical stimulation), traumatotropism (response to wound lesion), and galvanotropism, or electrotropism (response …
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the growth of roots of plants towards Earth called?
- Q. What are the types of tropism?
- Q. What is the meaning of tropism?
- Q. What is the function of auxin in plant growth?
- Q. What is the role of IAA in plants?
- Q. Who gave the term hormone?
- Q. What is meant by cytokinin?
- Q. What is auxin and cytokinin?
Q. What is the meaning of tropism?
Medical Definition of tropism : involuntary orientation by an organism or one of its parts that involves turning or curving by movement or by differential growth and is a positive or negative response to a source of stimulation also : a reflex reaction involving a tropism.
Q. What is the function of auxin in plant growth?
Answer: Auxin promotes cell growth and elongation of the plant. In the elongation process, auxin alters the plant wall plasticity making it easier for the plant to grow upwards. Auxin also influences rooting formations.
Q. What is the role of IAA in plants?
IAA is the main auxin in plants, regulating growth and developmental processes such as cell division and elongation, tissue differentiation, apical dominance, and responses to light, gravity, and pathogens. Roots are most sensitive to fluctuations in IAA level.
Q. Who gave the term hormone?
Ernest Starling
Q. What is meant by cytokinin?
Cytokinin, any of a number of plant hormones that influence growth and the stimulation of cell division. They move upward in the xylem (woody tissue) and pass into the leaves and fruits, where they are required for normal growth and cell differentiation.
Q. What is auxin and cytokinin?
auxin: a class of plant growth hormones that is responsible for elongation in phototropism and gravitropism and for other growth processes in the plant life cycle. cytokinin: any of a class of plant hormones involved in cell growth and division.