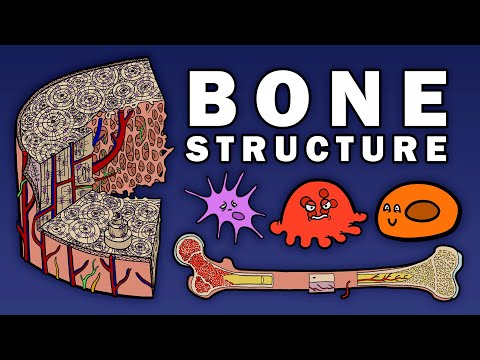
Q. What is the innermost layer of bone?
The innermost part of a bone contains the bone marrow. The layer of compact bone surrounds an interior cavity called the medullary cavity.
Q. What are the correct layers for a bone from innermost to outermost?
Let’s take a closer look.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the innermost layer of bone?
- Q. What are the correct layers for a bone from innermost to outermost?
- Q. What are the layers of my bones?
- Q. What is classified as an irregular bone?
- Q. Why is it important to classify bones?
- Q. What is the function of muscles?
- Q. What are the 4 functions of muscles?
- Q. What are the 6 major types of muscles?
- Q. Which is not a type of muscle in the body?
- Q. What connects bones and muscles together?
- Periosteum. The periosteum is a soft outer covering over the bone’s surface.
- Cortical Bone. This layer is hard and thick.
- Cancellous Bone. Cancellous bone is a spongy type of bone inside the cortical bone.
- Bone Marrow.
- A picture of the four bone layers.
Q. What are the layers of my bones?
There are three layers in your bones. The compact bone is the hard, white outer layer. The spongy bone is the hard layer with many holes. The bone marrow is the center layer where blood vessels run through.
Q. What is classified as an irregular bone?
The irregular bones are: the vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid, zygomatic, maxilla, mandible, palatine, inferior nasal concha, and hyoid.
Q. Why is it important to classify bones?
Why is it important to classify bones? – It is important to classify bones because each bone has a unique shape and function. Aside from length, what are some other common characteristics of a long bone? Are long bones typically associated with the axial or appendicular skeleton?
Q. What is the function of muscles?
The muscular system is composed of specialized cells called muscle fibers. Their predominant function is contractibility. Muscles, attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels, are responsible for movement. Nearly all movement in the body is the result of muscle contraction.
Q. What are the 4 functions of muscles?
The main functions of the muscular system are as follows:
- Mobility. The muscular system’s main function is to allow movement.
- Stability. Muscle tendons stretch over joints and contribute to joint stability.
- Posture.
- Circulation.
- Respiration.
- Digestion.
- Urination.
- Childbirth.
Q. What are the 6 major types of muscles?
Structure
- Comparison of types.
- Skeletal muscle.
- Smooth muscle.
- Cardiac muscle.
- Skeletal muscle.
- Smooth muscle.
- Cardiac muscle.
Q. Which is not a type of muscle in the body?
Rough is not a form of muscle tissue. The proper types are listed below: Cardiac- this is the muscle tissue within the heart, whose contractions…
Q. What connects bones and muscles together?
Tendons: Tendons connect muscles to bones. Made of fibrous tissue and collagen, tendons are tough but not very stretchy.