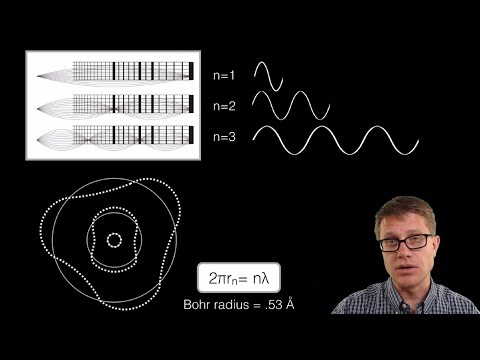
The wave-mechanical model is a current theory describing the locations of electrons in orbit around the nucleus of an atom. Lower-energy shells will be filled with electrons before higher-energy shells. The number of electrons in each shell of an atom may be described using electron notation.
Q. How does the wave mechanical model of the atom describe electrons?
The wave mechanical model proposed that the electrons act like particles as well as waves of energy. According to the fields around, the electrons change their path and they move very fast, hence they are not in one place during any particular time. The wave mechanical model was used for the construction of an atom.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does the wave mechanical model of the atom describe electrons?
- Q. What does the quantum mechanical model say about electrons?
- Q. What is the wave mechanical model of an atom required to explain?
- Q. What is the wave model of an electron?
- Q. What are the two aspects of wave-mechanical model of atom?
- Q. What is quantum mechanical description of an atom?
- Q. What is the quantum mechanical model of the atom quizlet?
- Q. Where are protons in the wave-mechanical model?
- Q. What is a mechanical wave and what are its characteristics?
- Q. What is the basis for the quantum mechanical model of an atom?
- Q. What does the quantum mechanical model determine about electrons in atoms quizlet?
- Q. Where are electrons located in the wave mechanical model?
- Q. How does the wave-mechanical theory explain the orbit of an atom?
- Q. How did Erwin Schrodinger describe the quantum mechanical model of the atom?
- Q. How does an atom act like a wave?
Q. What does the quantum mechanical model say about electrons?
In the quantum-mechanical model of an atom, electrons in the same atom that have the same principal quantum number (n) or principal energy level are said to occupy an electron shell of the atom. Orbitals define regions in space where you are likely to find electrons.
Q. What is the wave mechanical model of an atom required to explain?
describe the wave mechanical model of the atom. the wave mechanical model uses probability to predict the location of an electron and says electrons exist in clouds. it is different because it describes the atom mathematically and we don’t use it to draw atoms because the orbitals are difficult to draw.
Q. What is the wave model of an electron?
The model is based on de Broglie’s original electron wave-particle theories. Schrödinger’s wave function is revealed as the envelope of the de Broglie wave function. Since the electron model is based directly on the Special theory of relativity, it may also be used as an illustration of that theory.
Q. What are the two aspects of wave-mechanical model of atom?
1)The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. 2)These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of Schrodinger Wave Equation.
Q. What is quantum mechanical description of an atom?
The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. So, this model is based on probability rather than certainty.
Q. What is the quantum mechanical model of the atom quizlet?
CHM Chapter 7: Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom. a model that explains how electrons exist in atoms and how those electrons determine the chemical and physical properties of elements. a postulate which states that all matter has both components of a wave and a particle. For example, light.
Q. Where are protons in the wave-mechanical model?
The atom is mostly space with a small, very dense, centrally located nucleus that contains positively charged protons and neutrally charged neutrons and is surrounded by negatively charged electrons located in orbitals in the electron cloud.
Q. What is a mechanical wave and what are its characteristics?
A mechanical wave is a wave that is not capable of transmitting its energy through a vacuum. Mechanical waves require a medium in order to transport their energy from one location to another. A sound wave is an example of a mechanical wave. Sound waves are incapable of traveling through a vacuum.
Q. What is the basis for the quantum mechanical model of an atom?
-This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Thus, – This model is based upon the dual nature of the electron, i.e. the electron is not only a particle but has a wave character.
Q. What does the quantum mechanical model determine about electrons in atoms quizlet?
What does the quantum mechanical model determine about electrons in atoms? The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus.
Q. Where are electrons located in the wave mechanical model?
According to the wave mechanical model of the atom, electrons in an atom Are located in orbitals outside the nucleus Which group of atomic models is listed in historical order from the earliest to the most recent? Hard sphere model to electron shell model to wave mechanical model
Q. How does the wave-mechanical theory explain the orbit of an atom?
The wave-mechanical theory proposes that each electron circling an atom’s nucleus occupies a specific orbital and spins a certain direction, but the orbital is like a cloud or wave of energy, not the ring you might imagine thinking about the earth’s orbit around the sun.
Q. How did Erwin Schrodinger describe the quantum mechanical model of the atom?
Erwin Schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. . , represents the probability of finding an electron in a given region within the atom. An atomic orbital is defined as the region within an atom that encloses where the electron is likely to be 90% of the time.
Q. How does an atom act like a wave?
Electrons race around a central nucleus at such high speeds, that they act like waves of energy. As electrons push each other around, the electron orbital clouds form different shapes. Scientists propose that atoms can have up to seven principle energy levels of electrons around the nucleus.